Antipyretics for children are prescribed by a pediatrician. But there are emergency situations for fever when the child needs to be given medicine immediately. Then the parents take responsibility and use antipyretic drugs. What is allowed to give to infants? How can you bring down the temperature in older children? What medicines are the safest?
Ureaplasmosis is defined as an infectious and inflammatory disease of the genitourinary system, which is transmitted mainly through sexual contact and is caused by a microorganism Ureaplasma urealyticum or Ureaplasma parvum.
In humans, these bacteria primarily affect the urethra in men and the vagina in women. Ureaplasmosis as a separate disease is rare, more often found in association with and. Therefore, with symptoms characteristic of urogenital infections (mucous or purulent or), simultaneously with tests for ureaplasmosis, diagnostics for mycoplasmosis and chlamydia are always carried out.
Ureaplasmosis is isolated as a separate disease only if an inflammation pattern develops and the tests are positive only for ureaplasma (u.urealyticum or u.parvum).

Until now, there has not been a consensus in medicine regarding ureaplasmas. Some consider them pathogenic (pathogenic), others are confident in their complete harmlessness and classify them as normal microflora of the human body. The ways of transmission of ureaplasmosis also raise questions: almost 30% of girls who do not live sexually have ureaplasmas, and the household route of transmission has not been reliably proven. The carriage is also doubtful - in men, ureaplasmas may not be detected at all, however, in women after sexual contact with absolutely healthy men, for some reason, these bacteria were found.
As a result, modern medicine nevertheless formulated its attitude towards ureaplasmas. The “middle way” of selecting criteria has prevailed, according to which the diagnosis and treatment of various cases of ureaplasmosis is carried out.
- Ureaplasmas are opportunistic pathogens present in the normal microflora of the vagina in women (more than 60%) and the urethra in men (about 50%). In the majority, they do not manifest themselves in any way, do not give symptoms of inflammation, and therefore, even in the case of a positive diagnosis, such people do not need any treatment.
- Detection of ureaplasma during pregnancy does not give rise to panic: the very fact of their presence does not threaten complications or miscarriage and does not harm the health of the baby. All complications are possible only with the development of inflammation associated with the reproduction of ureaplasmas and other pathogenic bacteria. A decrease in immune defense is the main factor that provokes the onset of the disease, and maximum attention should be paid to the general health of expectant mothers.
- Almost always, ureaplasmas are found together with mycoplasmas and chlamydia. Therefore, the treatment is carried out with drugs to which all these microorganisms are sensitive. Usually a combination of various antibiotics is required, the scheme is always supplemented with immunomodulators and probiotics, vitamins and diet.
Ways of transmission and causes of development of ureaplasmosis
It has been proven that infection with ureaplasma occurs mainly through sexual contact, and a child can get an infection from the mother during pregnancy or during childbirth. Household (through objects, underwear) transmission routes are unlikely and practically not proven. Gateway of infection usually become the vagina and urethra, less often infection occurs orally or anally. Further spread of ureaplasmas is possible only with their active reproduction in a weakened organism. Incubation period lasts 1-3 weeks after sexual contact.
The causes of the manifestation of ureaplasmosis are considered a number of factors in which a decrease in the immune status of a given person is possible. The combination of several of them increases the likelihood of the transition of ureaplasmas from opportunistic to the category of pathogenic microorganisms.

Age period 14-29 years is considered the most active, including in relation to sexual life. Hormonal levels and social freedom, confidence in one's health or no thought at all about its vulnerability predispose to the spread of sexually transmitted infections.
During pregnancy occurring under conditions of physiological or moral stress, it is possible to exacerbate dormant infections that have never manifested themselves before. Poor nutrition, work to wear, high study loads, uncertainty about the future - all affect pregnancy and its outcome.
Concomitant sexually transmitted diseases caused by gonococci, chlamydia and mycoplasmas; simple viruses, papilloma or human immunodeficiency (and HIV) always contribute to the emergence and development of ureaplasmosis.
The immune system, weakened by prolonged stress or any chronic diseases, is not able to resist the reproduction of ureaplasmas. The result is the spread of infection and inflammation of the organs that make up the urogenital tract.
Weakening of the body after operations, hypothermia, a course of radioactive exposure in the treatment of cancerous tumors or due to deteriorating living conditions, it also contributes to the development of symptoms of ureaplasmosis.
The growth of opportunistic microorganisms is favored by uncontrolled treatment with antibiotics and hormonal agents, leading to dysbacteriosis- violation of the balance of microflora inside the human body.
Symptoms of ureaplasmosis in women
Primary signs of the disease associated with damage to the vagina and cervical canal, then the infection is introduced into the urethra. Symptoms develop and small mucous discharges appear from the cervix and vagina. At urethritis a woman complains of a burning sensation in the urethra during urination, and the urge to urinate also becomes more frequent. After a few days, if the immune system is in order and there is no dysbacteriosis, the symptoms may disappear altogether and never appear again. When the body is weakened, the spread of ureaplasmas will follow the principle of ascending infection, capturing the internal genital organs, bladder and kidneys.
Chronic ureaplasmosis can lead to cervical erosion, and subsequently to epithelial cancer, which quickly metastasizes. At first, a woman is concerned about small mucous secretions, then bleeding during menstruation joins - a sign of the infection moving to the endometrium. On examination, a bright red mucosal defect with jagged edges is visible. On ultrasound, a thickening of the endometrium is determined.

- Screening: pregnant; women under 25; having multiple sexual partners with unprotected intercourse.
- Diseases: inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs in men and women; urethritis, cystitis and pyelonephritis; asymmetrical arthritis; conjunctivitis; inflammation of the testicles and appendages; infertility.
- Infection control before medical procedures: before abortion, artificial insemination, the introduction of intrauterine contraceptives; before examining the patency of the fallopian tubes.
- To identify infected people and people from the circle of sexual contacts.
Material for analysis is taken from men - from the urethra, from women - from the cervix, vagina and urethra.

Remains preferable, despite the duration of its execution. First, the material from the patient is sown on an artificial nutrient medium, then isolated from the grown colonies of the pathogen and determined using tests. The identification of ureaplasmas is based on their specific enzymatic activity: ureaplasma is able to break down urea. Re-seeding is carried out to determine the sensitivity to antibiotics. The results are obtained in a week or 10 days, the final diagnosis is made and adequate treatment is prescribed.
(polymerase chain reaction) helps to identify bacterial DNA specific to a given type of microorganism. The method is 100% accurate if it is performed correctly and does not require other confirmation of the diagnosis.
Ureaplasma can persist throughout life, so their definition for diagnosis does not make sense: it is impossible to distinguish between “fresh” and “old” traces of infection.
Treatment
Treatment of ureaplasmosis Necessarily at the risk of complications during pregnancy, which are confirmed by objective examinations; with male and female infertility, if other causes, except for ureaplasmosis, have not been established. Ureaplasmosis is also treated if there are symptoms of inflammation of the urinary organs and tests confirm this fact. Before planned medical interventions (surgeries, invasive diagnostic methods) to prevent the spread of ureaplzm outside the infected area, short courses of antibiotics are used.
Fundamentally, the treatment of ureaplasmosis does not differ from the treatment of other STDs.

Tetracycline antibiotics ( doxycycline, unidox) are absolutely contraindicated during pregnancy. The modern treatment regimen puts them in the category of reserve ones also due to the appearance of ureaplasma resistance to these drugs in about 10% of cases.
Group fluoroquinolones(all drug names end in "-oxacin") in action is close to antibiotics, but has no natural analogues. Drugs used to treat co-infections ofloxacin, ciprofloxacin. The peculiarity of drugs in this group is contraindicated in children under 15 years of age and pregnant women; increase sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation and can cause skin burns, so it is not recommended to sunbathe and be treated with fluoroquinolones at the same time.
General treatment combined with local, for men, these are instillations of drugs into the urethra (solutions of protargol or collargol) and baths with antiseptics. Women are prescribed vaginal or rectal suppositories. Candles "Genferon" have an antibacterial and antiviral effect, anesthetize and restore tissues, activate the immune system. Use twice a day, a course of 10 days. suppositories "Hexicon" x 1/day will help cure uncomplicated ureaplasmosis in a 7-day course. It is allowed to use them during pregnancy and lactation.
In chronic disease, immunomodulators are used - methyluracil, cycloferon, thymalin And t-activin in order to activate the immune system and get first a controlled exacerbation, and then a stable improvement. Rehabilitation therapy: drugs with lacto- and bifidobacteria after a course of antibiotics; antifungals ( fluconazole); vitamin and mineral complexes. Complete nutrition with the exception of hot spices, alcohol and fried foods, with salt restriction. Sexual contacts are excluded for the entire period of treatment.
Folk remedies
The main tasks are to strengthen the body, reduce the effects of inflammation. For these purposes, locally used herbal antiseptics (sage, chamomile, calendula) in the form of douches or baths. Prepare infusions at the rate of 1 tbsp. a spoon (without a slide) of dry grass or flowers per 200 ml of boiling water, exposure 1 hour; then the infusion is filtered through 3-5 layers of gauze. You can add a decoction of oak bark, prepared in the same proportion. Infusions are not prepared for the future, each time you need to take care of a fresh portion. The course will require 7-10 procedures.

Drinks from herbs or berries will help reduce inflammation, avoid complications of ureaplasmosis on the kidneys and joints. Tea from lingonberry leaf and St. John's wort, a decoction of lingonberry berries and raspberry leaves work perfectly. However, it is worth remembering that diuretic the effect which these remedies exert may do a disservice during antibiotic treatment. Medicines will be more quickly excreted from the body, and their concentration will decrease below the therapeutic level. That's why all folk remedies of such action are acceptable only after the end of the main course of treatment.
Video: expert opinion on ureaplasmosis
Thank you
The site provides reference information for informational purposes only. Diagnosis and treatment of diseases should be carried out under the supervision of a specialist. All drugs have contraindications. Expert advice is required!
Introduction
Ureaplasmosis is one of the most common and so-called "commercial" diagnoses in urology and gynecology, which is often used by unscrupulous doctors. This diagnosis can be made to almost half of men and 80 percent of women.But is ureaplasmosis so dangerous? Does it need to be treated? And where does it actually come from? Let's try to deal with all these questions.
What kind of animal is ureaplasma?
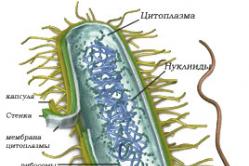
Ureaplasma was first discovered in 1954 by the American physician Shepard in the discharge of a patient with non-gonococcal urethritis. Further studies have shown that most people who are sexually active are carriers of ureaplasma. At the same time, it is not at all necessary that they will have any external signs of infection. Ureaplasma can be in the human body for years and even decades and not manifest itself in any way.Ureaplasma is a tiny bacterium, which in the microbiological hierarchy occupies an intermediate position between viruses and unicellular microorganisms. Due to the multilayer outer membrane that surrounds the bacterium on all sides, it is very difficult to detect under a microscope.
In total, five varieties of ureaplasma are known, but only two of its types are dangerous for humans - ureaplasma urealyticum (Ureaplasma urealyticum) and ureaplasma parvum (Ureaplasma parvum). It is they who have a special weakness for the cells of the epithelium located in the genitourinary tract. In other places of the body, ureaplasmas are almost never found.
By the way, the closest "relative" of ureaplasma is mycoplasma. Due to the great similarity in structure and preferences, both microorganisms often settle in the genital tract at the same time, and then doctors talk about mixed infections, i.e. diseases caused by mixed microflora.
Where does ureaplasma come from?
 Normally, a huge number of microorganisms live in the human genitourinary tract, and all of them, to one degree or another, take part in maintaining the purity of the vagina or urethra. As long as immunity is at the proper level, microorganisms are not dangerous. But as soon as the body's resistance decreases, the microflora of the genital tract is disturbed, some microorganisms begin to multiply rapidly, and that's when they become dangerous to human health.
Normally, a huge number of microorganisms live in the human genitourinary tract, and all of them, to one degree or another, take part in maintaining the purity of the vagina or urethra. As long as immunity is at the proper level, microorganisms are not dangerous. But as soon as the body's resistance decreases, the microflora of the genital tract is disturbed, some microorganisms begin to multiply rapidly, and that's when they become dangerous to human health. The same is true with ureaplasma. Many people live with it for a long time and do not even realize that they are carriers of this bacterium. It is discovered most often by chance, when the patient goes to the doctor for some completely different reason, and sometimes just out of curiosity. For a complete examination, the doctor sends smears to the laboratory. And this is where the fun begins. In the analysis, ureaplasma is detected, and the patient is urgently treated. And even the fact that a person does not have any complaints does not stop some doctors from taking active steps aimed at "expelling" the microbe from the human body.
The main argument in favor of urgent treatment is that in the absence of it, a man or woman will (possibly!) suffer from infertility, and the probability of giving birth or conceiving a child will become equal to zero. And a long struggle with ureaplasma begins. Carriers undergo multiple courses of drug treatment, which leads to many side effects. They, in turn, are often attributed to the manifestation of other latent infections, etc. It can be a long-term, and, unfortunately, useless running around in a vicious circle.
By the way, foreign experts have long ceased to treat ureaplasma as an absolute evil. They do not refute the fact that a microorganism can cause disease, but only in cases where the biocenosis in the genital tract is disturbed and the acidic environment characteristic of a healthy person has changed to alkaline. In other cases, ureaplasma should be considered as a conditionally dangerous cohabitant, and no more. Taking care of your health, an orderly sex life, proper nutrition and physical activity are the key to well-being in the urogenital area.
After many years of discussion at the scientific level, it was decided that only those people who have symptoms and complaints from the urogenital tract need treatment, and the presence of other pathogens is excluded. In other cases, no active influence on the microflora is required.
What does it mean? For example, a patient comes to the doctor with complaints of frequent cystitis (inflammation of the bladder). The doctor prescribes a series of tests aimed at identifying the cause of the disease. If studies have not revealed any other pathogens, then ureaplasma, and sometimes mycoplasma, is considered the root cause of the disease. In this situation, targeted treatment of ureaplasma is really necessary. If there are no complaints from the patient, then the appointment of any treatment remains on the conscience of the doctor.
There is still a lot of controversy about the involvement of ureaplasma in secondary infertility, miscarriage, polyhydramnios and premature birth. To date, this issue remains debatable, because not a single specialist has been able to reliably confirm the guilt of ureaplasma in these pathologies. Of course, if you need to identify ureaplasma in the genitourinary tract, then this is quite simple to do. As mentioned above, the carrier of this microorganism is the sexually active population, and therefore, if desired (or necessary), it is not difficult to sow ureaplasma.
Some researchers are still trying to prove the pathogenicity of ureaplasma, using as arguments its frequent presence in diseases such as urethritis, vaginitis, salpingitis, oophoritis, endometritis, adnexitis, etc. However, in most cases, treatment aimed only at eliminating ureaplasma does not give a positive result. From this we can draw a completely logical conclusion - the cause of inflammation of the pelvic organs is another, more aggressive flora.
How can you get infected with ureaplasma?
Ureaplasma is very unstable in the environment and dies very quickly outside the human body. Therefore, it is almost impossible to get infected in public places, for example, saunas, baths, swimming pools, public restrooms.Infection requires close contact with a carrier of ureaplasmosis. The most likely infection during sexual intercourse, which one - oral, genital or anal, does not matter. However, it is known that slightly different ureaplasmas live in the oral cavity and rectum, which are dangerous to humans in much more rare cases.
The detection of ureaplasma in one of the sexual partners is not a fact of treason, because a person could become infected many years ago, and sometimes during fetal development, or during childbirth from their own carrier mother. By the way, another conclusion follows from this - the infection can be detected even in infants.
Some people believe that ureaplasma refers to the "bad" sexually transmitted infections. This is fundamentally wrong, ureaplasma itself does not cause sexually transmitted diseases, but it can accompany them quite often. It has been proven that the combination of ureaplasma with Trichomonas, gonococcus, chlamydia really poses a serious danger to the genitourinary system. In these cases, inflammation develops, which almost always has external manifestations and requires immediate treatment.
How is ureaplasmosis treated?
 Strictly speaking, in the international classifier of diseases, such a disease as ureaplasmosis does not exist. As a result, we will talk about which drugs ureaplasma bacteria are sensitive to.
Strictly speaking, in the international classifier of diseases, such a disease as ureaplasmosis does not exist. As a result, we will talk about which drugs ureaplasma bacteria are sensitive to. Antibiotics against ureaplasma
All microorganisms are more or less "afraid" of antibiotics, and ureaplasma in this case is no exception. Unfortunately, not every antibacterial agent is able to suppress the activity of bacteria, because. ureaplasma lacks a cell wall. Drugs such as penicillin or cephalosporins do not actually have any positive effect. The most effective are those antibiotics that can affect the synthesis of protein and DNA in the microbial cell. Such drugs are tetracyclines, macrolides, fluoroquinolones, aminoglycosides, Levomycetin.The best indicators for ureaplasma infection in Doxycycline, Clarithromycin, and in case of detection of ureaplasma in a pregnant woman - Josamycin. These antibiotics, even in minimal doses, can suppress the growth of bacteria. As for other antibacterial drugs, they are used only if there is a sensitivity of ureaplasma to them, which is determined during a microbiological study.
Indications for prescribing treatment
To prescribe antibiotic treatment, at least one of the following conditions must be present:- The presence of obvious symptoms and convincing laboratory signs of inflammation of the genitourinary system.
- Laboratory confirmation of the presence of ureaplasma (ureaplasma titer must be at least 104 CFU / ml).
- Upcoming surgery on the pelvic organs. In this case, antibiotics are prescribed for prophylactic purposes.
- Secondary infertility, provided that other possible causes are completely excluded.
- Repeated complications during pregnancy or recurrent miscarriage.
Drugs that affect ureaplasma
Among some doctors, there is an opinion that the growth of ureaplasma can be suppressed with a single dose of Azithromycin in an amount of 1 g. Indeed, in the instructions for the drug and in medical recommendations for the treatment of sexually transmitted infections, it is indicated that Azithromycin effectively affects non-gonococcal and chlamydial urethritis nature in men and chlamydial cervicitis in women. However, numerous studies have shown that after Azithromycin, taken in such a dosage, the destruction of ureaplasma does not occur at all. But taking the same drug for 7-14 days is almost guaranteed to eliminate the infection.Doxycycline and its analogues - Vibramycin, Medomycin, Abadox, Biocyclind, Unidox Solutab - are among the recommended drugs for the treatment of ureaplasma infection. These drugs are convenient in that they need to be taken by mouth only 1-2 times a day for 7-10 days. A single dose of the drug is 100 mg, i.e. 1 tablet or capsule. It must be borne in mind that on the first day of treatment, the patient must take twice the amount of the drug.
The best results from taking Doxycycline were obtained in the treatment of infertility against the background of ureaplasmosis. After the treatment course, in 40-50% of cases, a long-awaited pregnancy occurred, which proceeded without complications and successfully ended in childbirth.
Despite such a high efficiency of the drug, some strains of ureaplasma remain insensitive to Doxycycline and its analogues. In addition, these drugs should not be used in the treatment of pregnant women and children under 8 years of age. It is also worth noting quite frequent side effects, primarily from the digestive organs and skin.
In this regard, the doctor may use other drugs, for example, from the group of macrolides, lincosamines or streptogramins. Clarithromycin (Klabaks, Klacid) and Josamycin (Vilprafen) have proven themselves best.
 Clarithromycin does not adversely affect the gastrointestinal tract and therefore can be taken with or without food. Another advantage of the drug is its gradual accumulation in cells and tissues. Due to this, its action continues for some time after the end of the course of treatment, and the likelihood of re-activation of the infection is sharply reduced. Clarithromycin is prescribed 1 tablet twice a day, the course of treatment is 7-14 days. During pregnancy and children under 12 years of age, the drug is contraindicated, in which case it is replaced by Josamycin.
Clarithromycin does not adversely affect the gastrointestinal tract and therefore can be taken with or without food. Another advantage of the drug is its gradual accumulation in cells and tissues. Due to this, its action continues for some time after the end of the course of treatment, and the likelihood of re-activation of the infection is sharply reduced. Clarithromycin is prescribed 1 tablet twice a day, the course of treatment is 7-14 days. During pregnancy and children under 12 years of age, the drug is contraindicated, in which case it is replaced by Josamycin.
Josamycin belongs to the group of macrolides and is able to suppress protein synthesis in ureaplasma. Its effective single dosage is 500 mg (1 tablet). The drug is taken 3 times a day for 10-14 days. Josamycin has the ability to accumulate, so at first it acts depressingly on ureaplasma, preventing its reproduction, and upon reaching a certain concentration in the cells, it begins to have a bactericidal effect, i.e. leads to the final death of the infection.
Josamycin practically does not cause side effects and can be prescribed even to pregnant women and children under 12 years of age, including infants. In this case, only the form of the drug is changed, not a tableted agent is used, but a suspension for oral administration. After such treatment, the threat of termination of pregnancy, spontaneous abortions and cases of polyhydramnios are reduced by three times.
In cases where the development of ureaplasma inflammation in the urogenital tract occurred against the background of reduced immunity, antibacterial agents are combined with immunomodulatory drugs (Immunomax). Thus, there is an increase in the body's resistance and a faster destruction of the infection. Immunomax is prescribed according to the scheme simultaneously with antibiotics. A single dose of the drug is 200 IU, it is administered intramuscularly on the 1-3rd and 8-10th days of antibacterial treatment - a total of 6 injections per course. It is also possible to take tableted immunomodulating agents - Echinacea-Ratiopharm and Immunoplus. They have a similar effect, but are taken daily, 1 tablet during the entire course of antibacterial treatment. At the end of such a combined treatment, in almost 90% of cases, ureaplasma goes away forever.
Naturally, if, in addition to ureaplasma, another pathology of the genitourinary tract was found, then additional treatment may be required to eliminate concomitant diseases.
When to treat ureaplasma - video
Conclusion
As a summary, I would like to emphasize the following: ureaplasma is transmitted mainly through sexual contact with a carrier or a sick person. Moreover, his infection could occur at any time period of life, starting from the moment of birth.Ureaplasma affects the epithelial cells of the genitourinary system and tends not to manifest itself for a long time. With a decrease in immunity, hormonal disruptions, malnutrition, frequent stress, hypothermia, the likelihood of ureaplasma activation increases with the development of symptoms characteristic of inflammation of the vagina or urethra.
Ureaplasmosis is a sexual infection that occurs in most women in a latent form. Some researchers generally put forward that for the female body, the causative agent of ureaplasmosis is part of the opportunistic flora, which, activated against the background of a decrease in immunity, causes the occurrence of inflammatory diseases of the urogenital organs.
Reasons for the development of ureaplasma in women
Infection with ureaplasma (the causative agent of ureaplasmosis) occurs mainly through sexual contact. But there is no reliable evidence that you can get this infection through everyday contact with a sick person (when lying in the same bed, using the same towel, in baths, pools, saunas), today there is no.
Children can become infected with ureaplasma when passing through the birth canal of a sick mother. However, for childhood, the phenomenon of self-healing is very characteristic, when the infection disappears from the body on its own without any therapy. If an adult is infected, the pathogen sooner or later provokes the development of acute or chronic inflammation of the genitals or urinary organs.
As for the features of the development of the disease in women, their ureaplasmosis rarely has an acute course. Ureaplasmas can live for a long time inside the cells (integumentary epithelium of the genitourinary organs, leukocytes), without causing serious harm to the female body . The starting factors for starting the pathological process, as a rule, are:

Symptoms of ureaplasmosis in women
As mentioned above, the disease in women can be asymptomatic. If pathological symptoms appear, then only non-specific ones - not different from the signs of other sexually transmitted diseases. It can be:
- Abnormal vaginal discharge (abnormal in amount, consistency, smell).
- Periodic.
Many patients note a clear connection between the appearance of these symptoms and menstruation, some stressful situations, diagnostic procedures, etc.
Ureaplasmosis is especially dangerous for pregnant women.. This infection can cause fetal fading, miscarriage, premature birth and other complications of pregnancy. In addition, a chronic inflammatory process in the uterine appendages caused by ureaplasmas can lead to the development of adhesions and tubal infertility or ectopic pregnancies.
Diagnosis of ureaplasmosis
The main method for diagnosing ureaplasmosis is the study of material taken from the vagina and urethra by PCR. In addition, cultures of vaginal and urethral scrapings are performed to confirm the diagnosis and select drugs to treat the infection.
It is necessary to undergo an examination for ureaplasmosis in the following cases:
- At .
- With chronic colpitis, adnexitis, salpingitis and other inflammatory diseases of the genital organs.
- If you have problems with conception and pregnancy.
- For any .
- In chronic inflammatory diseases of the urinary tract.
A doctor can make a diagnosis of "Ureaplasmosis" only if an inflammatory process is present in the patient's genital or urinary organs, and only ureaplasma has been isolated from possible pathogens.
Treatment of ureaplasma in women: indications
Not all women with ureaplasma in the genitals need to be treated with special antibacterial drugs. To prescribe such treatment, evidence is needed that it was this microorganism that caused the pathological process. A gynecologist can make such a conclusion in the following situations:

In parallel, it is necessary to examine and treat the sexual partner in order to avoid re-infection. This recommendation is especially relevant for couples suffering from infertility, since there is evidence that ureaplasma penetrates the spermatozoon and makes it unviable. In addition, ureaplasmosis can cause other problems with men's health that affect fertility.
Treatment methods for ureaplasmosis in women
Treatment of ureaplasmosis is a long process that requires patience and perseverance from the patient, since it is impossible to eliminate ureaplasmas in one short course of drug therapy. In addition, it is very important that a woman adheres to the doctor's recommendations regarding nutrition and lifestyle.
Gynecologists usually prescribe complex treatment for patients with ureaplasmosis, including:
- Sanitation of the vagina.
- Immunostimulating drugs.
- Enzymes with anti-inflammatory action.
- Restoration of normal microflora through the use of special drugs (probiotics) inside and out.
- Vitamin therapy.
- Physiotherapy procedures. Of the physiotherapeutic procedures for ureaplasmosis, gynecologists give preference to magnetotherapy, electrophoresis. Intravenous laser blood irradiation, mud therapy and gynecological massage also have good efficiency.
Antibacterial drugs are selected based on the results of determining the sensitivity of isolated ureaplasmas to antibiotics. Most often, patients are prescribed drugs from the group of macrolides, tetracyclines or fluoroquinolones. If the gynecologist chooses drugs blindly, there is a high probability that the treatment will be ineffective, ureaplasmas will survive and become insensitive to the drugs used. Sanitation of the vagina carried out with complex preparations (they are usually used in the form of vaginal suppositories), including an antibiotic and antifungal agents.
An important link in the treatment of ureaplasmosis is the restoration of the normal microflora of the genital organs, since the fact that ureaplasma caused the development of an inflammatory process in a woman clearly indicates that there is a decrease in immunity and vaginal dysbacteriosis. Interferon preparations (for example, Genferon) or endogenous interferon synthesis stimulators (for example, Cycloferon) are used as immunostimulating agents for the treatment of gynecological diseases.
Concerning probiotics, then they are prescribed orally (there are a lot of such drugs) and vaginally (for example, Vagilak). The treatment regimen may also include the anti-inflammatory enzyme preparation Wobenzym and multivitamin complexes.
It is clear that all of the listed drugs are not prescribed to patients at the same time. There are specially designed treatment regimens that are selected for each patient individually (depending on the clinical situation and test results). A woman must necessarily observe not only the dosage, but also the sequence of taking medications (for example, one drug for 3 days, another from 4 to 10 days, etc.), otherwise the treatment will be ineffective.

To get a good result from drug therapy, it is advisable for the patient to adhere to the following rules throughout the entire period of taking medications:
- Do not drink alcohol.
- Do not abuse sweet, fatty, spicy, smoked.
- Refrain from intimacy.
Prevention of ureaplasmosis
Preventive measures for this infection are not particularly different from those for other sexually transmitted diseases. It is necessary to refrain from unprotected intimate contacts with casual partners, to be regularly examined by a gynecologist and to be tested for sexual infections. It will also not hurt for the prevention of ureaplasmosis additionally take care of maintaining general immunity and maintaining a normal microbial background in the genitals. To do this, you should follow the rules of intimate hygiene, treat diseases such as bacterial vaginosis, thrush in a timely manner, eat well, play sports and generally lead a healthy lifestyle.
Zubkova Olga Sergeevna, medical commentator, epidemiologist
Ureaplasmosis is a rather dangerous disease, especially if it occurs in a pregnant woman.
If left untreated, the disease can lead to infertility, pregnancy complications, and even fetal death. In men, ureaplasma affects the prostate gland, leading to symptoms similar to those of prostatitis, and can also lead to infertility.
Ureaplasmosis is a disease caused by ureaplasma bacteria. These are pre-nuclear organisms with an unusual structure - their cell wall is covered with an additional membrane that other bacteria do not have.
If a person has become infected with ureaplasma, this does not mean that he will get ureaplasmosis, because the microbes that are part of the normal microflora of the genital organs (and certain microbes are always present on the mucous membranes) prevent the reproduction of ureaplasmas. When the beneficial microflora dies for some reason, the ureaplasma gets the opportunity to multiply and causes inflammation.
The "trigger" to the onset of the disease can be any factor that disrupts the normal microflora - taking antibiotics, treatment for other diseases of the genital mucosa, even the poor environmental situation in the city.
If found in the analyses?
 If ureaplasma is found in the tests, you need to contact a dermatovenereologist and start treatment. In addition, since the disease is sexually transmitted, it is necessary to test for other diseases that are transmitted in the same way.
If ureaplasma is found in the tests, you need to contact a dermatovenereologist and start treatment. In addition, since the disease is sexually transmitted, it is necessary to test for other diseases that are transmitted in the same way.
You also need to inform your sexual partner about the disease and explain to him that he may also be infected with both ureaplasma and other diseases transmitted in this way.
Do not start the disease, because the body is not able to get rid of such diseases on its own, that is, you are guaranteed not to recover without treatment, but only get infertility and other serious complications, regardless of your gender.
Diagnosis of the disease
The disease is diagnosed by several methods, which allows to achieve high accuracy of the result. These are methods such as:
- Immunofluorescent, based on the study of antibodies that are produced to a microbe that has entered the body. The method is indirect and can lead to errors, so it is used in combination with others.
- Polymerase chain reaction method - allows you to determine the DNA of the microbe itself. More accurate and complex method than the first one.
- Culture method based on growing a culture of a microorganism on a nutrient medium in a laboratory. A smear is taken from the mucous membrane, which contains bacteria, then placed on a nutrient medium, where they multiply, and they can be seen firsthand under the microscope.
Indications for testing are the following symptoms:
- Discharge from the urethra and signs of prostatitis in men;
- Burning during urination and pain in the lower abdomen in women.
What can not be done?
 When ureaplasma is detected categorically impossible ignore the diagnosis, self-medicate or use traditional medicine instead of adequate treatment. All this can lead to the fact that the disease will be launched, and the patient will become infertile, and you will still have to be treated in the hospital, but longer and at greater cost.
When ureaplasma is detected categorically impossible ignore the diagnosis, self-medicate or use traditional medicine instead of adequate treatment. All this can lead to the fact that the disease will be launched, and the patient will become infertile, and you will still have to be treated in the hospital, but longer and at greater cost.
You should also not have sex, especially unprotected sex, as this will lead to infection of the partner if he is not already infected. In addition, mechanical irritation of the genital organs will contribute to the development of the disease both during protected intercourse and during unprotected intercourse.
Disease prevention
Preventive measures are for the most part the same as for other sexually transmitted diseases, but there are some specifics:
- Do not have sex with casual partners, have a permanent partner whom you trust;
- Use condoms(although they do not provide a 100% guarantee of protection, being primarily a remedy for unwanted pregnancy);
- Monitor the health of the genital organs (carefully observe hygiene, contact specialists at the first sign of illness);
- After taking antibiotics, restore the microflora with the help of special preparations;
- Those living in areas with an unfavorable ecological situation leave the city if possible, use purified water for drinking and cooking (this is necessary to maintain normal microflora and immunity);
- Women - regularly checked by a gynecologist;
- If you are not sure about your sexual partner, take tests just in case, without waiting for the onset of symptoms.
Methods of treatment
 Treatment is carried out by taking antibacterial drugs. The first is antibiotics. Most often, azithromycin is used at a dose of 1 g / day, or doxycycline, 100 mg 2 times a day. The course lasts 7 days.
Treatment is carried out by taking antibacterial drugs. The first is antibiotics. Most often, azithromycin is used at a dose of 1 g / day, or doxycycline, 100 mg 2 times a day. The course lasts 7 days.
Fluoroquinolones are also used such as ciprofloxacin and others.
If the treatment does not help, they begin to combine several drugs (the lack of progress in treatment is due to the fact that bacteria can adapt to antibiotics in turn, but they are not able to adapt to two or three drugs at once).
Interestingly, bacteria gradually develop resistance to the aforementioned doxycycline, which is why it is used less and less.
Possibility of infection through oral sex
The question of the possibility of infection during oral sex remains open. Some sources say that infection is possible. In this case, the pathogen enters the oral cavity and affects the mucous membrane of the throat. The symptoms are similar to those of a sore throat. But the likelihood of infection is much less than with traditional sexual intercourse. Other experts dispute the possibility of developing the disease with this method of infection, although they acknowledge that ureoplasma is found in the mucous membrane of the throat in those who practice oral sex.
Disease in women
 In women, ureaplasmosis often occurs for a long time without any symptoms. But with the onset of pregnancy or an imbalance in the microflora of the vagina, the ureaplasma begins to actively multiply and cause inflammation. Symptoms are not specific, so ureaplasmosis can be easily confused with other diseases of a similar nature.
In women, ureaplasmosis often occurs for a long time without any symptoms. But with the onset of pregnancy or an imbalance in the microflora of the vagina, the ureaplasma begins to actively multiply and cause inflammation. Symptoms are not specific, so ureaplasmosis can be easily confused with other diseases of a similar nature.
This is a transparent discharge from the vagina, which, as the disease develops, begins to acquire an unpleasant putrefactive odor and become greenish. Pain comes later in the lower abdomen, namely in the area of \u200b\u200bthe uterus cutting in nature. This indicates that the disease has already reached the uterus.
In women, frequent urge to urinate is observed, during each urination the woman feels a burning sensation. During intercourse, there is discomfort in the vagina, sometimes pain.
As a complication, diseases of both the reproductive and excretory systems can appear. These are cystitis, pyelonephritis, kalpitis and other diseases. During pregnancy, there is a very high chance miscarriage, polyhydramnios, other complications. Also, a child can be born prematurely, or with birth defects.
The course of the disease in men
In men, in most cases, ureaplasmosis occurs without any external manifestations, which is why men often depict their sexual partners with this disease against their will. If the symptoms do appear, then at first they are very mild. It can also be a burning sensation during urination, a small discharge from the urethra, which has neither color nor smell.
If the disease is not treated at this stage, it can spread to the testicles and prostate gland. There are cramps, pain in the urethra, which accompany urination or appear independently of it. Rarely, such a complication as inflammation of the epididymis occurs.
If the disease has spread to the prostate gland, patients may experience difficulty urinating, frequent urination, and pain in the perineum. If the disease is not treated at this stage, it leads to impotence and infertility.
The principles of treatment of ureaplasmosis in men and women are the same.
Conclusion
 So, ureaplasmosis is a bacterial infection that is caused by opportunistic microorganisms ureaplasma. The infection affects the genitourinary system of both men and women, is transmitted sexually, and there is no evidence that there are other ways of transmitting the disease.
So, ureaplasmosis is a bacterial infection that is caused by opportunistic microorganisms ureaplasma. The infection affects the genitourinary system of both men and women, is transmitted sexually, and there is no evidence that there are other ways of transmitting the disease.
In both sexes, the disease may not manifest itself for a long time, especially in men. A person can live his whole life without ever falling ill with this disease, but remaining a carrier of bacteria, portraying his sexual partners. A person gets sick only when the balance of the microflora of the mucous membranes of the genital organs is disturbed.
The illness starts as inflammation of the mucous membranes of the genital organs, can later spread to the internal genital organs to the organs of the urinary system, leading to complications such as prostatitis, impotence, infertility in men, inflammation in the uterus and urinary system in women. This disease is especially dangerous for pregnant women, who can cause complications in pregnancy or miscarriage.
Treatment is carried out with antibacterial drugs, it is best to use several methods for diagnosis, since diseases can be easily confused with other diseases.
Ureaplasma is a conditionally pathogenic flora that is sexually transmitted during unprotected intercourse from a carrier or a sick person to a healthy one.
If you have a strong enough immune system that performs the protective functions of the body, ureaplasma may never manifest itself.
But in the event that the level of immunity is at the lowest level, and various concomitant factors (viral or infectious disease) have appeared, ureaplasma can be activated and cause inflammation of the genitourinary system.
Ureaplasma affects a healthy person not only during intercourse, but can also be transmitted intrauterinely from an infected mother to the fetus. Postpartum infection of the baby is also possible, when during childbirth the child passes through the infected birth canal. In medical practice, the oral-genital method of infection transmission is also common.
Today, there are two types of the causative agent of ureaplasmosis:
- Ureaplasma parvum.
Provocative factors for the activation of ureaplasma are various related aspects. First of all, it is too early sexual life and a large number of sexual partners with whom unprotected contact occurs.
Provocateurs of the disease are also sexually transmitted diseases, viruses. In some cases, the problem lies in the not very effective and high-quality treatment of a gynecological disease, as a result of which an infection appears in the body that provokes the disease. Ureaplasma can also be triggered by a course of antibiotic treatment, with which you are treating various diseases. The antibiotic violates the microflora and leads to some hormonal disruptions in the body, weakens the immune system.
An important factor is also such an impact factor as stress and nervous tension, which provoke a variety of diseases, including ureaplasma. After you have become infected with ureaplasma, you will not immediately see the symptoms of the disease, since the incubation period of the microorganism can last a very long time, and for this time you become a carrier of the infection that you pass on to your sexual partners.
As a rule, the incubation period can last from 2 to 4 weeks. At this time, the inflammatory process begins, and the infection spreads further, having a negative effect on the genitourinary system, as a result of which the disease begins to show symptoms.
If you have a sufficiently satisfactory level of immunity, then the disease will not be accompanied by obvious symptoms and develops into a chronic form. And this already carries a health hazard, since ureaplasma provokes the development of serious diseases with complications. The nervous system, joints, any other organ can be affected.
Ureaplasmosis: symptoms and methods of transmission of the disease
 The disease ureaplasmosis shows symptoms in men and women almost the same.
The disease ureaplasmosis shows symptoms in men and women almost the same.
In women, many diseases that are sexually transmitted can be completely asymptomatic without menstrual irregularities, pathological discharge from the vagina, pain in the lower abdomen.
But when the immune system is at a poor level, the pregnancy period begins and there are other negative and concomitant factors, then the symptoms of ureaplasmosis begin to manifest themselves. Note that many characteristic signs of ureaplasmosis are similar in nature to many sexually transmitted diseases.
Ureaplasmosis in women has the following symptoms:
- Discharge of a transparent color from the vagina, not accompanied by a smell. Over time, the discharge may take on a dirty yellow or greenish color, and have an unpleasant odor. These symptoms already indicate that an inflammatory process has begun, which can develop into a chronic one.
- The pain in the lower abdomen indicates that ureaplasmosis begins to cause inflammation in the uterine appendages.
- If there was an oral-genital method of infection, then a sore throat may develop, the tonsils become covered with a whitish, purulent coating.
- When urinating, there is a sharp pain and burning sensation, the urge to urinate also becomes more frequent.
- During sexual intercourse, pain in the vagina may also be present.
In any case, a woman should be examined not only when they notice the unpleasant symptoms of ureaplasmosis, but regularly - preferably once every six months, in order to prevent the development of chronic diseases caused by ureaplasma. You may not have severe symptoms, you may be a carrier of the infection and pass it on to your partner.
More about the disease
Symptoms in men ureaplasmosis are manifested as follows:
- non-gonococcal urethritis develops;
- cloudy discharge from the urethra;
- objective symptoms may be absent (pain when urinating, frequent urge to urinate);
- discharge may appear and disappear, then reappear;
- testicular inflammation develops.
The consequences of the lack of adequate treatment can manifest themselves in damage to the genitourinary system, infertility, and joint tissues. Treatment of the disease begins with diagnosis by seeding and PCR. The doctor, based on these tests, prescribes a therapy that will make it impossible for the development and spread of infection in the body. To improve the general state of health, special preparations are prescribed to correct immunity, suppress infection and get rid of other infectious and viral diseases that reduce the level of immunity.
According to the culture data, the doctor determines the level of sensitivity of pathogenic microflora to different types of antibiotics in order to prescribe the most effective drug and select the optimal and individual treatment regimen for the patient.
In addition to a variety of specific drugs, immunostimulants, bactericidal agents of local action, and the use of physiotherapy are also prescribed. One of the most important conditions for recovery is the treatment of not one, but two sexual partners in order to rid their bodies of the presence of a problem and re-infection. In the process of treatment, you should not live sexually, you need to apply a special diet and follow all the recommendations of your doctor.
What diseases provokes ureaplasma in women and men
 Ureaplasma in women can occur with symptoms and asymptomatically, if there are no negative factors that activate inflammatory processes. Therefore, the gynecologist always recommends visiting him at least once every six months in order to conduct examinations to identify all, even hidden problems and infections, viruses.
Ureaplasma in women can occur with symptoms and asymptomatically, if there are no negative factors that activate inflammatory processes. Therefore, the gynecologist always recommends visiting him at least once every six months in order to conduct examinations to identify all, even hidden problems and infections, viruses.
If adequate treatment is not carried out, ureaplasma in women can develop into a chronic form and cause various complications.
When a chronic process begins, then the harmful microflora of ureaplasma remains on the walls of the mucous membrane of the genital organs, and at any time, under unfavorable conditions, it can be activated and cause inflammation, exacerbation, and damage to the urinary tract. Vaginal discharge may not have color or smell, but this may already indicate the presence of an infection that can lead to such negative consequences as infertility, complete inability to conceive, miscarriage of the fetus at different stages of pregnancy.
Strong provocateurs of infection include colds, stress, low immunity, viral problems, increased physical activity and other aspects. Therefore, ureaplasma in men and women is a certain danger and should be treated. With untimely and inadequate treatment, pathogenic microflora causes urolithiasis, colpitis, cystitis, endodermatitis, arthritis. If the infection process goes too far, then ureaplasmosis can cause infertility in women, as adhesions occur in the appendages and uterus.
If ureaplasmosis is activated during pregnancy, it can cause miscarriage or premature birth. Treatment of ureaplasmosis in women is carried out only on the recommendations and under the supervision of a physician. The most effective is antibiotic therapy. In this case, the doctor determines the antibiotic that best suits the individual characteristics of the patient, her body and the course of the disease. The scheme and dosage of the drug is chosen by the doctor. In combination with antibacterial therapy, local treatment is also carried out with the help of vaginal suppositories.
Immunomodulating drugs are also used, which prevent the further development of the pathogenic flora of the vagina and gastrointestinal tract (due to antibiotics). It is necessary to temporarily abandon intimate relationships for the duration of treatment so as not to injure the mucous membranes of the genital organs. If a pregnant woman is being treated, then therapy begins only after 22 weeks of pregnancy. In most cases, therapy lasts up to 2 weeks.
 As preventive measures, you should lead a normal intimate life with one partner, use protective equipment and periodically visit a doctor and do tests.
As preventive measures, you should lead a normal intimate life with one partner, use protective equipment and periodically visit a doctor and do tests.
Ureaplasma in men is as common as in women. The course of the disease can also be asymptomatic in the early stages, when there are no activation factors. And this is the main danger, because when symptoms appear, they indicate those complications and diseases that were provoked by ureaplasmosis. The first signs may appear several months after infection. Most often, ureaplasma in men causes pain and burning during urination, secretion, inflammation of the urethra.
A frequent manifestation of the problem is urethritis, which is accompanied by cuts and pains, burning and discomfort during urination. Very rarely, but the disease goes away by itself, but most often leads to the fact that it becomes chronic with periodic exacerbations that adversely affect the quality of life. or inflammation of the epididymis is rare, but quite possible. The disease is not accompanied by any discomfort and pain, but the appendage thickens and increases.
These symptoms make a man visit a urologist, and then he will find out what is causing the problem. Prostatitis can have a variety of causes, including ureaplasmosis in men. Symptoms of the disease are all the same pain when urinating, burning and discomfort in the perineum. If left untreated, the disease leads to impotence and male infertility.
Therapy for ureaplasma in women and men is the same, an individual treatment regimen is also being developed with the use of antibiotics, immunostimulants. If one type of drug does not give quick and effective results, it is replaced by adequate drugs with more effective action. Prevention of the disease should be carried out constantly, especially if you are sexually active, then your partner should also be examined.
Ureaplasmosis: treatment with antibiotics and folk remedies
If you have been diagnosed with the disease ureaplasmosis, treatment is carried out using innovative drugs that give effective results.
This disease should be treated in the following cases:
- When studies and symptoms show that an inflammatory process is taking place in the body, which can cause complications and other diseases of the genitourinary system.
- If you are a sperm donor.
- Those women who have a history of infertility and have the opportunity to resolve this issue positively.
- Before planning a pregnancy.
 Doctors use an integrated approach to treatment, as it is necessary to get rid of pathogenic microflora, have a local effect on foci of inflammation and increase the level of immunity.
Doctors use an integrated approach to treatment, as it is necessary to get rid of pathogenic microflora, have a local effect on foci of inflammation and increase the level of immunity.
Therapy with antibiotics is considered the most effective. This virus has one bad property - it is able to mutate and resist antibiotic treatment. Therefore, the treatment takes place under the supervision of a doctor, and if the therapy does not give the desired results, then the antibiotic is replaced with another one. To test the propensity of this harmful microorganism to antibiotics, a culture is carried out, which shows which groups of antibiotics can cope with the problem and destroy the infection. The most commonly used macrolide antibiotics are they can cope with the microorganism, fluoroquinols are also effective.
It is very important to carry out a full course of therapy, which will completely cleanse the body of the presence of infection and you no longer have to worry about relapses and acute forms of the disease. You can help yourself using folk remedies. In this case, medicinal herbs are used that have antibacterial properties, immunostimulating, cleansing. Medicinal collections are perfect, from which you will make infusions and decoctions.
As medicinal herbs are suitable:
- chamomile;
- licorice;
- leuzea;
- alder cones;
- kopeck root;
- succession;
- wild rosemary;
- yarrow;
- burnet;
- lungwort;
- violet;
- thyme;
- wild rosemary;
- plantain.
You can make a medicinal decoction of several herbs, taking them 1 tbsp each, pour boiling water over them and leave for 40 - 60 minutes. The infusion is filtered and consumed before meals (30 minutes) 2 times a day, half a glass. Insufficient treatment of ureaplasmosis can lead to a variety of consequences. If there is no treatment, the problem fades, and after a certain period of time it manifests itself in an acute form, and this can last indefinitely.
Ultimately, the disease leads to problems such as impotence, infertility, other severe pathologies, problems during childbirth and miscarriages. In addition to the great danger posed by the ureaplasmas present in your body, other negative changes may also occur. For example, the development of diseases from mild to severe and chronic forms.
Varieties
Very often, this infection can be combined with other viruses and diseases in your body. For example, it can be chlamydial and gonococcal lesions, the presence of Trichomonas, etc. When these infections mix, an acute and severe course of the disease is obtained, which has a very negative effect on overall health. The treatment of such infections takes a very long time and it is necessary to use strong broad-spectrum drugs.
The presence of an infection in the body often indicates that the patient has a very low level of immunity, and this suggests that the body can easily “catch” any infectious and viral disease, which will complicate the state of health. Therefore, it is so important to start treating this problem - ureaplasmosis, as early as possible, to use effective drugs, to follow all the doctor's recommendations.
Ureaplasmosis during pregnancy and the effect of the disease on the fetus
 Ureaplasmosis during pregnancy is a danger of infection of the unborn baby with an infection.
Ureaplasmosis during pregnancy is a danger of infection of the unborn baby with an infection.
The difficulty in diagnosing an infection at this point lies in the fact that the main symptoms are vaginal discharge, which are characteristic of pregnancy and ureaplasmosis. And in some cases, infection is completely asymptomatic. Therefore, for an accurate diagnosis, you should undergo an examination so as not to aggravate your condition and take timely treatment measures. If the problem was noticed at the wrong time, then pain and pain in the abdomen are added to the discharge, which causes severe discomfort and fear for the fetus. Any infection and ureaplasmosis during pregnancy is a risk of losing a child or giving birth to him with various pathologies. The percentage of miscarriage diagnosed with ureaplasmosis today is up to 35%.
The presence of infection in a weakened body of a pregnant woman helps other viruses to enter the body and cause diseases, impaired growth and development of the fetus. Previously, such a diagnosis as ureaplasmosis during pregnancy could serve as an indicator for its termination, since the infection infects the fetus, which leads to serious consequences and pathologies. Today, the treatment of various infectious and viral diseases, as well as ureaplasmosis before conceiving a child and during pregnancy, is effectively treated.
If infection occurs in the first trimester of pregnancy, the mother's body protects the fetus from infection. But the infection itself negatively affects the condition of the walls of the uterus - it causes their loosening, which is the cause of miscarriage or premature birth. In this case, the walls of the uterus are sutured to keep them in good shape and reduce the risk of premature termination of pregnancy.
Ureaplasma therapy is carried out with antibiotics and therefore, in order not to harm the development of the fetus, treatment of a pregnant woman with these drugs begins from the 22nd week of pregnancy. It is at this time that the fetus is already reliably protected, it has good immunity and all internal organs are already developing. In parallel with antibiotics, immunostimulating agents are also prescribed, which increase the protective functions of the body and prevent the risk of infection with other diseases.
Ureaplasmosis in an “interesting” position during pregnancy is dangerous, therefore, before conception, you should undergo all the necessary examinations, and in the event that the infection is diagnosed, it must be eliminated immediately.
To date, ureaplasmosis has not yet been fully studied, and no doctor can predict the course of pregnancy with such a diagnosis, a variety of scenarios of pregnancy, childbirth, and postpartum complications are possible. Treat your health carefully and carefully, as ureaplasmosis can often be diagnosed just during pregnancy. Infection occurs during pregnancy, so avoid those situations in which you can catch unwanted viruses and infections.