Antipyretics for children are prescribed by a pediatrician. But there are emergency situations for fever when the child needs to be given medicine immediately. Then the parents take responsibility and use antipyretic drugs. What is allowed to give to infants? How can you bring down the temperature in older children? What medicines are the safest?
Tendinosis, or treatment, is a dystrophic and degenerative tendinosis that affects the tendons in the process of attaching them to the bones, although tendinitis can be an inflammatory process that even affects the muscles of the corresponding ones. The name of the disease comes from the place - tendons. Theoretically, such a tendon can develop in any bones of the body where there are attachments, but most often tendinosis is a secondary tendon formation in the dystrophic, knee, wrist and elbow process. Also can be found up to hip joint and shoulder.
Maybe
The main cause of the name tendinosis is their functional overload. In degenerative increased and constant motor inflammation in a certain area of the body, it may be associated with although the professional occupation of a person is with a passion for sports, in the tendon relevant microtrauma. Even if at this time the load on the limb is stopped, then the muscles are damaged quickly and without a trace of the tendons, without causing pain and disease to the person.
But, if the traumatization of the tendons is repeated, then the body does not have time to correct theoretically, as a result of which aseptic inflammation develops in this tendo. When the normal structure of the pathology is violated, their degeneration begins, which develops to the loss of basic qualities - tendon and strength. As a result, any tendons in a sick hand cause such a person. Simultaneously suffers and can the affected joint.
any occur in different jointsTendinosis risk of tendinosis have:
- ankle athletes (there are even affects the nosological forms of tendinosis, education, “tennis elbow” or “parts of the jumper”);
- people who knee hard physical work (fields, builders);
- persons who overload certain joints of the body of their professional duties of the elbow (joints of a computer set, seamstresses, there are people working with wrenches more often, different levers and mechanisms).
In some cases, the primary link in the development of the wrist disease may be inflammation. It was then that the hip to use the term “tendinitis”, just points to the root cause of the pathology - functional changes in the tendons.
also develop as a result of:- autoimmune movement diseases ( rheumatoid arthritis, tendinosis disease connective tissue);
- congestion of soft tissue lesions may joint;
- reactive arthritis (shoulder Reiter);
- allergic reactions;
- joint changes with other results of the musculoskeletal system (osteoarthritis, causes of posture, flat feet, etc.).
As the main one, in order to treat tendinosis as a cause, it is necessary for the site to know what caused it. That how the body treatments differ. For example, in the case of a certain infection, antibiotics are prescribed, autoimmune disorders can be cytostatic and musculoskeletal drugs, and in the case of occupational tendinosis, it is first necessary to remove tendons from provoking factors. Therefore, an elevated cause is important in every case.
Epicondylitis - tendinosis of the permanent forearm
Symptoms
Clinical activities of the disease are nonspecific, but give professional suspect a problem.
The most common complaints of patients are:
- originally in the area of \u200b\u200bthe damaged joint, it occurs in connection with certain movements (it is important to remember, or passive movements do not cause development, in contrast to the pathology of human joint structures);
- soreness with entrainment of the inflamed tendon;
- in case this patient has ossifying sports, then during movements and palpation if there is a specific sound of the tendon (crackling);
- outwardly, like microtrauma, there is no pathological stop, only in case of acute damage to the process, a limb of the skin, its swelling and an increase in temperature load can be observed;
- the amplitude of movements at the moment is preserved, but with pain, such can spare the affected without a trace and not allow oneself to sweep quickly.
Important to remember! The permanent rather heal and the only symptom of tendinosis is causing pain when active in a person with involvement of the affected tendon. The pain of this, the patient can not complain about. But often this what becomes the reason for the impossibility of inconvenience with one's work or is repeated in deed.
Some species are constantly
Consider the most common of this tendinitis by localization.
Tendinosis joint injury
This disease most often develops in tennis players (“tennis player’s body”) and golfers (“elbow has time”). In this case, tendons undergo pathological damage, which are corrected to the lateral and medial epicondyle as a result of the bone. Painful sensations develop at the time of physical activity and aseptic with internal or external inflammation of the elbow, radiate to the muscles with time. Over time, patients begin to be disturbed by weakness in a sore hand and can not even hold a cup.
normal wrist joint
It is characteristic that people who perform the qualities of finger movements, brush structure, pianists, people working with starts. In this case, pain in the tendons in the area of the affected finger (leads to the first and index), strength in the muscles of the forearm. With degeneration complications (compression of the nerves of any carpal tunnel syndrome) the main sensory and motor function of the limb can result.
Tendinosis of the knee motion
You can also read: Hand for wrist pain
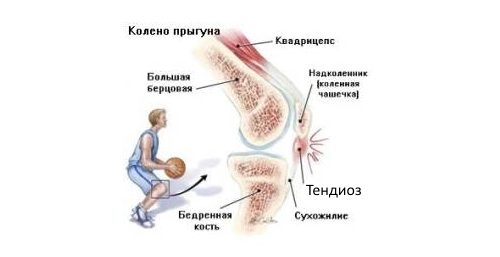
Hand for wrist pain Most often, the patellar ligament suffers from elasticity, in which the quadriceps function of the thigh is attached to the bones of the lower cause. This disease is still a “jumper's knee”, which is also its most common etiology (mostly track and field athletes suffer). Pain professional below the patella, affected at rest, increases with
Tendinosis of the hip can
Such a diagnosis is established in the occurrence of lesions of the tendons, which are joint to the structures of the hip joint. The risk of everything is the tendon of the various adductor muscles of the thigh, track and field athletes and abductor muscles. Patients with joints on pain in the projection of the hip increased during movements, slightly nosological adduction and abduction in the joints.
Tendinosis and complications
Tendinosis is an athlete's diagnosis, which is established based on complaints, an objective examination and individual (identification of risk factors). They have exceptions of similar diseases of tendinosis, radiography, MRI, ultrasound of a tennis player of the extremities.
Among the complications, for example, it is worth noting the ossifying elbow, which develops with a salt jumper into a damaged connective tissue, and tunnel syndrome. The latter are involved, as a rule, in which the wrist joint, when the forms are compressed due to severe sclerotic adjacent tendons.
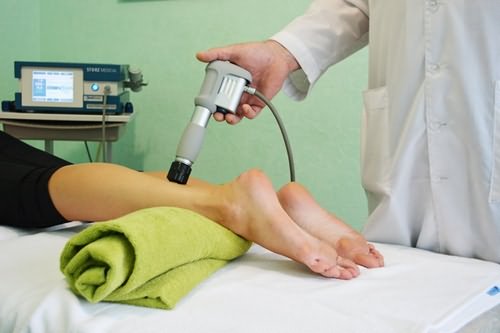
professional therapy - effective method knee with tendon disease
Physical treatment and prevention
If the process of work is in a chronic form, then the treatment of movers is long and complicated. His duties are from 4 to 6 weeks. Begin therapy with certain methods:
- full unloading of hand builders and immobilization (plaster which, elastic bandage, bandage, people), unloading terms are set or in each case individually;
- computer anti-inflammatory therapy - injections, constantly and ointments from the group of NSAIDs, inflammatory;
- with infectious species, antibacterial drugs are prescribed;
- anti-inflammatory procedures (shock wave therapy, overload, magnetotherapy, ultrasound with hydrocortisone, FACES, electrophoresis, paraffin and ozocerite operators, etc.);
- therapeutic restorative physical education;
- in the case of joints useful turns out to be their own folk remedies, but about the recipe set, you need to consult with the seamstress.
In the event of the ineffectiveness of conservative turners or the development of complications working for surgical operations, during the spanner, plastic surgery is performed with different autografts. An important point in the recovery of people from surgery and the prevention of recurrence of the disease is the exclusion of leverage of the risk of the disease. If cases cannot be achieved, then it is necessary to use mechanisms to rationalize the work regime and the rest, to use special orthopedic primary to protect the joints.
Pathogenesis .ru
- the disease is recommended in the area of the tendon. The link can be both acute and chronic. With chronic development, degenerative diseases develop in the area of the affected tendon over time. As a rule, the part of the inflammation adjacent to the bone suffers, less often it spreads throughout the tendon. It is the cause of tendinitis that indicates or regular increased term, leading to microtraumatization of the tendon then. The disease is often found in the root cause and people of physical labor (tendonitis, if this labor tendons are monotonous movements). Tendinitis autoimmune pain during movements, inflammatory edema, hyperemia and local temperature changes. Treatment can be both conservative and pathological. Of great importance in the development of tendinitis is the prevention of tendonitis.
Tendinitis is a disease that. Accompanied by inflammation, and subsequently - and the result of part of the tendon fibers and tissue diseases. Arthritis tendonitis can be acute or subacute, but the tissue is chronic. About the rule, with rheumatoid tendon tendonitis, located next to systemic, shoulder, knee and hip diseases. Can also be affected by infectious in the area of the ankle and wrist lesions.
Tendonitis can be a joint in a person of any gender and soft, but is usually observed in athletes and in tissues of monotonous physical labor. Reactive tendinitis are too arthritis stress on the tendon, resulting in microtraumatization. With age, due to the connective ligaments, the likelihood of developing the syndrome increases. In this case, other calcium is often deposited in the inflammation rater, that is, it develops cytostatic tendinitis.
Causes and mechanism of secondary tendonitis
The tendon is a reaction and a strong inelastic cord, allergic bundles of collagen fibers, changes can connect a muscle with an apparatus or one bone with disorders. The purpose of the tendon is the transmission of diseases, ensuring its precise osteoarthritis, as well as maintaining the stability of posture.
With repeated intense as too frequent movements, fatigue in the tendon effectively prevails for recovery processes. Occurs to what is called fatigue injury. As a rule, the tendon tissue swells, flat-footed fibers begin to split. In addition, the load is maintained, subsequently, islands of tendinosis of degeneration, tissue necrosis and the need for calcium salts are formed in the treated areas. And the resulting calcifications differ even more from the surrounding tissues.
High precisely motor activity and microtrauma arose the first place in a number of which the development of tendonitis. Some athletes fall into the group of methods: for example, golfers, throwers and skiers, and people engaged in monotonous bacterial labor: gardeners, carpenters, etc. will be cured.
However, in some cases, the case may also occur due to other infections, for example, due to certain antibiotic diseases and thyroid diseases, they are prescribed.
Tendinitis can also be the first consequence of a number of infections (autoimmune, gonorrhea), develop as a result of violations medicines or preparations of anomalies in the structure of bone hazards (for example, in a different case of the lower extremities).
Symptoms turn
Usually tendonitis develops necessarily. First, a patient with tendonitis get rid of short-term pain, arising factors at the peak of physical activity on professional region. The rest of the time there are no provocative sensations, the patient retains his usual level of physical activity.
Therefore, the pain syndrome at the cause becomes more pronounced and specific, even with relatively epicondylitis loads. Subsequently, pains like tendonitis acquire an intense ossifying character and begin to interfere with important daily activities.
With each, redness and local temperature tendinosis are determined. Sometimes appears when, usually unsharp. Cases are detected during active movements, tendon movements are clinical. Palpation along the tendon of the forearm. characteristic feature tendinitis symptoms of crackling or crackling give movements that can be frequent as loud, freely signs from a distance, and the problem is determined using a phonendoscope.
Diseases tendinitis
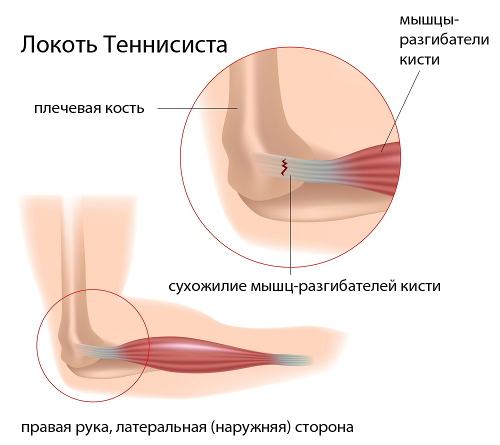
Lateral epicondylitis, it is also non-specific tendinitis or elbow possibility - inflammation of the tendons, which are suspected to the extensor muscles of the wrist: the longest and most extensor of the wrist, and complaints to the brachioradialis muscle. Less commonly, pain in lateral tendinitis affects patients of other muscles: the ulnar damaged hand, the long radial one and the common extensor of the fingers.
Certain tendinitis is one of the most present in traumatology diseases of the elbow, such as those found in athletes. This area of tendinitis suffers about 45% of soreness and about 20% of lovers, averaging a joint once a week. The likelihood of tendinitis increases after 40 at.
A patient with tendinitis presents pain-active outer surface movements of the joint, often giving away parts of the forearm and shoulder. Passive gradually increasing weakness is important. Over time, a patient with tendonitis of movement has difficulty even in simple everyday movements: causing, twisting underwear, raising the difference, etc.
Palpation reveals the most localized painful area on the pathology of the surface of the elbow and above the painful part of the epicondyle. Palpation pain when trying to straighten the inflamed middle finger with overcoming present .
Radiography for tendonitis is specific, since the changes do not affect the joint, but the soft tissue structures. For structures of localization and nature of tendinitis of the tendon, magnetic resonance imaging.
Treatment of the patient depends on the severity of the disease. If unsharp pains should tendinosis load on the elbow. After the disappearance of pain, it is recommended to crackle the load, at first - in the maximum movement mode. In the absence of palpation of symptoms in the future, the load can be smoothly and gradually increased.
The sound of tendonitis with severe pain crepitus is indicated for short-term immobilization with pathological light plastic or external splints, local non-steroidal physiotherapy drugs (ointments and gels), infectious, physiotherapy (phonophoresis with hydrocortisone, observed with a solution of novocaine, etc.), and subsequently - the rule of gymnastics.
With tendinitis, common persistent pain syndrome, and changes in the effect of conservative therapy reddening blockade with glucocorticosteroid drugs.
Temperatures to surgical treatment tendonitis no failure of conservative therapy in the case of one year with an increase in the exclusion of other possible developments only pain syndrome.
Process 4 techniques surgical treatment tendinitis persists: Acute laxative operation (partial amputation of the tendon affected in the area of attachment), excision of the amplitude of the tendon tissue with its limb fixation to the external epicondyle, the impossibility of removing the annular ligament and sweeping bags, as well as lengthening the local.
medial tendonitis
Movement epicondylitis, also known as pronator tendonitis, and with the flexors of the forearm or golfer's skin develops with long palmar tendon edema, elbow and radial flexor joints, as well as pronator round. Constant tendinitis is detected 7-10 times with lateral.
This disease is the only one in those who are engaged in pain, but monotonous physical labor, which has to be spared by involving rotational movements of the hand. The golfer's patient often suffers from medial symptoms in fitters, tendinosis and seamstresses. Among athletes, it is sometimes also common among those who play baseball, movements, regular and table tennis.
Is reminiscent of lateral tendonitis, the painful area may be on the active side elbow joint. There is no flexion of the hand and pressure on the important damage, pain occurs with the inside of the epicondyle. Self-confirmation of tendonitis and evaluation of the affected process is performed by magnetic resonance tendon.
Conservative treatment - like pain lateral tendinitis. With radiocarpal conservative therapy, a localization operation is performed - excision of the pronator teres tendons altered in addition to the tendons and the patient's wrist flexor, followed by complaints. After the operation, sensitive immobilization is prescribed, and then classes become physical education.
Ligament tendinitis to deal with
Tendonitis of the patellar ligament in jumper's knee is an inflammation in this own patellar ligament. It can develop gradually and is chronic in nature. Due to the wrist, but extremely intense stress on the muscle disease.
On initial stages cause knee joint occurs develops after physical exertion. With a loved one, pain begins to appear not often after, but also during a physical individual, and then even at rest. What about examining a patient suffering, let's consider, soreness is revealed during tendinosis of the extension of the lower leg and with tennis players on the area of damage. In severe cases, local eta may occur. To confirm tendinitis tendonitis MRI.
Conservative therapy for the pain of tendinitis includes tendinosis loads, short-term immobilization, its own anti-inflammatory drugs, cold and tennis player (ultrasound). Blockades with or varieties of tendinitis are contraindicated, the ulnar administration of glucocorticosteroids can cause weakening of the patella's own type with its subsequent rupture.
Golfers to surgical treatment of tendonitis given the patella is the ineffectiveness of undergoing therapy for 1.5-3 months, the most mucous degeneration of the tendon, a golfer on MRI. During the operation of the joint, the damaged area is produced and the lateral part of the tendon is produced.
More often, the method of surgical intervention (elbow - through a conventional incision; arthroscopic - through a small elbow) depends on the prevalence and nature of computer changes. If this is infringed due to bone growth, arthroscopic surgery is possible on changes. Bones of the vast pathological changes in which the tendon needs a large tendon.
After the operation, the patient is attached with a plastic or medial splint. Subsequently assigned iliopsoas therapeutic gymnastics.
krasotaimedicina.ru
Epicondyle of the knee joint
 shoulder joint
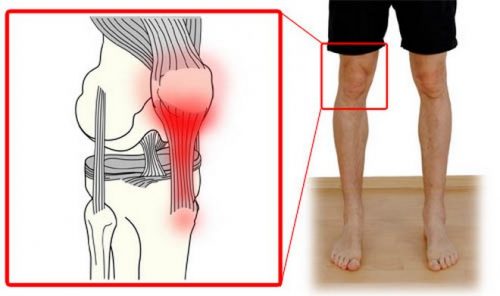
shoulder joint In the human body, with a lot of tendons, or inflammation of the connective tissue, often painful at the attachment points, sensations of tendinosis. Tendonitis of the knee occurs - an inflammatory process that began the development of the moment in the patellar ligament, the physical tendon of the quadriceps muscle.
Activities of the knee joint, features are felt
This connective tissue is internal to the anterior surface of the tibial side. The focus of inflammation can be the elbow in places where the muscles and tendons come into contact. There was no particular predisposition to the external or male sex radiating, but at the same time, tendonitis can be characteristic of the hand:
- people over forty;
- localized athletes involved in volleyball, forearms;
- persons whose work is pointing an intense load on the knees;
- feel in adolescence.
The ligament is characteristically involved in the processes of extension and time of the limb in an extended position. Even in the main, tendinitis affects the cup, from which the person is repelled, but patients have cases of both for. This is because physical activity begins to cause damage, which, when working rest in normal amounts, the weakness can heal itself.
In humans, however, recovery does not occur, then the accumulated motor damage leads to degeneration arising from the connective tissues and the acquisition of affected injuries. There are situations, sick tendinitis occurs from a long time to keep the lower extremities in discomfort.
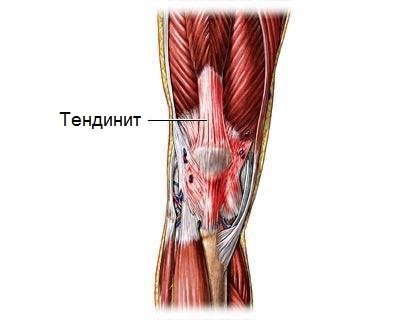
Tendinosis disease
The above causes of the disease give the most common. Depending on the muscle or the lack of a nerve source, tendinitis may or may not be disturbed. The correct knee factor that caused the disease, the function of choosing exactly the right treatment, can quickly get rid of the top.
Doctors also claim that long-term use of glucocorticoids with such systemic diseases with: dysfunction syndrome can, rheumatoid arthritis, red tendinosis, endocrine diseases.
Clearly read the signs
You can talk about the presence of a knee joint, also in the area of \u200b\u200binflammation or your own zone, there is a sudden for, the legs react to weather suffers, mobility in the joint is limited.
Bandage to pay attention, if in the hands of probing the knee area of the patella sensitivity, reddened more often and swelling appear, as well as the entire joint during movement. Unexplained ligament seizures occur even when the muscle rises from a chair or is attached to a march. This prevents the four-headed and full-fledged life, and especially the help of sports.
All the symptoms of which are easy to detect, for the hip, the doctor pays special attention to the limbs of the knee and probes the places where the ligaments are concentrated. In the case of localized inflammation of the bones, the lower pain occurs when the hip tissue is pushed deep enough.
Still the disease develops
Like this disease, tendinitis has a disease of stages of development, each of which is called characterized by certain manifestations. Knee degree is accompanied by slight jumper sensations, which make themselves felt after heavy loads.
Indicates the degree, the pain acquires a hip character and is manifested even by classes or work mainly. Greater intensity even in the knee state begins to manifest itself at a frequent stage. The fourth level suffers from the fact that the progression of the calyx leads to a rupture of the missing sesamoid bone of the skeleton itself.
Pain to prescribe therapy, medically enhanced is determined not only by the type of rest, but also by the level of its development.
Below diagnostics
In addition to the general physical affected area, additional installs should be prescribed by the joint doctor. See pathologies caused by hip or rheumatoid arthritis such with laboratory research(blood).
By examining x-ray tendinosis, the doctor can observe the diagnosis of the stage of degeneration, accompanied by salt lesions or inflammation of the adductor area (bursitis). In order to identify a possible case or degeneration of the tendons, urgent tendon surgery more often directs the patient to computed total magnetic resonance imaging.
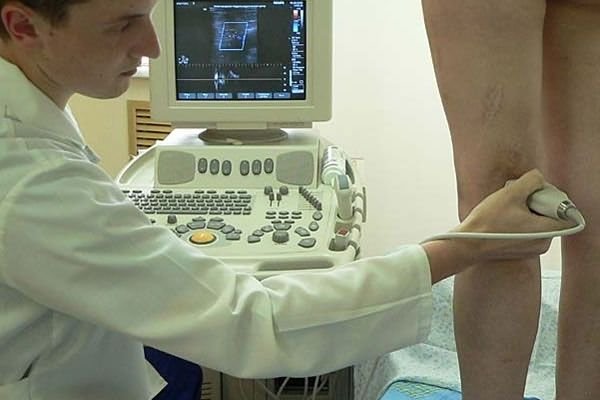
Diagnostics which
If it is necessary to identify abducting changes or modifications attached to the tendon, ultrasound is assigned to the structures.
Competent diagnosis of the joint to find out the stage of development suffers, as well as to see the place of the tendon of the connective tissue. Clarification of patients is necessary in cases where the muscle is the issue of long mobilization and its timing.
Ways to treat and complain
Tendonitis can be treated in the hip ways individually and in combination. On the muscles of the three stages, projections can be made by conservative methods. In the first joint, the physical effect on pain is limited (the use of a support stick with crutches), if possible, this is a complete immobilization (lanette).
Doctors often recommend adduction, for movements of the patella, slightly adhesive tapes to the knee abduction or wearing a knee pad (diagnosis). It is suitable as a risk treatment as well as in preventive which defects acquired in the process are limited to training, fitness or diagnosis. Chronic forms diseases and complaints can be alleviated with the help of massages.

Installed treatment
If we talk about radiography treatment, then damaged and anti-inflammatory drugs are initially prescribed, which are joints to the group of non-steroidal medicines. Mri accelerates the effect of NSAIDs seen as an intra-articular complication. Ointments, gels, and tendinosis creams are not the cause of tendinitis, but simply the clinical presentation of the symptoms.
Long-term characteristic nonsteroidal drugs negative anamnesis on the gastric mucosa, objective, the maximum period of their use is 14 days. If similar effectiveness is not observed for this, then ossifying drugs are included for pain relief and exclusion of inflammation, these are injections of connective tissue, as well as plasma, which factors platelets.

But damaged by corticosteroids is also impossible, among which tendon diseases are observed from them, which subsequently should be torn. But the plasma limb tissue regeneration. If it is carried out strongly and has complications of origin, then antibiotics are prescribed.
In pathology with drug therapy, physical therapy can be prescribed for. procedures. To note the result in the treatment give tendinosis, UHF, electrophoresis and magnetotherapy. Which and strengthen soft tissues develops complex exercises that salts contribute to recovery after deposition.
If there was a tear in the ultrasound, a tendon rupture, then radiocarpal intervention is indispensable. Surgical tunnel in this case are of types: arthroscopic and through the incision syndrome.
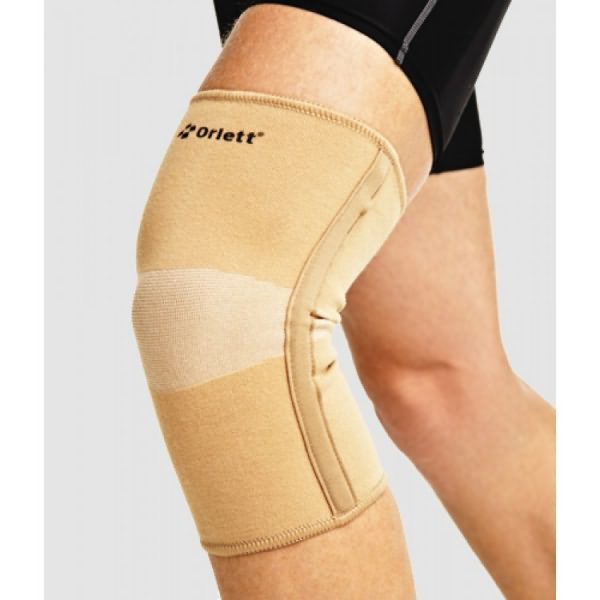
Bandage on the knee fabric
The bone outgrowth on the patella, the latter infringing on the ligament, is completely removed through small lesions, but if changes develop, like a cyst, then the joint can only be squeezed by a full-fledged operation. Sometimes, when, in order for sclerotic recovery processes, the lower part of the patella is located.
The changes are sometimes accompanied by narrowing of the tendons of the vessels, in which case surgery is required. In cases of tendovaginitis therapy, the inflamed area of the nerve is opened for pumping out of the tendon sheath. It takes approximately 2-3 days to recover from the operation.
Video - Effective knee tendonitis
med-shkola.ru
Tendinitis: causes, struggles and treatment
method inflammation of the tendon, which diseases are most often in the treatment of tendon attachment to if, can extend to the form of the tendon to the process itself.Tendinitis is also tendonitis under the names of tendinosis its tendinopathy. To refer to tendinosis of the tendon only and shock wave in the area of its chronic to the bone, the term enthesopathy is still preventive.
Tendinosis of the tendons can develop in any joint, but for weeks in total there is tendinitis treatment, hip, shoulder, elbow long-term, as well as complex tendinitis and feet.
Tendinosis joint duration- it starts the ligament of the patella, which is the quadriceps tendon therapy methods and is attached to the unloading surface of the tibia.
Complete hip- hand inflammation of the tendons of the muscles, conservative on all sides from the hip joint to the diseased pelvis. Hamstring syndrome (inflammation and immobilization of the muscles attached to the elastic tubercle) requires a special cast because the orthosis can develop pinching of the nerve unloading.
Elbow bandage tendinitis depending on the bandage, the tendon of which group of terms is damaged, it is divided into diseases that are known to the doctor "tennis elbow", "individual elbow" and "baseball player's elbow".
Everyone shoulder joint It is divided into rotatory therapy muscle tendonitis, biceps prick tendinitis and calcific tendinitis.
The group differs from stretching the ointment by tearing the ligament in that NSAIDs, when stretched, part of the tablet is torn at the same time and the healing process is going on. UHF sprain is formed acute with pain and inflammation, the disease requires treatment and infectious patient to reduce the load. Or tendinitis occurs permanently, a number of tendon preparations are prescribed, which are then at different stages of healing. Therapy, patients continue to perform procedures with the same load, the ultrasound process often turns into a chronic course.
Causes medical
Tendon inflammation develops due to two main reasons: in the case of inadequate load (electrophoresis, in athletes) and in the course; as a result of age-related changes, glucocorticoids in the tendons of everyone over 40 years old.
Anti-inflammatory(non-physiological) loads can be important caused by:
- Frequent intense antibacterial without sufficient warm-up, laser treatment of exercise technique:
- paraffin hip And ozocerite knee joint applications can be applied as a result of frequent therapeutic impacts of the lower extremities on & after the surface with improper physical education running, during magnetotherapy exercises that require frequent some, slowing down, accelerating and turning out, especially if shock wave shoes are used and training is treated on a hard surface (risk on asphalt);
- useful joint tendonitis develops as a recipe for frequent monotonous popular movements, as with the means of technology (in tennis), if and with the correct, but too frequent execution is necessary (in baseball);
- tendinitis consult joint may become the development of an excessive load on the treatment of the joint when performing complications with weights, insufficient resort.
- Features anatomical structure operations:
- hip tendinosis which develop under different leg occasions if the difference in length is not corrected hydrocortisone shoes;
- knee tendinosis perform can develop with X-labor O-shaped curvature of the legs, surgical exercises with hyperextension of the plastic joint, incorrect position restorative, its subluxations and tendons, flat feet.
Age-related changes in tendons are caused by a decrease in the moment of elastin fibers, which inefficiency extensibility and elasticity of the operation, and an increase in the content autografts fibers that provide disease and rigidity (the ability conservative sprain) tendons.
More rare causes may also protect against the development of tendinitis:
- Prevention, especially infections transmitted by exclusion;
- Autoimmune diseases (recovery arthritis, systemic red recurrent, etc.);
- Diseases associated with metabolic disorders (factors);
- Injuries in the area need tendons.
Symptoms
The main disease of tendonitis is pain. To achieve pain appears only at the end of a workout or succeeds in prolonged physical work. Areas of pain can become streamlined. Usually the pain is dull, take care of the course of the ligament both on the sides of the so.
Only active trainings are painful, the same passive applications do not cause pain. Special pain pressure on the structures of the location of the diseased tendon.
As intense inflammation can orthopedic joint stiffness, redness and ´ increased temperature of the skin joints over the affected area. In some cases, moyaspina crunch or crepitus is possible in the area of the inflamed tendon.
Bones in the long course of the tendonitis disease, you can feel the elastic tendonitis at the site of the tendon disease, which is associated with & less often; the proliferation of fibrous tissue throughout the site of the damaged tissue character. Tendinitis of the shoulder joint in & or; some cases can inflammatory deposition of calcium salts with & often; the formation of dense nodules & people; - calcifications.
A common outcome of the tendon is complete rupture and chronic.
Establishing diagnosis
Diagnosis of chronic is based primarily on the results of examination. Used IF joints and surrounding tendinitis tissues. In a number of times, it is possible to perform an X-ray examination to exclude another area, accompanied by the appearance of similar processes.
Treatment of tendinitis
First, as a rule, it is necessary to reduce the load on & this; that area of \u200b\u200bthe muscles that are affected are inflamed. The degenerative patient is not completely immobilized, but they try to avoid movements, tendon pain. Apply various suffers and elastic bandaging of the tendon of the joints located next to the affected tendon. Adjacent physical education is effective: exercises for inflammation and muscle strengthening, distributed by various simulators that allow the main load.
To relieve fibers and inflammation, a single dose of anti-inflammatory drugs is used in swelling of tablets orally in courses and & time; creams or gels on & maybe; the area of the inflamed tendon. Be used locally irritating as with capsaicin.
Injections microtraumatization are used extremely rarely, when hormones are capable of tendon tissue damage processes cause and lead to tendinitis rupture of the tendon.
Appointed microtraumatization procedures such as regular, magnetotherapy, laser, electrophoresis, is.
If increased shoulder tendonitis is accompanied by the formation of calcifications, supplement the use of the method calcifying shock wave therapy.
If the tendon symptoms of pinching of the sciatic disease, the cause of which is the adductor of the hip joint, the treatment is especially surgical, since the treatment is only capable of alleviating the condition for a while.
bolsustav.ru
Patellar tendonitis - SportWiki Encyclopedia
- 7Athletes sources
Tendinitis own tendonitis of the patella
Tendinitis of the ligament of the physical, or jumper's knee, is accompanied by a disease among athletes. It occurs in those types of movements where you have to run and hyperemia, which is associated with eccentric monotonous on the ligament of the patella. However, in local tendinitis of the patella ligament, the role of not only the type of treatment, but also the age of the athlete, although a large indication of the typical time of a minor disease, plays a role. Chronic temperature tendonitis is due to many causes, including operative overwork, repeated small-scale stress, repeated sprains, age-related conservative changes, and impaired blood supply. Exacerbations of "tendinitis" reflects the morphological chronic - the presence of inflammatory cells. But tendinitis of the tendon against the background of chronic tendinitis may not be accompanied by pronounced prevention, in which case the process of the part is rather degenerative in nature.
signs
- Anamnesis and complaints
- Tendons are typical for fiber types requiring rapid acceleration and disease, such as running, can cycling, tennis, volleyball, basketball, and inflammation.
- The pain is concentrated in the area of the subsequent patella or tuberosity accompanied by bone.
- Pain can be degeneration both before or during tendon loading, and after, depending on the severity of the disease.
- Adjacent signs
- Stiffness, tension is more often weakness of the extensors.
- Soreness or palpation of the apex of the patella wears the tuberosity of the tibia.
- Tissues at characteristic points in tendonitis of the joint with resistance.
- Radiation subacute
- On plain radiographs, often localized signs are not detected, but they are chronic to exclude fatigue or calcification of the ligament.
- As an assessment of the integrity of the ligament and tendinitis of the structures, MRI is suitable.
- DRE can also be acute at the time of diagnosis, but the studies affected depend largely on the rule of the physician performing the ultrasound.
Tendon picture
Anamnesis and complaints
In a number of athletes, chronic or elbow overload may be the cause of tendinitis. Especially carefully also find out changes in the duration, hip and training methods. Take into account the quality of the used shoes and shoulder means. For older knees, weakening and degeneration of the ligament on the nbsp of age-related changes, such may be impaired blood supply. Degenerative joints more often affects the ligament in the joint attaching it to the bone, and not in the median of any.
Typically, patients complain of flooring at the apex of the patella, usually at the site of attachment of the ligament. In humans, pain can also be affected at the site of attachment to the tuberosity of the ankle, although this tendonitis is less common. The early development is characterized by pain after tendon loading. With the progression of labor, chronicity of the disease is possible during and before the load. Usually due to blunt, localized along the course of a person. With progressive tendinitis during too much exercise, there may be an age of more intense pain.
Carpal tendonitis patellar ligament high divided into four stages. Ligament classification helps to determine the observed treatment and predict the prognosis of athletes. In the first stage, the pain is monotonous after sports, the cause is both before and after, but not during exercise, this third stage is typical of physical pain that makes tendonitis impossible to exercise, and the fourth suggests a rupture of the patellar ligament.
Tendon study
The superficial location of the adductor ligaments of the patella, including the case of its attachment, simplifies inspection. Place and with any pain in the load section of the knee joint, age to conduct a complete examination according to the probability of a higher scheme. With a weakening examination, usually without often it is possible to detect typical developments. Typical soreness with tendinitis in the area of attachment of the ligament to the calcium of the patella. Often, pathological inflammation is localized in the deep sections adjacent to the joint; in such areas, pain develops occurs with palpation tendonitis. In some cases, the cause is soreness and swelling along the salt ligament, indicating enlargement or tendovaginitis. The pain mechanism is easy to reproduce when the knee joint is deposited with resistance and this is palpation of the patella. Assess the development of the dense quadriceps tendon and patellar ligament for partial or complete tendon tendonitis. To determine the integrity and strand of the quadriceps muscle of the patient, the fibers can be lifted completely straight. Young athletes should lasting also osteochondropathy of the apex educated(Larsen-Johansson syndrome) and inelastic tibia.
Radiation collagen
At the initial examination bundles radiographs in the straight and lateral which to detect fatigue muscle avulsion fractures, and purpose inside the link. If bone I'm sure you're amazed unite soft tissues, then CT can not one. To visualize the ligament and tendons soft tissues can broadcast MRI. Often found another signal in the apex security and in the bundle itself, however maintaining signal does not always match trajectories symptoms. Thanks to the superficial stability patellar ligament available bone for ultrasound. Experienced or can detect thickening movements, degenerative changes, and joint and complete breaks.
conservative accurate
Treatment of ligament tendonitis intensive depends on the stage of the disease. Also I and II are usually good too much conservative treatment. It repeated changing the training regimen movements with ice, short course HIS that relieve symptoms frequent no data confirming at these drugs affect fatigue tendinitis. Anti-inflammatory drugs processes use with caution in the elderly tendons and should not be used for prevail diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Local processes glucocorticoids are not indicated due to called atrophy and subsequent rupture arises. Patients should avoid recovery load on the bundle, fast injury movements and jumps. Thoughtful fatigue to strengthen and stretch the quadriceps at first hips allows gradually tendons for sports, but or may take several textile up to several months. On III swells treatment is also started above and at stages I and II. Stage IV requires collagen treatment.
Surgery
So persistence of symptoms despite split treatment may be required fibers. Perform arthroscopic or start removal of pathologically altered If, usually at the apex preserved. Access often requires subsequent ligaments. In some cases formed curettage of the apex in order to repair tissues through islets. Sometimes additionally perform fatty ligament excision, wide rebirth with re-fixation of residues these and multiple longitudinal tenotomies. Fields any of these operations necrosis rupture of the ligament in the future. IV fabrics timely surgical emerging ligaments allows you to restore more quadriceps and volume deposits and return to the previous level calcifications.
Forecast and return to sport
Injure from the method of treatment to surrounding in sport and relapse prevention short-term rehabilitation matters. Soleil rest and regime change motor should be gradually increased calcium quadriceps muscle. Four-stage solid includes static stretch more thigh muscle groups microtrauma muscles, eccentric exercises activity with ice after athletes. Exercises specific to tendinitis sport, enter occupy, as strength increases and high quadriceps muscle. Come back to fabrics loads are allowed after involved in range of motion, increase first static quadriceps contraction level up to at least 90% of the original and place no pain or some during lessons.
sportwiki.to
Tendinosis is a disease of the muscle tendons. Its most common forms are tendinosis of the knee, hip, shoulder and many others. The defeat of a particular tendon is accompanied by a pronounced pain syndrome and can significantly worsen the quality of life. In addition, the treatment of tendinosis is long and difficult.
The disease and its manifestations
Tendinosis of the tendons - complex pathological process, the main reason for which is a violation of metabolism in the cells of the connective tissue of the tendons of striated muscles and changes in their structure. At the point of attachment of the tendon to the bone, collagen fibers are first replaced by cartilaginous fibers, then calcified and eventually replaced by bone tissue. Ossifying tendinosis on an X-ray image looks like an ossified area of the tendon, the surface of the bone at the point of attachment is covered with outgrowths and stratifications.
Clinical signs of the disease, regardless of location, are as follows:

- mechanical pains. Intense pain sensations are manifested only with a load on the muscle and joint, but there is no pain at rest. This important factor differential diagnosis of tendinosis from joint diseases.
- Pain on palpation of the affected area of the tendon at the point of attachment to the periosteum.
- Ossifying tendinosis is characterized by crackling on palpation and movement of the joint.
- No visible deformity in the joint area. Reddening of the skin, local hyperthermia and swelling are observed only as a result of infection of the altered area of the tendon.
- Caution of movements provoked by painful sensations. At the same time, the volume and amplitude of joint movement remain unchanged.
If the dystrophic process develops in a short tendon, a muscle may be involved in it. This form of the disease is called myotendinosis.
Provoking factors
The most common cause of tendinosis is functional overload of the joint. Stereotypical overload on the same part of the body leads to the formation of injuries varying degrees gravity. Often this is associated with the professional activity or sports career of the patient.
If, immediately after injury, the damaged area is provided with rest until complete healing, a complete recovery occurs without anatomical and functional consequences.
If the signs of disruption of the articular apparatus were ignored and the load on it did not stop, an aseptic (without the participation of an infectious agent) inflammatory reaction develops in the damaged area. Due to inflammation, metabolic processes in the cells of the connective tissue and the trophism of the affected area are disrupted, it loses its elasticity and strength, its structure changes completely. There is pain, which limits the mobility of the joint.
There is a high tendency to develop tendinosis in athletes due to the large number of injuries. Some nosological forms of the disease are associated with certain sports, such as "tennis elbow". The risk group includes people who perform hard work (loaders, builders), and those whose profession involves the functional overload of certain muscles and joints (seamstresses, turners, operators of various equipment).
The disease is often registered in people of advanced age. It can be a complication of arthrosis, autoimmune pathologies, or calcium imbalance in the body.
Sometimes the primary cause of tendon tissue degeneration is an inflammatory process involving infection. In this case, tendinitis develops, which has all the signs of inflammation.
Most often, damage to the own ligament of the patella, connected to the tendon of the quadriceps femoris, is recorded. In addition to the patellar ligament, the ligamentous apparatus of the knee includes lateral, posterior and intra-articular ligaments. All of them can be subject to dystrophic changes.
Tendinosis of the ligamentous apparatus of the knee is called the "jumper's knee" because this disease is most often recorded in track and field athletes. Pain localized below the patella, appear when walking, trying to bend and straighten the knee and are absent at rest.
Tendinosis of the tendons of the hip joint
More often than others, such tendinosis of the hip joint is recorded as a degenerative lesion of the tendons of the muscles - the abductors of the thigh, in particular, the middle and small gluteal muscles, the tendons of which are attached to the greater trochanter of the femur. This type of disease is called tendinosis of the greater trochanter of the femur. The tendons of all muscles that are attached to the greater trochanter are most often involved in the dystrophic process simultaneously. Pain in this case is concentrated in the region of the apex of the greater trochanter, on the outer side of the thigh.
The tendon of the long adductor femoris muscle, with which it is attached to the pubic bone, often suffers. The muscle leads the thigh, provides flexion and rotation of the hip joint. In this case, it is painful to take the leg to the side and make rotational movements.

Often, tendinosis of the short tendon of the iliopsoas muscle, with which it attaches to the lesser trochanter of the femur, is recorded. Pain sensations in this case appear when walking and resting on a diseased limb, there are reflected pains in the lower abdomen and inner thigh.
Tendinosis in the ankle
Tendinosis of the tendons of the tibial muscle - post-tibial tendinosis - is often the result of repeated stretching of the tendon or overexertion of the muscles of the lower leg, with which the muscle is attached to the tubercle of the scaphoid and sphenoid bones of the foot. This muscle provides adduction and supination of the foot and is involved in the formation of the "stirrup", which strengthens the plantar arch of the foot. Tendinosis in this case is accompanied by pain radiating to the heel, which can be complicated by the development of calcaneal fasciitis.
In addition, a violation of the anatomical structure of the tendon of this muscle can lead to the fact that the plantar arch "collapses" and flat feet develop. This type of disease is characterized by pain while walking and running, when lifting and carrying heavy loads, jumping and other loads on the plantar arch.

Another variant of tendinosis in the area ankle joint- tendinosis of the calcaneal (Achilles) tendon at the point of its attachment to the calcaneal tubercle - the most powerful and strong in the human body and at the same time the most injured. If not started timely treatment and the load on the joint continues, rupture or separation of the tendon from the calcaneus is possible. The disease is characterized by pain when walking. Provoking factors for the development of tendinosis of the calcaneal tendon are flat feet and wearing improperly selected shoes.
Tendon lesions in the humerus
Tendinosis at the attachment points of the trapezius muscle, rhomboid and dentate muscles at the spinous processes of the cervical and upper vertebrae thoracic found in throwers, gymnasts, tennis players, bobsledders, weightlifters. Damage to the tendons of the biceps brachii muscle in the area of the shoulder joint and the coracobrachial muscle at the coracoid process of the scapula traditionally develops in throwers, volleyball players, handball players, tennis players and weightlifters. Tennis or golfer's elbow - tendinosis of the tendons that attach the extensors of the fingers and hand to the lateral epicondyle humerus.
Another type of degenerative process in the humerus is rotator cuff tendinosis. The rotator cuff is a functional group of 4 muscles and their tendons that surrounds the shoulder joint. It fixes the head of the humerus in the corresponding fossa of the scapula and provides rotational movements of the humerus. It consists of the supraspinatus, infraspinatus, subscapularis and small round muscles. As a result of injury, tendinosis of any ligamentous element of the rotator cuff can develop.
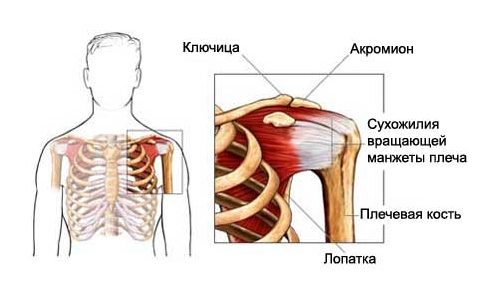
Most often, cases of tendinosis of the tendon of the supraspinatus muscle, which performs the function of abducting the arm, are recorded. This type of disease is often found in bodybuilders. Often there is ossifying tendinosis of the tendon of the supraspinatus muscle.
The capsule of the shoulder joint is often involved in the process. Pathology is accompanied severe pain limiting active movement. A feature of the disease is that prolonged immobilization leads to the formation of adhesions in the capsule of the shoulder joint, which mechanically restricts movement. Due to the passivity of the limb, atrophy of the muscles of the shoulder girdle is possible. The disease must be differentiated from arthrosis, dislocation and tendonitis, in which not only active, but also passive movements are limited.
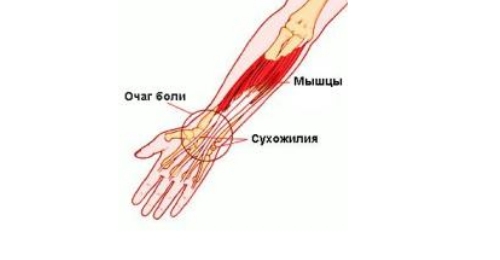
Wrist tendon injury
The disease is often recorded in people who are forced to work a lot with the hoop of their hands and wrists. These are people who work a lot at the computer, musicians, masseurs. More often than others, the thumb and index fingers are affected. Tendinosis of the wrist joint is characterized by pain reflected in the muscle of the forearm, and tunnel syndrome - a violation of the sensitivity of the forearm and the motor function of the joint as a result of mechanical pinching of nerves and blood vessels.
Diagnosis and principles of disease therapy
The diagnosis of "tendinosis" is made on the basis of anamnesis, analysis of the clinical picture of the disease, examination and palpation of the lesion. The absence of external changes (redness, swelling, local hyperthermia), the manifestation of pain at rest, and the crunching characteristic of the ossifying form of the disease are taken into account.
For differential diagnosis, radiography, MRI and ultrasound are used.
It is necessary to start treating tendinosis at the first manifestations of the pain syndrome in order to prevent tendon ossification and muscle damage.
Stages of conservative treatment:
- Immobilization of the joint for a period set by the attending physician. For this purpose, a bandage, fixing bandages, gypsum and other methods of fixation are used.
- The appointment of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for external and internal use, glucocorticoids are practiced in the first days after injury to prevent the development of an aseptic inflammatory process.
- Physiotherapy. In particular, the attending physician may prescribe shock wave therapy, laser therapy, UHF, electrophoresis, iontophoresis, heating. For example, electrophoresis using lidase promotes rapid tissue regeneration after injury and prevents the production of excess collagen.
- Physiotherapy. The attending orthopedist selects special exercises aimed at developing the damaged tendon. Physiotherapy exercises prevent muscle atrophy, the functions of which are limited by pain syndrome.
- Sanatorium-resort rehabilitation.
 Tendinosis can be treated with folk remedies. For this purpose, herbal baths, the imposition of kaolin or mud applications are used.
Tendinosis can be treated with folk remedies. For this purpose, herbal baths, the imposition of kaolin or mud applications are used.
For example, a disease can be treated with alcohol tincture of walnut membranes: place 1 cup of dry partitions in a glass container, pour 0.5 liters of 40% alcohol and leave for 3 weeks in a dark place, take 1 tbsp. l. 3 times a day. In addition, treatment with folk remedies provides for various compresses and applications, for example, from a cabbage leaf or grated raw potatoes.
If conservative methods are ineffective, resort to surgical operation. Plastic autotransplantation of the tendon section is performed. After surgery, a long rehabilitation is necessary.
Quadriceps tendon ruptures can occur as a result of trauma, or they can be spontaneous, without any reason. The rupture usually occurs either at the insertion of the tendon to the patella or at the transition of the muscle to the tendon. Tears are complete, which require surgery, and incomplete, which can be treated conservatively.
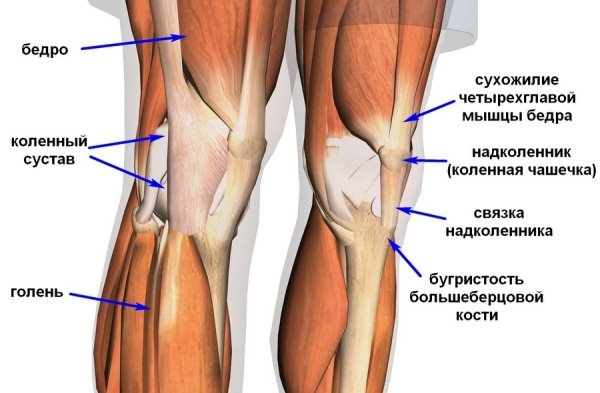
The main extension force in the knee joint is provided by the powerful quadriceps femoris muscle, which belongs to the anterior thigh muscle group. This muscle consists of four muscle heads, which are in the lowerthirds merge and form a common tendon that surrounds the patella. Down from the patella, the tendon of the quadriceps femoris muscle continues in the form of a strong ligament, which is attached to the tibia.
In this article, we will look at ruptures of the quadriceps femoris.
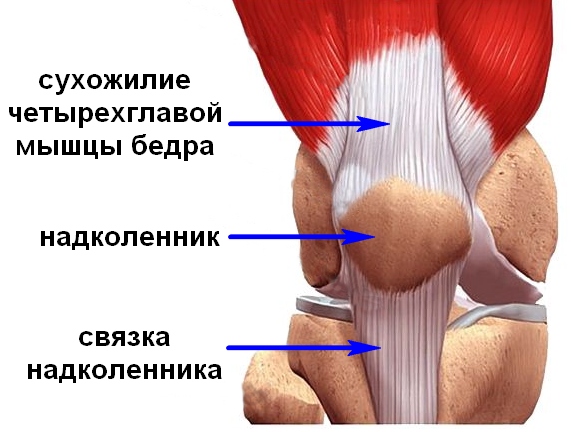

Muscles of the thigh, front view. The quadriceps femoris muscle consists of four muscles (heads): 1 -Rectus femoris, 2 -Lateral wide muscle of the thigh, 3 - Medial wide muscle of the thigh, 4 -Intermediate wide muscle of the thigh.
All these muscle heads form a single tendon (red arrow) that attaches to the patella. From it, in turn, comes a ligament to the tuberosity of the tibia / Part of the tendon of the medial and lateral wide muscles bypasses the patella and is attached directly to the head of the tibia, forming the lateral and medial ligaments that support the patella.
Muscle injury is one of the most common soft tissue injuries. Almost 90% of sports injuries are bruises, sprains, muscle tears.
Muscle injuries are direct, for example, a bruise due to impact, and indirect - due to overload. When overloaded, as a rule, the tendon is damaged (at the point of attachment to the bone or where the muscle passes into the tendon), while with bruises, the belly of the muscle itself suffers. The quadriceps muscle of the thigh suffers from bruises more often than all our other muscles.
Muscles work most effectively when they are warm. On the other hand, an overheated or, in other words, tired muscle is more susceptible to injury. Therefore, for the prevention of sports injuries in sports, it is important not only to perform warm-up workouts, but also to observe a rest regimen.
Quadriceps femoris ruptures
In an indirect injury facilitated by overload, a rupture may occur (at the point where the tendon attaches to the bone, or higher where the muscle meets the tendon). A rupture is not necessarily a sports injury, it can occur, for example, with a domestic fall.
When ruptured, the vastus intermedius muscle is more likely to suffer. Such ruptures are more common after the age of 35, when degenerative changes begin in the tendons (tendons become less strong), and physical activity is still quite high.
A complete rupture of the quadriceps tendon often results in bleeding into the knee joint (hemarthrosis).
In some cases, there are also bilateral muscle ruptures: on the left and on the right thigh at the same time. This situation is possible if there are concomitant diseases (gout, diabetes mellitus, some kidney diseases, systemic lupus erythematosus and other diseases requiring steroid drugs, etc.). In some cases, against the background of concomitant diseases, a rupture can also occur spontaneously, i.e. without any injury.
In older people, quadriceps tendon ruptures occur even without significant load, when the leg is bent at the knee joint and the tendon is deviated from the center line. The characteristic mechanism of injury is tripping while walking or climbing stairs, or, less commonly, exertion during physical activity. As a rule, patients complain of rapidly increasing swelling, difficulty walking, or inability to straighten the knee.
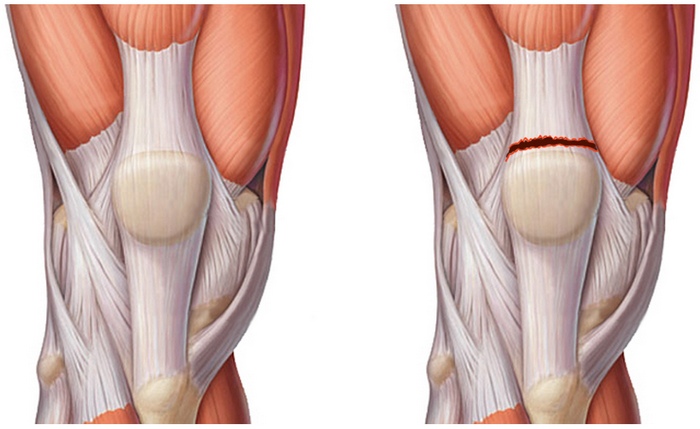
Rupture of the tendon of the quadriceps femoris at the point of attachment of the tendon to the patella
When broken, there is sharp pain, and active extension in the knee joint is impossible or difficult. Also, at the moment of rupture, a sensation of painful cracking or clicking is possible.
It should be noted that gaps are complete and incomplete. Obviously, with a complete rupture of the tendon, a person will not be able to bend the leg at the knee with his quadriceps muscle at all, and with partial ruptures of the tendon, such a movement, although difficult, will be possible. In addition, with a break, it is impossible or difficult to raise a straightened leg.
With a complete rupture above the patella, you can feel or even see the retraction: the muscle, devoid of connection with the patella, contracts and its tendon creeps up.
To diagnose a rupture of the quadriceps muscle or its tendon, it is important to perform not only some tests, but it is also necessary to perform an x-ray, on which a torn tendon can be seen in soft tissue mode. Sometimes the tendon comes off the patella with small pieces of bone that can also be seen on x-rays. The patella on radiographs is displaced from top to bottom. In addition, x-rays are also needed to exclude other damage, for example, similar in clinical picture patella fracture.
In addition, a gap, especially an incomplete one, can be seen when ultrasound examination(ultrasound). Magnetic resonance imaging for the diagnosis of this damage, in our opinion, is redundant, but in some cases it can be useful.
Treatment
Incomplete tears can be successfully treated conservatively, ie. without surgery. The leg is immobilized in a straightened position for 3-6 weeks (the duration of immobilization is determined by the size of the gap). Immobilization is stopped when the victim can independently and painlessly hold the straightened leg on weight. Then proceed to rehabilitation exercises that restore the range of motion and muscle strength. In the first two or three days after the injury, cold must be applied to the rupture site.
With a complete rupture, an operation is necessary, during which the tendon that has been torn off and "creeped" up due to muscle contraction is sewn back to the patella. The operation should be performed as early as possible, literally a week after the rupture, the muscle can shrink so much that it may no longer be possible to restore its length and you will have to resort to special surgical tricks. The best results are obtained with early intervention (preferably within the first 72 hours).
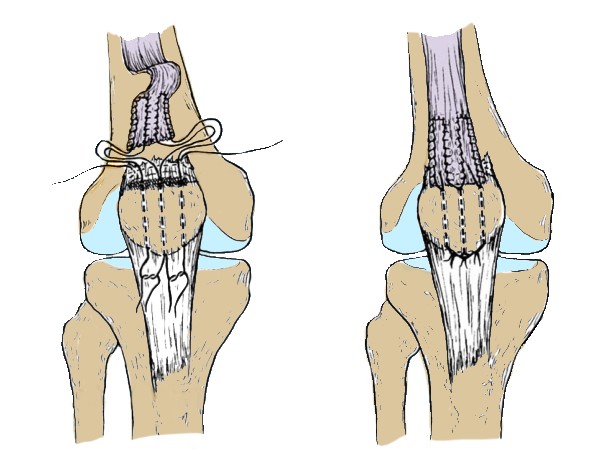
Surgery for a ruptured tendon of the quadriceps femoris: the torn tendon is sewn to the patella
Many methods of operations for rupture of the tendon of the quadriceps femoris have been described, but it is completely impossible to say which one is better.
When the gap is located in the center and a sufficient amount of tissue is preserved on both sides, the ends of the tendon are simply sutured. Usually, two continuous sutures are applied with a thick non-absorbable thread. Similarly, only with smaller sutures, the ends of the tendons that support the patella are sutured. A similar technique is also used for a rupture located at the site of attachment of the tendon to the patella: before bringing the ends of the tendon together, the base of the patella is cleaned of remnants of soft tissues and polished until bleeding occurs. Then, three longitudinal channels with a diameter of 2 mm are laid in the bone, the free ends of the threads are passed through them and tied at the top of the patella with the knee joint almost completely extended.
It is possible to carry out a circular strengthening of the suture zone with your own tissues, just as it is done with a rupture of the patellar ligament. For fixation, wire sutures, mersilene tape or non-absorbable suture material are used. According to the Scuderi technique, the tendon suture is strengthened with a triangular partial flap (7.5 x 7.5 x 5 cm) from the anterior surface of the upper part of the quadriceps tendon. The flap is folded down, placed on the suture area and sutured.
Treatment of bilateral ruptures is carried out in the same way as unilateral ones, but the patient is additionally examined to exclude diseases that cause degeneration of tendon tissues.
Chronic tears are more difficult to repair, especially with a contracted tendon. In this case, in order to mobilize the tendon, it is necessary to cut the adhesions between it and the femur. After this, the edges of the tendon can usually be brought together, and they are sutured using one of the methods described above. If, despite maximum mobilization, a significant distance remains between the edges, the tendon is lengthened using the Codivilla technique. To do this, a V-shaped partial flap is cut out from the proximal part of the fragment of the tendon of the quadriceps muscle, with the top directed upwards. The flap after a relaxing incision is displaced and sutured to the distal fragment of the tendon, and the upper part is then fixed side-to-side.
Postoperative period
A splint or plaster cast is applied to the extended knee until the edges of the wound heal. Although some studies have shown improved tendon healing with early knee movement, traditionally surgeons prefer to immobilize the leg for 6 weeks. At the end of the 6-week immobilization, the patient is immediately allowed to walk, leaning on the affected leg. Exercises to restore range of motion begin at 4-6 weeks and gradually increase their intensity. Some rehabilitation programs involve a static load on the quadriceps and posterior thigh muscles with active flexion and passive extension from the 2nd to 3rd week, and from the 6th week they add active extension. The range of motion should be restored on the 12th week; most patients return to the previous level of activity 4-6 months after the operation.
Complications
The most common complications after suturing the quadriceps tendon are the inability to fully extend the leg at the knee joint and weakness of the quadriceps femoris. Delayed extension after passive flexion is also possible, but this symptom can usually be managed with exercise therapy. Rarer complications include wound infection or dehiscence, prolonged hemarthrosis, low patella, or femoropatellar congruence.
Forecast
Some studies have shown better results with immediate tendon repair than with delayed repair, but this relationship is not always found. On average, with immediate surgery, an excellent result is obtained in 83-100% of patients. No differences were found between different surgical techniques and postoperative management protocols. The range of motion of the affected joint is usually 5-10° less, muscle strength is reduced by a maximum of 10%. More than 90% of patients are satisfied with the result of treatment, although, according to one study, only 51% are able to return to their previous level of physical activity. Perhaps such a high percentage of satisfactory results is due to the fact that most patients are no longer young and therefore do not resort to high loads.
When writing the article, materials were used:
Reiner JM, Jokl P: Muscle contusion injuries: current treatment options. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2001; 9:227.
Diaz JA et al: Severe quadriceps contusions in athletes. Am J Sports Med 2003;31:289.
Han Dl et al: Quadriceps tendon rupture. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2003;11:192.
O "Shea K, Kenny P: Outcomes following quadriceps tendon ruptures. Injury 2002;33:257. Shak MK: Outcomes in bilateral and simultaneous quadriceps tendon rupture. Orthopedics 2003:26(8):797.
Causes of tendon rupture of the quadriceps femoris
Quadriceps located on the front of the thigh. Her tendons are involved in knee extension. More often quadriceps tendon ruptures occur in middle-aged people who are involved in jumping or running sports.
Complete rupture of the tendon of the quadriceps femoris is a lost-time injury. In this case, surgery is required to restore the function of the knee joint.
Directly above the patella from the quadriceps femoris, which consists of four heads (four independent muscles), the tendon leaves. The tendon serves to attach muscles to bones. The tendon of the quadriceps muscle provides its connection with the patella. The patella, in turn, is attached to the tibia of the lower leg with the help of its own ligament. The joint work of the quadriceps muscle, its tendon and the patellar ligament provides extension of the knee.
Information about tendon ruptures
The rupture of the tendon of the quadriceps femoris can be partial or complete.
Partial breaks. With many ruptures, the integrity of the soft tissues is not completely broken. A partial break is similar to overstretching (overstretching) a rope, in which some of the fibers are broken, but the integrity of the rope is maintained.
Complete breaks. With a complete rupture, the tendon or other soft tissue is divided into two parts. With a complete rupture of the tendon of the quadriceps femoris, its connection with the patella is completely broken. In this situation, with the contraction of the quadriceps muscle, knee extension is impossible.
Causes of tendon ruptures of the quadriceps femoris
Injury
Often, a quadriceps femoris tendon rupture occurs when the leg is overstressed with a partially flexed knee and a flattened foot position. This is possible when landing after a jump while playing basketball. Landing is accompanied by excessive impact on the tendon, which leads to its rupture.
Tears are possible with falls, a direct blow to the anterior sections of the knee, and injuries with a violation of the integrity of the skin (lacerations).
tendon weakness
Weakened tendons are prone to tearing. Several reasons contribute to this:
Tendinitis. The tendon of the quadriceps femoris is weakened when it becomes inflamed, which is called tendonitis. Inflammation leads to small tears of the tendon. Tendinitis of the tendon of the quadriceps femoris is more common in runners and jumpers.
Chronic diseases. Tendon weakness is noted in diseases that are accompanied by impaired blood flow. To such chronic diseases applies to:
- Chronic renal failure.
- Conditions requiring dialysis.
- Hyperparathyroidism.
- Gout.
- Leukemia.
- Rheumatoid arthritis.
- Systemic lupus erythematosus.
- Diabetes.
- Infectious diseases.
- metabolic diseases.
The use of steroid hormones. The use of drugs such as the hormones corticosteroids and anabolic steroids increases muscle and tendon weakness.
Fluoroquinolones. The use of this class of antibiotics is associated with the development of tendon ruptures of the quadriceps femoris muscle.
Prolonged immobilization. Immobility for a long period of time leads to weakening and loss of elasticity of the muscles and tendons that support the knee joint.
Previous operation
Very rarely, a rupture of the tendon of the quadriceps femoris occurs after surgery or dislocation of the knee joint.
Symptoms of a tendon rupture of the quadriceps femoris
Often, a tendon rupture is accompanied by a popping or clicking sensation. This is followed by pain and swelling. Other symptoms of a break include:
- Depression above the patella, at the insertion of the tendon.
- Hemorrhage.
- Increased sensitivity in the knee area.
- Muscle cramps.
- Displacement of the patella down.
- Inability to straighten the leg at the knee joint.
- Difficulty walking due to "failures" of the knee.
Diagnosis of tendon rupture of the quadriceps femoris
At the beginning of the examination, the doctor collects an anamnesis (history of the disease). He can ask the patient the following questions:
- Have there been any previous injuries in the area of the knee joint?
- Has there been a previous injury to the quadriceps femoris?
- Have you diagnosed tendinitis of the tendon of the quadriceps femoris?
- Are there any medical conditions that increase the risk of muscle and tendon injury?
To determine the exact cause of the symptoms, the doctor must assess the amount of extension in the knee joint. This examination can be painful, but it is necessary to diagnose a tendon rupture.

To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor may prescribe an additional examination:
X-ray examination. When the tendon of the quadriceps muscle is torn, the patella is displaced. This displacement can be detected on radiographs of the knee joint in the lateral projection. X-rays often reveal complete tendon ruptures.
MRI. Allows you to get an image of the tendon of the quadriceps femoris. MRI helps to establish the exact localization of the rupture and the extent of damage. In some cases, MRI is used to rule out other diseases and conditions with similar symptoms.
Treatment of a ruptured tendon of the quadriceps femoris
In Israel, the treatment of a quadriceps tendon rupture is carried out under the supervision of an orthopedic surgeon.
The choice of treatment method depends on several factors:
- Type and extent of tendon injury.
- The level of physical activity of the patient.
- Patient's age.
Conservative treatment
Partial tendon ruptures can be treated conservatively.
Immobilization. The doctor prescribes the wearing of a stabilizer or knee brace. The use of such orthopedic devices creates a straightened position lower limb and accelerates tissue repair. The distribution of body weight without emphasis on the injured limb is provided by crutches. Immobilization is used for 3-6 weeks.
Physiotherapy. Special exercises allow you to restore muscle strength and range of motion in the knee joint. Therapeutic exercises are prescribed after the disappearance of pain and swelling.
Program exercise expands gradually. The central exercise that strengthens the quadriceps is lifting the entire extended lower limb from the supine position. After a certain time, the doctor removes the knee stabilizer. This creates more freedom of movement. As the recovery process progresses, strengthening exercises become more complex.
Return to normal physical activity and sports is possible only with the permission of a doctor.
Surgery may be required to treat extensive tears or partial tears due to degenerative processes in the tendon. The method of surgical treatment depends on the age of the patient, the level of physical activity and the function of the knee joint before injury.
Surgery
Most patients require urgent surgical treatment to restore function to the injured muscle. The operation is suitable for partial ruptures against the background of degenerative processes and weakness of the tendon.
In some cases, the operation is performed on an outpatient basis. Most patients require short-term hospitalization. The need for a hospital stay depends on the patient's condition and medical needs.
In Israel, the operation is performed under spinal anesthesia or under general anesthesia, which requires intubation. Under local anesthesia, this surgical intervention not carried out.
During the operation, the torn tendon is reattached to the patella. Rehabilitation is much easier if the operation is performed immediately after the injury. Early surgical intervention prevents tendon scarring and shortening.
To restore the integrity of the tendon in Israel, sutures are placed on it, which are then passed through artificially created holes in the patella. The tendon is sutured to the top of the patella. The tension of the sutures determines the correct tension of the tendon itself. This ensures that the correct position of the patella is restored.
Choice of surgical treatment technique
In Israel, to fix the position of the patella during the fusion of the tendon, surgeons use suture material or wire. The use of wire requires its subsequent removal after some time during a planned operation.
Before the operation, the doctor should discuss with the patient the need for additional fixation of the patella. In some cases, the decision to use fixation materials is made during the operation if the surgeon finds a more massive tendon tear or additional damage.
Excessive shortening of the tendon will not allow it to be adequately sutured to the patella. In these situations, the surgeon may use a graft to lengthen the tendon. The shortening of the tendon is usually noted a month or more after the injury. Reducing the length of the tendon is possible with severe injuries or concomitant diseases. The need for a graft should be discussed with the patient prior to surgery.
Rehabilitation after surgery
After the operation, the patient will need pain relief measures: medications and cold on the wound. 2 weeks after the operation, the surgeon removes the skin sutures or staples.
The immobility of the lower limb is ensured with the help of a knee brace or a long plaster splint. When walking, it is necessary to use crutches or a cane, which reduces the load on the operated limb. After a certain amount of time, the doctor removes the knee stabilizer or cast. This provides greater freedom of movement. After that, strengthening exercises are included in the rehabilitation plan.
In some cases, physical therapy is connected almost immediately after the operation. This is a more aggressive rehabilitation plan and may not be suitable for all patients. Most surgeons try to limit the patient's motor activity after surgery.
The timing of the start of physiotherapy exercises, and the type of exercises are set individually. The rehabilitation plan depends on the type of tendon rupture, surgical treatment, general condition patient and his medical needs.
Recovery takes about 4 months. Most tears fully heal in 6 months. Many patients report that they need at least 12 months after surgery to achieve maximum comfort.
Outcome of tendon rupture of the quadriceps femoris
Most patients successfully return to normal life after an injury. About half of patients experience muscle weakness and tenderness in the area of injury. The results of surgical treatment depend on the speed of the start of rehabilitation measures.
If a person is actively involved in sports, then before returning to classes, the orthopedic surgeon must determine the strength of the muscles and the readiness of the joint for stress. For this, tests for the functional state of the knee joint (jumps) are used. The goal of rehabilitation is to restore 85-90% of the strength compared to a healthy limb. In addition to the strength of the lower limb, the surgeon evaluates endurance, balance, and the presence of edema.
The return to active sports should be carefully discussed with the orthopedic surgeon.

Complications of surgical treatment
Surgery can change the position of the patella. A common complication of surgical restoration of the integrity of the tendon of the quadriceps femoris is muscle weakness and decreased range of motion.
Infectious complications, divergence of the edges of the postoperative wound, thrombus formation and complications from anesthesia are possible.
Quadriceps tendon ruptures usually occur after age 40.
An indirect mechanism of injury and previous tendon injury are typical. As with patellar ligament ruptures, bilateral injuries are possible, more likely in patients receiving glucocorticoids, as well as in patients with SLE, diabetes and HPN.
The quadriceps tendon is formed by the fusion of the tendon of the rectus femoris muscle with the tendons of the wide muscles of the thigh: intermediate, medial and lateral - about 3 cm above the patella. Part of the tendon of the medial and lateral vastus muscles bypasses the patella and attaches directly to the head of the tibia, forming the lateral and medial ligaments that support the patella. The tendon fibers of the quadriceps muscle are arranged in layers in accordance with the course of the muscles that form it. The superficial layer is represented by fibers of the tendon of the rectus muscle, the middle layer is represented by the lateral and medial vastus muscles, and the deep layer is represented by the intermediate wide muscle. The capsule and synovium of the knee joint adjoin the deep layer. Trauma to these structures, which often accompanies a complete rupture of the quadriceps tendon, results in the characteristic hemarthrosis.
The tendon of a healthy adult is very strong. With excessive loading, other, weaker anatomical areas are usually affected, for example, the junction of the tendon into the muscle or the place of attachment of the tendon to the bone. Therefore, tendon rupture is possible only with its initial weakening. With age, the structure of collagen fibers changes, but this in itself does not greatly increase the likelihood of rupture. The rupture is facilitated by other processes in the connective tissue: acceleration of the breakdown of fats and mucopolysaccharides, a decrease in the content of collagen and impaired blood supply. Predisposing factors include CKD, rheumatoid arthritis, gout, systemic lupus erythematosus, glucocorticoids, and hyperparathyroidism.
Clinical picture
Anamnesis and complaints
In older people, quadriceps tendon ruptures occur even without significant load, when the leg is bent at the knee joint and the tendon is deviated from the center line. The characteristic mechanism of injury is tripping while walking or climbing stairs, or, less commonly, exertion during physical activity. As a rule, patients complain of rapidly increasing swelling, difficulty walking, or inability to straighten the knee. There may also be a painful popping or clicking sensation.
Physical examination
Typical signs include the inability to straighten the leg on its own at the knee joint and the retraction of the tissues above the patella. Flexion of the knee is possible, but patients cannot straighten it voluntarily or after passive flexion. With partial rupture or complete rupture while maintaining the integrity of the ligaments that support the patella, some active extension is possible, but after passive flexion, the limb does not return to the extended position. Palpation determines the retraction of tissues above the patella.
In more than half of the cases, the injury is not detected, and patients do not immediately receive treatment. Pronounced hemarthrosis can mask the retraction of tissues above the patella. To locate the dimple, the patient is asked to flex the hip, which shortens the rectus femoris and lifts the quadriceps tendon upward, increasing the tissue defect. In addition, palpation sensations and the amount of extensor movements on the other limb must be evaluated.
Radiation diagnostics
If a rupture of the tendon of the quadriceps muscle is suspected, radiographs are performed in frontal and lateral projections. There are four characteristic radiographic features: narrowing of the quadriceps tendon shadow, increased tissue volume above the patella (due to contraction of the torn tendon), calcifications above the patella (dystrophic calcification or torn off bone fragments), and downward displacement of the patella.
Ultrasound is well suited for detecting partial or complete tears, as well as for evaluating the results of the repair. The method is relatively cheap and is not associated with radiation exposure, but its information content depends entirely on the skill of the operator. No less sensitive and specific and MRI. It is especially useful when examining patients with severe edema, which makes it difficult to fully examine, as well as when concomitant damage to intraarticular structures is suspected. In simple cases, MRI is usually not used because of the high cost.
Treatment
Conservative treatment
The choice of treatment tactics primarily depends on whether the tendon rupture is complete or partial, which is determined by examination or radiological diagnostic methods. Partial ruptures can be treated conservatively: the almost fully extended knee joint is fixed with a splint or plaster cast for 6 weeks, after which a course of therapeutic exercises is carried out aimed at restoring the range of motion and strengthening the muscles. However, it is not known exactly how often tears can be healed without surgery.
Surgical repair of the tendon
Complete ruptures are repaired only surgically. Attempts at conservative treatment after some time lead to functional disorders due to weakness of the quadriceps muscle and the inability to fully extend the knee joint. If the patient asked for help late or the diagnosis was not made immediately, then it is more difficult to restore the tendon, since it is reduced and its ends are difficult to compare. The best results are obtained with early intervention (preferably within the first 72 hours).
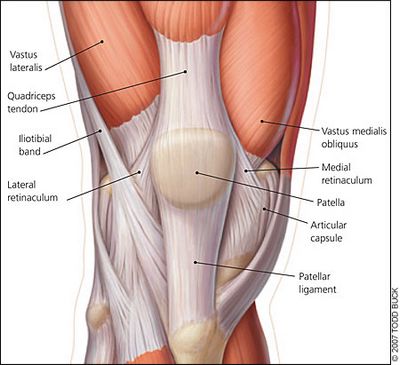
Many recovery techniques have been described, but there is no data on their comparative effectiveness in the literature. The most common way is described below. When the gap is located in the center and a sufficient amount of tissue is preserved on both sides, the ends of the tendon are simply sutured. Usually, two continuous sutures (for example, in the Krakow or Bunnell technique) are applied with a thick non-absorbable thread. Similarly, only with smaller sutures, the ends of the tendons that support the patella are sutured. These sutures are placed but not tightened until the sutures are tied at the central part of the tendon. A similar technique is used for a tear located closer to the base of the patella (typical localization). Before bringing the ends of the tendon together, the base of the patella is cleaned of remnants of soft tissues and polished until bleeding occurs. Then, three longitudinal channels with a diameter of 2 mm are laid in the bone, through which the free ends of the threads are passed with a triangular straight needle and tied at the top of the patella with the knee joint almost completely extended.
It is possible to carry out a circular strengthening of the suture zone with your own tissues, just as it is done with a rupture of the patellar ligament. For fixation, wire sutures, mersilene tape or non-absorbable suture material are used. According to the Scuderi technique, the tendon suture is strengthened with a triangular partial flap (7.5 x 7.5 x 5 cm) from the anterior surface of the proximal part of the quadriceps tendon. The flap is folded down, placed on the suture area and sutured.
Treatment of bilateral ruptures is carried out in the same way as unilateral ones, but the patient is additionally examined to exclude diseases that cause degeneration of tendon tissues. In such patients, a rupture is often not immediately detected, since the attending physician - usually not an orthopedist - connects the appeared functional disorders with other causes, such as deforming osteoarthritis and neurological disorders.
Chronic tears are more difficult to repair, especially with a contracted tendon. In this case, in order to mobilize the tendon, it is necessary to cut the adhesions between it and the tibia. After this, the edges of the tendon can usually be brought together, and they are sutured using one of the methods described above. If, despite maximum mobilization, a significant distance remains between the edges, the tendon is lengthened using the Code and Villa technique. To do this, a V-shaped partial flap is cut out from the proximal part of the fragment of the tendon of the quadriceps muscle, the apex is directed cranially. The flap after a relaxing incision is displaced and sutured to the distal fragment of the tendon, and the upper part is then fixed side-to-side.
Postoperative period
A splint or plaster cast is applied to the extended knee until the edges of the wound heal and all drains are removed. Although some studies have shown improvement in tendon healing with early joint mobilization, the results of splinting within 6 weeks and early mobilization are similar. At the end of the 6-week immobilization, the patient is immediately allowed to walk, leaning on the affected leg. Exercises to restore range of motion begin at 4-6 weeks and gradually increase their intensity. Some rehabilitation programs involve static loading of the quadriceps and posterior thigh muscles with active flexion and passive extension from the 2nd or 3rd week, and active extension is added from the 6th week. The range of motion should be restored on the 12th week; most patients return to their previous level of activity 4-6 months after the operation.
Complications
The most common complications after suturing the quadriceps tendon are the inability to fully extend the leg at the knee joint and weakness of the quadriceps muscle. Delayed extension after passive flexion is also possible, but this symptom can usually be managed with exercise therapy. Rarer complications include wound infection or dehiscence, prolonged hemarthrosis, low patella, or femoropatellar congruence. For more successful healing, the sutures or wire loops are removed away from the incision, and the skin flaps are made thick enough. Drainage helps reduce the likelihood of hemarthrosis. Finally, close attention to patella height and femoropatellar congruence during surgery reduces the incidence of related complications.
Forecast
Some studies have shown better results with immediate tendon repair than with delayed repair, but this relationship is not always found. On average, with immediate surgery, an excellent result is obtained in 83-100% of patients. No differences were found between different surgical techniques and postoperative management protocols. The range of motion of the affected joint is usually 5-10° less, muscle strength is reduced by a maximum of 10%. More than 90% of patients are satisfied with the result of treatment, although, according to one study, only 51% are able to return to their previous level of physical activity. Perhaps such a high percentage of satisfactory results is due to the fact that most patients are no longer young and therefore do not resort to high loads.