Antipyretics for children are prescribed by a pediatrician. But there are emergency situations for fever when the child needs to be given medicine immediately. Then the parents take responsibility and use antipyretic drugs. What is allowed to give to infants? How can you bring down the temperature in older children? What medicines are the safest?
The hip joint plays a huge role in the human body, since it is on it that the longest and largest load falls. It not only supports the bulk of the weight of the human body, but also maintains its balance and provides movement. Therefore, pain in hip joint gives a person great discomfort and can be a serious obstacle to normal life. Similar pain chronic nature require examination and immediate treatment.
Pain in the hip joints, causes
Pain in the hip joint may be the result of damage to its various structures, as well as tissues located nearby: cartilage, bones, muscles, tendons, etc. If we talk about the main causes of pain in the hip joints, we can distinguish the following:
- physical injury;
- Arthritis;
- Coxarthrosis;
- Bursitis of the trochanteric bag;
- tendinitis;
- Infectious diseases;
- hereditary diseases;
- Tumors of soft tissues and bones.
The most common cause of pain in the hip joints are injuries of a traumatic nature. Since the most vulnerable part of the hip joint is the femoral neck, its fracture is a very common injury. Elderly people are especially susceptible to it. This fact is due to the fact that over the years, a huge number of people develop osteoporosis, in connection with which the bones become brittle and lose strength. In young people, such a diagnosis may be the result of traffic accidents or a sports injury.
Often, pain in the hip joint is provoked by its dislocation. This physical injury is usually the result of an underdeveloped acetabulum that easily protrudes from the femoral head. Such a diagnosis can also be the result of an accident, falls or work injuries. In this case, at the first symptoms of pain in the hip joint, the help of a doctor is necessary, since the pain can become simply unbearable.
Arthritis is called inflammation of the joint. This disease is a typical ailment of the elderly, since in old age inflammatory and degenerative processes in the joints are often observed, and the hip joint is exposed to them, perhaps, in the first place. With arthritis, as a rule, the leg hurts a lot, pain also moves to the groin area, is given to the front or side of the thigh, sometimes reaching the knee. Symptoms of pain in the hip joint in this case are exacerbated during walking, when the load on the leg increases.
Coxarthrosis is also known as deforming arthrosis. This disease is more common among middle-aged people. In its early stages, pain in the hip joint is tolerable, but as the disease progresses, pain also worsens. Already in the second stage of the disease, the patient complains of pain when turning the body and when standing up. Almost any movement causes discomfort. In addition, the symptoms of pain in the hip joint with coxarthrosis are accompanied by constant muscle tension in the affected area, even during sleep. That is why pain often disturbs patients at night.
Inflammation of the trochanteric bursa, which is located above the protrusion of the femur, is also called bursitis. This disease is characterized by pain in the outer region of the buttocks. If the patient lies on the affected side, the pain in the hip joint increases dramatically. There are cases of inflammatory processes in other fluid bags of the joint, but the trochanteric bag is damaged much more often.
Inflammation of the tendons, or tendinitis, usually affects people who are subject to regular strenuous exercise. Most often these are athletes. It is worth noting that this disease sometimes goes unnoticed, especially if the patient reduces the load on the hip joint. And, conversely, with too active movements and heavy loads, the pain becomes very strong.
The cause of pain in the hip joints can also be infectious processes. For example, with infectious arthritis, swelling forms in the area of the affected joint, fever may begin. When touching or even slight movements, there is acute pain in the hip joint. Tuberculous arthritis develops somewhat differently, which manifests itself gradually. Initially, the patient is disturbed by slight pain in the area of the knee and thigh while walking. As the disease progresses, the hip is limited in movement, the affected area swells.
Sometimes pain in the hip joint is the result of a hereditary disease. For example, Legg-Calve-Perthes disease, which predominantly affects boys in early age. This pathology is unilateral in nature: pain is observed either in the right or in the left hip joint. Sometimes the disease is manifested not only by pain specifically in the joint area, but also in the knee part.
Neoplasms in the bone and muscle tissue also cause pain in the hip joint. However, the nature of pain and additional symptoms directly depends on benign tumor in humans or malignant.
Pain in the hip joint, treatment
Treatment of pain in the hip joint should be carried out in accordance with the disease that caused it. Therefore, it is not recommended to self-medicate until an accurate diagnosis is established. Depending on the nature of the disease, the following are used to eliminate pain:
- Medical treatment;
- Surgery;
- massage procedures;
- Therapeutic exercise.
 As a rule, in inflammatory processes, the doctor prescribes non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in the form of tablets, injections, gels and ointments. In the case of degenerative processes (for example, osteoarthritis), substances are added to them that promote nutrition cartilage tissue. They are called chondroprotectors.
As a rule, in inflammatory processes, the doctor prescribes non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in the form of tablets, injections, gels and ointments. In the case of degenerative processes (for example, osteoarthritis), substances are added to them that promote nutrition cartilage tissue. They are called chondroprotectors.
Surgical treatment of hip pain is usually used for physical injuries. For example, in case of a fracture of the femoral neck in the elderly, arthroplasty is used, that is, the head and neck are replaced with artificial elements. In young people, the injury is treated by fixing the bones with special screws.
Good for treating hip pain massage treatments. The main thing is that they do not cause pain. The most effective course consists of at least 10 procedures.
Therapeutic exercise is recommended for the rehabilitation process and should be carried out under the supervision of a physician. It is also very important that the exercises do not cause pain. Many experts advise to conduct classes in warm water: it helps to relax the muscles, and the patient's body becomes more flexible. By the way, the best view physical activity of people suffering from pain in the hip joint, doctors call swimming. Sometimes it can cure a person without additional methods.
Of the 3,500 joints in the human body, the hip joint (HJ) is the largest. It provides support for the balance of the body, its upright posture, activity during movement.
All its constituent parts (the neck, the spherical head of the femur with a cartilaginous coating, the cavity in the articular cavity of the pelvic bones) are constantly under heavy loads. Therefore, the occurrence of pain in the hip joint on the left side is an alarm signal that cannot be ignored in any case.
Important to remember! Even the occurrence of constant discomfort - serious symptom the beginning of the development of serious pathologies in our musculoskeletal system. To prevent them, it is necessary, first of all, to determine the cause of even recently appeared pains.
One of them is the received various injuries that violated its integrity, caused tangible pain symptoms: bruises / subluxations / dislocations of the hip, fractures of its neck / bone.
Pain in the hip joint requires an immediate search for the cause and elimination of it
The occurrence of pain in the hip joint, both on the left and right sides, can also be explained by the presence of an infection. It is accompanied by redness, swelling of the tissues of the hip joint, fever, fever.
Such malaise is often provoked by systemic and hereditary health problems: osteochondrosis, rheumatism, tuberculosis, various kinds of tumors, etc.
Among the broad classification in modern medicine There are many similar diseases by nature of origin and symptoms.
The "leaders" of the causes of inflammatory, destructive pain in the hip joint on the left side, most often, are the following diseases.
Arthritis
Arthritis is a disease in the form of inflammation of the joint of a rheumatoid, infectious, rheumatic, reactive nature. Its occurrence can be the result of metabolic disorders in the body, infections, injuries. It occurs most often and, especially, among people of a very mature age.
Pain sensations are supplemented by swelling of the outer surface of the joint, its modification, pain in the groin with spread in front or on the sides of the thigh from above and up to the knee itself, stiffness of movement, shootings when trying to change the position of this part of the body.
Viral infections
Infections in the form of viral influenza, staphylococcus, streptococcus often provoke pain in the hip joint with different symptoms.
Infectious lesions develop intensively with fever, acute pain. There is swelling and hyperemia of the skin on the surface of this part of the body. Suppression of the infectious process affects the disappearance of painful sensations.
Tumor
Tumors of tissues and bones in the area of the hip joint are “companions” of benign/malignant formations directly in the joint. Initially, a person begins to feel pulling pain after their appearance. Symptoms appear chronic fatigue, dizziness. The intensity and severity of the painful state of the joint depends on the nature of the formations.
Coxarthrosis
Coxarthrosis is also called deforming osteoarthritis. It is based on dystrophic processes of cartilage, which lead to the destruction of the hip joint, a change in the coordination of leg movements.
Along with the problems of cartilage elasticity, muscle activity decreases, the surface is deformed, and the functioning of the hip joint is disrupted. It most often affects people over 40 years of age.
 Coxarthrosis of the hip is most common in older people
Coxarthrosis of the hip is most common in older people Among the reasons for its occurrence may be excessive loads, overweight, changes in the course of metabolic processes, both throughout the body and directly in the joint itself.
Already at an early stage, the symptoms of the disease are manifested by tangible severe pain in the hip joint on the left / right side when walking, with a gradual transition to a aching state.
Bursitis
Bursitis - inflammation of the fluid in the synovial bags of the joint (bursae): trochanteric, ischial, iliac. Most often it is provoked by injuries, as well as pathology of the legs, spine, intensity of physical activity, prolonged standing position. The disease is manifested by pain in the muscles adjacent to the HJ, swelling and redness of tissues, rapidly increasing body temperature, and decreased mobility.
Subluxation
Subluxation (second-degree dysplasia) can be congenital in children and acquired in different ages person. There is some displacement of the joint and partial prolapse from the underdeveloped acetabulum, the absence of complete contact between them.
 Bumps and injuries are the most common causes of pain
Bumps and injuries are the most common causes of pain The reasons for acquiring this pathology may be accidents, falls, strong blows in the thigh area with hard objects.
Pain may occur instantly or increase gradually. Before its appearance, motor activity is slightly limited, but the victim experiences constant discomfort. If ignored, consequences are likely in the form of a change in the length of the legs from the side of damage, lameness.
Note! Even athletes often complain of pain in the hip joint on the left side due to bursitis, subluxation, and various injuries, if it is subject to a greater load than the right one.
Hip injury
Hip injury is mechanical in nature. These are dislocations, fractures during falls to the side, even from a small height and strong blows. We are talking about damage to the bones (sciatic, pubic, iliac), muscles of the large and small pelvis, tendons, cartilage, nerves.
Fracture of the femoral neck affects more people of mature age
He is truly considered the scourge of the elderly. And young people are at risk of getting subtrochanteric, transtrochanteric fractures. Injuries of this kind are recognized by a pronounced sharp pain in the hip joint on the left side, or right, depending on the nature of the fall / impact.
 Cane - an assistant for people suffering from pain in hip joint
Cane - an assistant for people suffering from pain in hip joint Symptoms of such injuries are also an unnatural position of the leg, a noticeable swelling of the entire thigh, the acquisition of a bluish tint by the skin, and a sharp limitation of mobility. Often, the victims go into shock.
It is important to know! The effectiveness of the treatment of these severe injuries depends, first of all, on the timely, competent first aid to the victim. Otherwise, he may be doomed to disability.
Causes of pain in the hip joint
The resulting pain in each individual case has its own characteristics. Their knowledge is important for understanding the nature of diseases, eliminating the causes of their occurrence, preventing the dynamics and recurrence of ailments.
Orthopedists use the generally accepted classification of pain in the hip joints in the following categories:
- Aching, as a rule, accompany acute and are their "companions". They tend to rise or fall different stages damage. Due to the fact that such pain is quite widespread with any type of damage.
 Causes of hip pain can be a symptom of serious diseases
Causes of hip pain can be a symptom of serious diseases The reason for their appearance may be the wear of this complex joint, when the cartilage, together with their fragments, becomes thinner, less elastic. This phenomenon provokes inflammation of the entire articular part, the appearance of discomfort while walking, horizontal position. In this case, pain appears, which tends to spread throughout the thigh to the lower leg.
- Cutting pains in the hip joint on the left side, most often, are characteristic of fractures, sprains during falls, accidents.
It should also be remembered that vascular damage is inevitably accompanied by hematomas. And after the healing of the ligaments, they remain very sensitive, which allows for the possibility of recurrence of their stretching or even rupture in subsequent injuries.
Carefully! The appearance of long sharp pains in the hip joint, both on the left and right sides, is very problematic for diagnosis. To identify the root cause of the pain, it may not be necessary to treat conservatively, but only surgery.
 Surgery is sometimes the only way to determine the causes of severe pain in the hip joint.
Surgery is sometimes the only way to determine the causes of severe pain in the hip joint. - acute pain TBS is characterized by short duration and the ability to determine the sources of occurrence. It is a kind of signal of a probable illness, damage.
Initially, the severity of unpleasant sensations, as a rule, is localized in a small area, and then it spreads more widely. This type of "diagnostic" pain is the easiest to treat.
- Drawing pain during pregnancy, which affects about 205 women out of a thousand, has a slightly different nature. It occurs due to an increase in the load on the ligaments due to a change in weight. future mother. It can appear as a signal of the biochemical transformation of the skeleton, hormonal, metabolic abnormalities, lack of calcium and vitamins of group D.
- TBS pain syndrome during pregnancy is often a sign of osteomalacia, in which fractures, movement restriction, and threats of abortion occur.
The resulting discomfort in the pelvic area should not be ignored, since it is quite high probability of orthopedic pathology, the development of "duck gait"(symphysis).
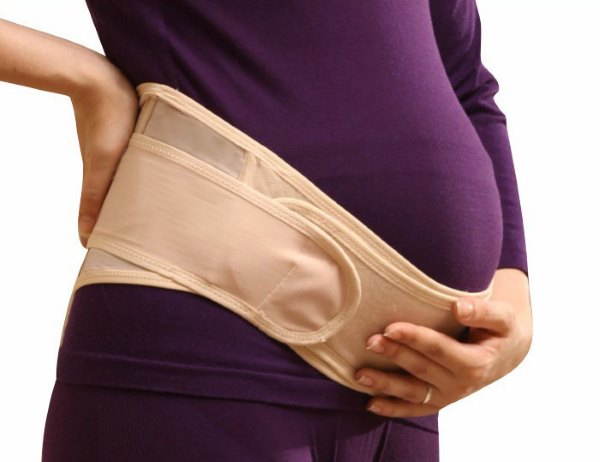
First of all, their prevention helps to protect yourself from possible negative consequences: wearing comfortable clothes and shoes from the first months of pregnancy, and from 21 weeks - compression underwear, a bandage.
Useful daily special gymnastic exercises for the muscles of the pelvis, painless stretching of his bones. This will help to achieve normal childbearing, fairly easy childbirth.
What can be confused with pain in the hip joint
The painful state of hip joint is not always associated directly with the joint itself, when even a thorough examination does not indicate its disease. The root cause of pain in the hip joint on the left or right side may be negative changes in the spine, lower back, connection with the sacrum, tissues, etc. Only an experienced specialist using modern methods can determine the correct diagnosis.
How to eliminate pain when making a diagnosis
Ways to get rid of various types of pain in each case can be conservative (medicines, physiotherapy), surgical, ethnoscience. Treatment should have an integrated approach, since a monotonous effect on the focus of the disease is ineffective.
 The pharmacist will suggest an analogue of the drug if there is no medicine prescribed by the doctor
The pharmacist will suggest an analogue of the drug if there is no medicine prescribed by the doctor A variety of manifestations of pain in diseases of HBS, causes, stages of development requires professional diagnostics, careful selection of means to eliminate them. The use of only drugs for pain relief is unlikely to eliminate the cause, prevent its further occurrence.
Painkillers fail to eradicate the cause of the pain
One of the most common, not contradicting the views of professionals, is to reduce the load, increase the time to rest the joint, strengthen the muscles and the entire surface of the thighs. Of the conservative methods for eliminating pain in the hip joint on the left / right side, this is folk methods and medicines.
Folk methods
They should be used according to the principle "Do no harm!", in agreement with the attending physician, as an addition to his appointments. For pain relief, wraps, compresses, lotions from decoctions, tinctures of various plants are made.

Leaves of ficus, lilac, cinquefoil, plantain, celery, as well as garlic, hot peppers can be used. Ease the suffering of ointment from honey with lemon, pork / visceral fat with a step.
Here it is important to know the feasibility of using warming or cooling mixtures. So, for example, with bursitis it is better to resort to cooling the site of inflammation, and with arthritis - to warm it.
Medication treatment
Drug relief of pain, as a sign of inflammation, consists in the use of medicines from a pharmacy prescribed by a doctor, which are available without prescriptions.
They are represented by analgesics, a group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) at different prices, namely:
- Butadion (from 59 rubles)
- Diclofenac (from 12.3 to 40 rubles)
- Indomethacin (from 11.4 to 29.5 rubles)
- Ibuprofen (from 5.5 to 15.9 rubles)
- Ketoprofen (60 rubles, and its analogue Ketorol - from 12.78 to 64 rubles)
- Nise (from 111 to 225 rubles)
- Nimesulide (from 65 to 79 rubles).
Prolonged use of drugs is fraught with the destruction of the cartilage of the joint
These include symptoms such as allergies, nausea, problems with gastrointestinal tract and others.
To relieve pain muscle spasms muscle relaxants are used at night: Sirlapud with a price of 340 rubles. (its analogue is Mydocalm from 300 rubles), Milgamma - from 500 rubles. At unbearable pain hormonal drugs help, for example, Prednisolone at a cost of 80 rubles.
 Painkiller hormonal drug"Prednisolone"
Painkiller hormonal drug"Prednisolone" Its small doses help improve blood circulation, relieve inflammation. There may also be individual intolerance, the appearance of drowsiness, nausea, dry mouth. side effects in all cases, a qualified doctor at the stage of prescribing a medicine will help to avoid.
Interesting fact! The cost of drugs depends on their composition, dosage, manufacturer, retail and wholesale allowances. Based on this, the price of the same medicine in different pharmacies may differ.
Is self-treatment of pain possible?
Despite the similarity of the pain clinic, the causes of their occurrence, the course and treatment are different in each individual case. At all stages, professional help is needed from a traumatologist, orthopedist, rheumatologist, neurologist, physiotherapist.
 The doctor will examine the pelvic area and determine possible cause pain
The doctor will examine the pelvic area and determine possible cause pain Treatment is possible only after an examination by a doctor, his appointments, with follow-up monitoring of their implementation, the course of the disease until complete recovery. Here self-treatment is excluded!
Prevention of diseases of the hip joints
To prevent the disease, the quality of life is important: a balanced diet, optimal weight, moderation of physical activity, exercise therapy, wearing orthopedic insoles.
So, in order to avoid one of the root causes of pain - infection, it is important to adhere to basic hygiene rules, do not forget about vaccinations.
 Vaccination will protect against viral infections
Vaccination will protect against viral infections The first pains should lead to a doctor and a person must certainly follow his recommendations.
We hope that the information will help you not to fall into the trap of illness, or find a useful format for getting out of it. After all, as Somerset Maugham said: "What can be more useful than learning to live in the best possible way"!
What are the causes of hip pain? Check out this helpful video:
All about hip pain: watch a video consultation with a specialist:
Exercise for pain in the hip joint: advice from an osteopath. Watch an interesting video:
The site provides background information. Adequate diagnosis and treatment of the disease is possible under the supervision of a conscientious physician.
 Pain in the hip joint
usually occur in response to inflammation and damage to the anatomical structures that make up this joint. This symptom is a characteristic feature of mechanical injuries of the hip joint, it occurs with infectious and endocrine diseases. Pain syndrome can be observed as physical activity, as well as in their absence. pain
that appear in the hip joint can sometimes radiate ( give away) into areas close to the joint ( inguinal, gluteal, femoral region, etc.).
Pain in the hip joint
usually occur in response to inflammation and damage to the anatomical structures that make up this joint. This symptom is a characteristic feature of mechanical injuries of the hip joint, it occurs with infectious and endocrine diseases. Pain syndrome can be observed as physical activity, as well as in their absence. pain
that appear in the hip joint can sometimes radiate ( give away) into areas close to the joint ( inguinal, gluteal, femoral region, etc.).
Pain is often accompanied by lameness, limited joint mobility, gait disturbance, shortening of the leg length, which is caused by destructive pathological processes in the articular tissues. Such processes, in the absence of them timely treatment, lead to muscle atrophy, muscle weakness and decreased ability to work.
Anatomy of the hip area
In the area of the hip joint are the following anatomical formations:
- bones that form the hip joint;
- tissues and structures of the hip joint;
- anatomical structures located near the hip joint.
Bones that form the hip joint
The hip joint is formed by the junction of the femoral head and the acetabulum ( clippings) of the pelvic bone, which, in turn, is formed by the bodies of three other bones fused in childhood - the ilium, pubis and ischium. The acetabulum is a kind of depression located on the outer surface of the pelvic bone.The following bones form the hip joint:
- pubic bone;
- ischium;
- ilium;
- femur.
The pubic bone forms the anterior part of the pelvic bone. It consists of a body, an upper and lower branch. The body of the pubic bone is involved in the formation of the anteroinferior part of the acetabulum. The upper branch is a continuation of the body and has an oblique shape. It goes obliquely down at an acute angle to the medial ( inner side) the side where it connects to the lower branch of the pubic bone. The place of their connection is called the pubic tubercle, which can be felt in the center and at the top of the pubic region.
Ischium
The ischium forms the lower part of the pelvic bone. This bone consists of a body and a branch. The body is attached to the bodies of the pubis ( located on top) and ilium ( is in front) in the region of the acetabulum, thus forming the posterior inferior part of the acetabulum. The branch of the ischium is thinner than its body and has the shape of an uneven curved line that goes obliquely upwards at an acute angle from the body and connects at its anterior end with the inferior pubic branch ( part of the pubic bone).
Ilium
The ilium is the upper part of the pelvic bone. It consists of a wing and a body ( located below the wing). The wing of the ilium, for the most part, forms the lateral part of the pelvis, and behind it connects to the lateral surface of the sacrum. From below, the wing passes into the body of the ilium, which, connecting with the bodies of the pubis ( front and bottom) and ischial ( behind and below) bone, forms the upper part of the acetabulum.
Femur
The femur is a large tubular bone consisting of a body and two ends, upper and lower, called the epiphyses. The lower epiphysis connects to the bones of the lower leg ( tibia and fibula) and forms the knee joint. The upper epiphysis, connecting with the acetabulum of the pelvic bone, is involved in the formation of the hip joint. This epiphysis has a complex structure. It consists of a large trochanter ( blunt bony process), necks and heads.
The greater trochanter forms the outer lateral part of the upper epiphysis, while the neck and the head following it form the inner lateral part. The greater trochanter can be felt on palpation of the upper lateral thigh. The femoral neck has a cylindrical oblique shape and is directed from the femur ( from a large skewer) to medial ( inner side) side. At the free end, the neck thickens spherically, this place on the femur is called the head.
Tissues and structures of the hip joint
The hip joint is a complex anatomical formation, which includes a large number of various structures that perform their specific functions.The hip joint is made up of the following tissues and structures:
- articular cartilage;
- ligament of the femoral head;
- subcartilaginous areas of the pelvis and femur;
- articular capsule of the hip joint.
The hip joint is formed by the connection of two bones - the pelvic and femoral, which, together with their contact, have articular surfaces covered with cartilaginous hyaline tissue. Thus, the bone tissue of the acetabulum and the head of the femur is covered with articular cartilage. It is worth noting the fact that, unlike the femoral head, the acetabulum of the pelvic bone is not completely covered with cartilaginous hyaline tissue, but only in its upper and, partially, its lateral part. In its middle and lower zone, it contains adipose tissue and a ligament of the femoral head, covered with a synovial membrane ( tissue that envelops the joint from the inside).
Ligament of the femoral head
The ligament of the femoral head is located directly in the hip joint itself. It directly connects the head of the femur to the acetabulum and attaches it to it. This ligament originates in the lower middle part of the acetabulum and connects to the center of the femoral head. In its thickness there are vessels that supply the head of the femur. The ligament of the femoral head has a protective function and protects the hip joint from dislocations during external rotation of the femur or during its adduction.
Subcartilaginous regions of the pelvis and femur
The subchondral areas of the pelvis and femur are devoid of periosteum and are represented by bone tissue, which consists of cells ( osteoblasts, osteoclasts, osteocytes) and mineralized connective extracellular substance ( predominantly collagen fibers).
Acetabular lip of the hip joint
The acetabulum is a connective tissue formation that is fused in a circle with the edge of the acetabulum and its transverse ligament. The acetabular lip is localized in the joint cavity, from the outside it is limited by the articular capsule. Its main tasks are to increase the depth of the acetabulum and better fixation of the femoral head in the hip joint.
Articular capsule of the hip joint
The articular capsule of the hip joint is a bag-like hollow structure that envelops and limits the cavity of the hip joint. Its wall consists of three layers. The outer layer is formed by fibrous tissue, the inner layer is the synovial membrane, and the middle layer is formed by dense connective tissue fibers. The synovial membrane normally constantly secretes a small amount of serous secretion, which lubricates the adjacent articular surfaces.
The ends of the capsule of the hip joint, on the one hand, are connected to the edge of the acetabulum, and on the other hand, to the neck of the femur ( in its outer lateral third). Thus, most of the femoral neck is in the cavity of the hip joint. A feature of the articular capsule of the hip joint is the presence in its thickness of a ligament called the circular zone, which in the form of a ring covers the neck of the femur.
Anatomical structures located near the hip joint
The anatomical structures that are located near the hip joint can also be damaged when the upper thigh is injured. They can also become inflamed in autoimmune, infectious diseases, tumors, diseases associated with metabolic disorders ( e.g. pseudogout, diabetes ). Therefore, during the diagnosis of pain in the hip joint, one should take into account the fact that inflammation of these formations, and not the tissues of the joint itself, is the true cause of pain.The following anatomical formations are located near the hip joint:
- skin and subcutaneous tissue;
- muscles;
- extra-articular ligaments of the hip joint;
- periarticular bags.
The skin and subcutaneous tissue are located above the muscles and form the outer cover of the hip region of the human body.
muscles
In the area of \u200b\u200bthe hip joint there is a huge number of muscles that are attached ( with tendons) either to the pelvis or to the femur and belong to different muscle groups. Some muscles belong to the muscles of the thigh ( e.g. quadriceps femoris, adductor magnus, pectineus), others - to the pelvic muscles ( e.g. obturator internus or externus).
Extra-articular ligaments of the hip joint
Extra-articular ligaments strengthen the hip joint and are located around the joint capsule. On the one hand, they are attached to the pelvic bone, and on the opposite side, to the femur, below the attachment of the hip joint capsule. Above the joint capsule is the iliofemoral ligament, below is the ischiofemoral ligament, and in front and slightly below the pubic-femoral ligament.
Periarticular bags
The pouch is an elastic bag made of connective tissue, which prevents friction between soft ( muscles, ligaments) and solid ( bones) tissues. Near the hip joint are the trochanteric ( located next to the greater trochanter of the femur), ischial ( located near the body of the ischium) and iliopectineal ( placed anterior to the femoral neck) periarticular bags.
What structures can become inflamed in the hip area?
 Pain in the hip area is a characteristic feature of inflammation of the tissues of the hip joint itself or those anatomical structures that surround this joint. Inflammation of the tissues of the hip region is most often found in various mechanical injuries, as well as when they are infected with certain pathogens. bacteria.
Pain in the hip area is a characteristic feature of inflammation of the tissues of the hip joint itself or those anatomical structures that surround this joint. Inflammation of the tissues of the hip region is most often found in various mechanical injuries, as well as when they are infected with certain pathogens. bacteria.In the hip area, the following structures can become inflamed:
- skin and subcutaneous tissue;
- muscles;
- periarticular bags;
- extra-articular ligaments;
- ligament of the femoral head;
- articular cartilage;
- acetabular lip of the hip joint;
- subcartilaginous areas of the pelvic bone and the head of the femur.
The main causes of pain in the hip joint
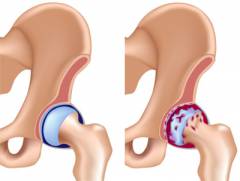 Pain in the hip joint occurs as a result of inflammation or violation of the integrity of its anatomical structures. The main cause of inflammation of the hip joint are various pathogens that cause infectious diseases. arthritis. Sometimes, due to a compromised immune system, autoimmune damage to the hip joint can occur, caused by damage to its own tissues by immune cells or antibodies ( protein defense molecules). This is often observed in rheumatoid arthritis And reactive arthritis.
Pain in the hip joint occurs as a result of inflammation or violation of the integrity of its anatomical structures. The main cause of inflammation of the hip joint are various pathogens that cause infectious diseases. arthritis. Sometimes, due to a compromised immune system, autoimmune damage to the hip joint can occur, caused by damage to its own tissues by immune cells or antibodies ( protein defense molecules). This is often observed in rheumatoid arthritis And reactive arthritis.The next main cause of pain in the hip joint is mechanical trauma to the joint, which often causes damage to its articular surfaces, ligaments, capsules and other joint formations. Such traumatization often occurs during heavy physical exertion in athletes or in the elderly as a result of insufficient regeneration processes ( recovery) articular cartilage. Pain in the hip joint can be observed in children and adolescents, this is due to the inferiority of the development of their joints and various endocrine changes that occur at their age.
Pain in the hip joint can also occur in some diseases accompanied by metabolic disorders. For example, they are often seen in diabetes (violation of glucose metabolism in the body), pseudogout ( violation of calcium metabolism in the body), obesity.
There are the following main causes of pain in the hip joint:
- Legg-Calve-Perthes disease;
- Koenig's disease;
- diabetic osteoarthropathy;
- pseudogout;
- intermittent hydrarthrosis;
- synovial chondromatosis;
- reactive arthritis of the hip joint;
- infectious arthritis of the hip joint;
- juvenile epiphyseolysis;
- hip joint injury;
- rheumatoid arthritis of the hip joint.
Legg-Calve-Perthes disease
Legg-Calve-Perthes disease ( osteochondropathy of the femoral head) is a pathology that is characterized by necrosis of the tissues of the articular cartilage of the femoral head. It occurs as a result of impaired blood supply and constant microtrauma of the hip joint. Most often, the disease appears in boys under the age of 10 years.Its main symptom is constant pain in the hip joint, which increases with physical exertion and often radiates to the knee. Necrosis ( necrosis) articular hyaline cartilage of the femoral head leads to its deformation and limitation of flexion and rotational movements in the hip joint.
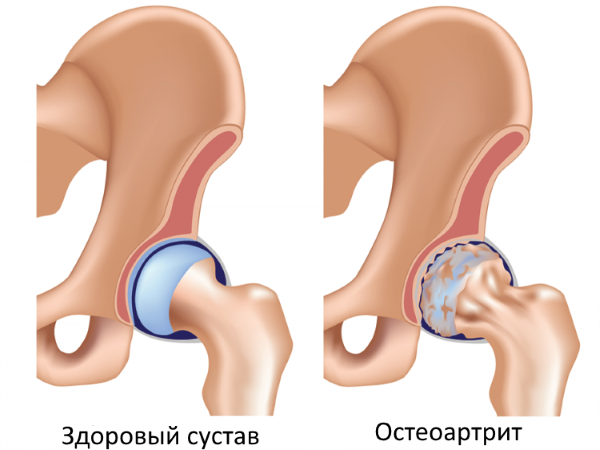
Coxarthrosis
The cause of pain in the hip joint with coxarthrosis ( osteoarthritis of the hip joint) serves as a violation of metabolic processes in articular cartilage which leads to their gradual degeneration. These processes occur under the influence of various provoking factors. They can be a violation of the blood supply to the hip joint, its periodic injuries, prolonged physical exertion, a genetic predisposition to this disease, the age of the patient ( the disease occurs more often in people over 40 years of age).Pain in coxarthrosis at the onset of the disease is unstable and more often localized in the groin, buttock, and lower back. As the disease progresses, they become more frequent, become longer, occur during physical exertion in the area of the hip joint and subside at rest. Such pains are often associated with lameness, that is, the inability to shift half ( or the whole mass) body weight per affected leg.
Koenig's disease
Koenig's disease ( dissecting osteochondrosis articular surfaces) is a disease that can cause pain in the hip joint, cause a violation of its function, and is also accompanied by synovitis (inflammation of the synovium of the hip joint). This disease is associated with subcartilaginous necrosis of the epiphyseal articular surface of the femoral head, which occurs with mechanical trauma to the hip joint or excessive physical exertion. Pain in the hip joint in Koenig's disease is intermittent and often aggravated by movement of the affected leg.Diabetic osteoarthropathy
Diabetic osteoarthropathy is a disease of the joints due to diabetes ( a disease characterized by high blood sugar). With this metabolic pathology ( pathology associated with metabolic disorders) can damage almost any joint, including the hip, which is very rare. This pathology is characterized by a gradual deformation of the articular surfaces of the hip joint, which is accompanied by pain in its area.The intensity of pain in the hip joint is practically not related to the severity of violations of its structure, often there are no pains at all or are mildly expressed. This phenomenon is associated with nerve damage ( innervating the hip joint) in diabetes. Diabetic osteoarthropathy is a complication of diabetes and appears late, 6–8 years after its onset, and often against the background of ineffective antidiabetic treatment.
pseudogout
Pseudogout ( pyrophosphate arthropathy or chondrocalcinosis) is a pathology associated with a violation of calcium metabolism and the deposition of its crystals ( calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate) in various joints. Most often, it occurs against the background of a genetic predisposition to this disease or with certain endocrine diseases ( hyperparathyroidism, hypothyroidism and etc.).Pain that appears in the hip joint with pseudogout is associated with the deposition of calcium salts in the articular cartilage, ligaments, synovial membrane of the hip joint and their mineralization ( hardening). The appearance of a large amount of calcium in the structures of the joint causes their inflammation and degenerative processes. Over time, the hip joint undergoes deformation, sometimes bone outgrowths appear in its vicinity - osteophytes.
Pain in the hip joint is paroxysmal in nature, appear suddenly and increase within 12 to 24 hours. After some time, after 1 - 2 days, also suddenly, the pain begins to subside, gradually disappearing.
Intermittent hydrarthrosis
Intermittent hydrarthrosis is a disease of the joints of unknown etiology, in which the appearance of fluid in the joints is periodically observed. The hip joint is rarely affected in this pathology. However, if this happens, then in his area there is a slight soreness. Intermittent hydrarthrosis most often affects young women from 20 to 40 years old. Pain in the hip joint appears spontaneously and has some pattern, occurring every 1 to 2 weeks and quite often associated with menstrual cycle.Synovial chondromatosis
Synovial chondromatosis is a disease, which is based on the appearance in the joint cavity of a pathological cartilaginous formation ( chondromic body), resulting from abnormal development of the synovial tissue of the hip joint ( or other joints).Synovial chondromatosis is more common in men aged 30-40 years. The disease is characterized by the appearance of pain in the hip joint and the limitation of its motor abilities, since the chondromic body often blocks the movement of the articular surfaces ( femoral head and acetabulum of the pelvic bone) of this joint relative to each other.
Reactive arthritis of the hip
Reactive arthritis of the hip reactive hip inflammation) can be observed after the transferred urogenital ( urogenital) or intestinal infection. It occurs due to damage to the synovial membrane ( and other structures) of the hip joint with autoimmune antibodies that cause inflammation. Such antibodies ( proteinaceous protective particles circulating in the blood) are first formed to protect the body from bacteria and other microorganisms that have penetrated into it ( with intestinal or urogenital infections ), that is, they are one of the protective immunological reactions of the body. After recovery, antibodies remain in the blood.Sometimes it happens that due to immunological disorders in the immune system, these antibodies begin to take over the structures of various joints ( hip, knee, wrist) of the body for foreign tissues and then they attack them. This is how reactive arthritis occurs, and the antibodies that cause it are called autoimmune antibodies.
Types of reactive arthritis of the hip
| Type of arthritis | When does this type of arthritis occur? | To what types of pathogenic microorganisms do autoimmune antibodies form? | Features of arthritis |
| Post-enterocolitic reactive arthritis | Occurs after a while in people who have had an intestinal infection. |
| This type of arthritis often affects multiple joints at once. lower extremities (including the hip joint). Post-enterocolitic reactive arthritis of the hip joint is characterized by the appearance of pain in this joint, which disappears over time, as well as uveitis (inflammation of the choroid of the eye) And conjunctivitis (inflammation of the conjunctiva of the eye). |
| Urogenital reactive arthritis | Appears after transfer urethritis (). Sometimes occurs simultaneously with this pathology. |
| The hip joint is rarely affected in urogenital reactive arthritis. However, if he arthritis of the hip) still occurs, it is accompanied by the appearance of pain in this joint, a decrease in body weight, an increase temperature, ulceration of the oral mucosa, inflammation of the tongue. |
| Reiter's syndrome | More often occurs 2 to 3 weeks after the transferred urogenital ( urogenital) or intestinal infection. | With the venereal (urogenital) form of Reiter's syndrome:
| Pain in the hip joint in Reiter's syndrome is often associated with urethritis ( inflammation of the urethra) and conjunctivitis ( inflammation of the conjunctiva of the eye). Sometimes pain occurs after urethritis and conjunctivitis. It is worth noting that the hip joint is not always affected in this syndrome. |
Infectious arthritis of the hip
Infectious arthritis of the hip joint is an inflammation of the tissues of the hip joint caused by pathogenic microorganisms that have entered its cavity. Such arthritis is characterized by the appearance of pain in the hip joint, an increase in body temperature, with it often pathological fluid and pus accumulate inside the joint.Patients with infectious arthritis of the hip joint often limp, they have limited mobility of the affected joint, and the muscles on the leg gradually atrophy. Depending on the type of etiological agent ( microbe) all infectious arthritis are divided into types.
Types of infectious arthritis of the hip joint
| Type of infectious arthritis | What microorganism can cause it? | Features of arthritis |
| Acute septic arthritis
(non-gonococcal septic arthritis) |
| Acute septic arthritis of the hip joint is accompanied not only by pain, but also by fever, weakness. This type of arthritis is more common in children. |
| Brucella arthritis | Brucellosis arthritis often leads to the destruction of the articular cartilage of the hip joint and its deformation. Also a typical manifestation of this arthritis is inflammation of the periarticular tissues of the hip joint ( ligaments, joint capsule, muscles, etc.). | |
| tuberculous arthritis |
| IN initial stages tuberculous arthritis pain in the hip joint is rarely present. They appear at the later stages of the development of the pathology, when there is a melting of the cartilaginous tissue of the articular surfaces of the hip joint and its deformation. |
| Viral arthritis |
| Most often, inflammation of both hip joints is observed, however, deformation of their articular surfaces does not occur. The course of this type of arthritis is mild and patients recover quickly. |
| Lyme disease |
| When bitten by an ixodid tick, pain in the hip joint appears after 5 to 6 months. Most often, both hip joints or one of them with other joints become inflamed ( knee, ankle, shoulder). |
Juvenile epiphysiolysis
Juvenile epiphyseolysis is a pathology consisting in the gradual slipping of the femoral head from the acetabulum of the hip joint upwards and backwards. This disease is observed mainly in children 11-14 years old. Its appearance is associated with various factors risks, among which are permanent injuries of the hip joint, hereditary predisposition, endocrine disorders, obesity, diabetes mellitus.Pain in the hip joint appears during prolonged static physical exertion, has an increasing character and is sometimes associated with pain in the groin or knee joint area.
Hip injury
The hip joint can be subject to various injuries that occur during falls from a height, traffic accidents, sports training, falls during ice, etc. Almost every injury is accompanied by pain in the hip joint area, impaired function, lameness and sometimes the appearance of bruising on the skin of the hip area.Types of hip injuries
| Type of injury | What is damaged in this injury? | The mechanism of pain in this type of injury |
| Fracture of the femur |
| Pain in the hip joint is caused by damage to the tissues of the joint ( articular cartilage, capsules) fragments of the femur, which appeared during fracture her neck or head. Also, pains are caused by blood accumulated in the cavity of the hip joint, which stretches its capsule. It is worth noting that fractures of the neck and head of the femur can occur both together and separately. |
| hip dislocation |
| The mechanism of pain that occurs with dislocation of the hip joint, is associated with mechanical damage to its articular cartilage, rupture of the joint capsule and the ligament of the femoral head that feeds it. The latter leads to rapidly progressive aseptic necrosis ( necrosis of tissues due to impaired blood supply). |
| Bursitis |
| Pain in the hip joint bursitis arise due to inflammation of one or more periarticular synovial bags of the hip joint. |
| Acetabular lip rupture |
| Pain sensations appear as a result of mechanical separation of the acetabular lip from the marginal surface of the acetabulum. |
| Hip injury | Any structures located both near the hip joint and in the joint itself can be affected:
| Pain in the hip joint is caused mild inflammation tissues located around the joint, as well as its own structures. The intensity of the pain syndrome depends on the severity of the injury and on the depth of the lesion resulting from a mechanical injury. |
Rheumatoid arthritis of the hip joint
In patients with rheumatoid arthritis, sometimes there is a lesion of the hip joint, which is accompanied by pain and a violation of its functions. The mechanism of pain development in this pathology is associated with tissue inflammation ( cartilage, capsules, etc.) of the hip joint, destruction and deformation of its articular surfaces and aseptic necrosis ( necrosis of a tissue site without the participation of pathogenic microbes) head of the femur.Rheumatoid lesion of the hip joint is a rather rare phenomenon, which is caused by autoimmune reactions that occur in the body during rheumatoid arthritis. Their essence lies in the fact that the body's own tissues are affected by immunocompetent cells ( cells that are responsible for the immune response), whose activity is disrupted for reasons unknown to medicine so far.
Which doctor should I contact if my hip joint hurts?
 A traumatologist and a rheumatologist are involved in the diagnosis and treatment of pain in the hip joint. To help the patient in choosing a qualified specialist should family ( precinct) the doctor to whom you should contact if this symptom occurs.
A traumatologist and a rheumatologist are involved in the diagnosis and treatment of pain in the hip joint. To help the patient in choosing a qualified specialist should family ( precinct) the doctor to whom you should contact if this symptom occurs. Sometimes the patient does not have the opportunity to contact the local doctor, in this case it is worth acting depending on the situation. Usually, if the hip joint began to hurt after playing sports, falling, lifting weights, household or other injuries, then you should contact a traumatologist. If pain in this joint appeared spontaneously and without any explainable reason, then it is better to go to a rheumatologist.
Diagnosis of the causes of pain in the hip joint
 There are several methods that help the attending physician reliably determine the cause of pain in the hip joint. Some of them ( anamnesis, external examination, palpation) he can carry out independently, he appoints others to the patient. They are various laboratory studies ( tests) and instrumental research methods ( X-ray methods of diagnostics and endoscopic examinations). The choice of each of the methods depends on the patient's complaints, his external condition, the presence of concomitant diseases, the availability of research, the competence of the doctor and other important factors.
There are several methods that help the attending physician reliably determine the cause of pain in the hip joint. Some of them ( anamnesis, external examination, palpation) he can carry out independently, he appoints others to the patient. They are various laboratory studies ( tests) and instrumental research methods ( X-ray methods of diagnostics and endoscopic examinations). The choice of each of the methods depends on the patient's complaints, his external condition, the presence of concomitant diseases, the availability of research, the competence of the doctor and other important factors. There are the following methods for diagnosing the causes of pain in the hip joint:
- anamnesis;
- external examination and palpation;
- microbiological research;
- immunological blood test;
- endoscopic examination of the hip joint;
- lab test for effusion ( pathological fluid) of the hip joint.
Anamnesis
The anamnesis is the usual collection of information regarding the symptoms of the disease, the conditions for their appearance, environmental factors that could contribute to the development of this particular disease ( for example, the presence of domestic or other injuries, physical overload, difficult working conditions). During the patient's history, the patient is also asked about the presence of concomitant pathology, which may indirectly affect the disease that has appeared or its treatment.External examination and palpation
The actual external examination includes a visual examination of the external integuments of the patient's body, an assessment of the symmetry of the left and right foot And general condition patient. Examination of the outer covers ( mucous membranes, skin) consists in determining their color, structure and studying their properties.On palpation ( palpation of the outer coverings) determine the development of the skin, subcutaneous tissue, muscles, bones. Also, this study can determine the temperature of the skin, its elasticity, mobility. Palpation can detect some anatomical abnormalities ( For example, fracture of the femur, its displacement, the presence of a space-occupying formation). With the help of palpation, the doctor often tries to determine a more accurate localization of the pathological process.
Radiography
Radiography is the main radiation method of diagnostics, which is based on the use of x-rays, through which the irradiation of the studied area of the human body occurs ( For example, abdominal cavity, hip joint, spine etc.). Passing through the tissues of the body, X-rays are absorbed by them, depending on their density and structure.The remaining radiation ( which has not been absorbed) falls on x-ray film and forms an image on it. Such a film will henceforth be referred to as a radiograph. On it you can find dark and light areas. Dark areas are body tissues that have strongly absorbed x-rays ( e.g. femur, pelvic bone). Light areas indicate structures that absorbed this radiation weaker ( e.g. skin, subcutaneous tissue, muscles). Radiography is a fast, cost-effective and practically harmless method of radiation diagnostics.
CT scan
CT scan ( CT) is a type of X-ray examination. Although this method is based on the same principle as radiography, it is incomparably better and more accurate, so it has found its wide application in the diagnosis of various pathologies that cause pain in the hip joint. Pictures at computed tomography differ from the images obtained by radiography, they look like transverse black-and-white sections of a certain part of the human body ( for example, the hip joint, chest and etc.).Magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging ( MRI) is a diagnostic method that consists in irradiating tissues and organs with electromagnetic radiation of a certain length, against the background of a specially created magnetic field. The molecules that make up the tissues of the body, under the influence of this radiation, begin to be excited and release wave signals, which are recorded by the MRI machine. The information about the anatomical structure of organs and tissues that has entered this device is processed and appears in the form of an image on the screen of the device or as MRI images that look like layer-by-layer transverse sections of tissues.Theoretically, magnetic resonance imaging can be used in the diagnosis of many diseases of the hip region that cause pain in the hip joint area, however, due to the high cost of the method, its use is, in most cases, very limited. Therefore, this study is prescribed in severe clinical situations.
Microbiological research
Microbiological examination includes bacteriological and virological diagnostic methods.The bacteriological diagnostic method is carried out in order to detect pathogenic bacteria in the biological material taken from the patient. It usually consists of microscopy, inoculation on special media, and identification of the bacterial species. Microscopy is the first stage of bacteriological examination, which consists in the study of pathological material under a microscope lens. Having examined the structure of microbes, the bacteriologist sows them on special nutrient media. When bacteria of the same species grow, they join and group to form colonies ( accumulation of bacteria), which are studied in the laboratory.
In the future, these bacteria determine their ability to break down various chemical compounds, bind to certain viruses, antibodies, etc. Based on the results of all studies, the bacteriologist determines the causative agent of the infection. Also bacteriological examination used to determine the susceptibility of bacteria to different types antibacterial drugs- antibiograms.
Virological diagnostic method is used in the diagnosis viral diseases. This study consists of microscopy, cultivation of viruses on cell media, detection of viral DNA, and it also includes the use of immunological methods. Microscopy and cultivation of viruses on media are currently not widely used due to their high cost. The most commonly used PCR method ( method polymerase chain reaction ) to detect viral DNA ( genetic molecule) and immunological methods for detecting virus particles in the blood of patients.
Immunological blood test
Immunological analysis is often used to assess the state of the body's immune system in various infectious conditions, as well as to identify the cause of some inflammatory and infectious diseases hip joint ( infectious arthritis of the hip). It is also used to detect specific autoantibodies ( antibodies of the own immune system that affect the hip joint) in autoimmune diseases ( e.g., reactive, rheumatoid arthritis).Endoscopic examination of the hip joint
Endoscopy ( arthroscopy ) of the hip joint is a type of endoscopic examination that allows you to examine the joint cavity with a special probe - an arthroscope ( elastic tube, which is equipped with a camera). This diagnostic method is rarely used to identify the cause of pain in the hip joint, but only in some cases when other studies are powerless. This method also allows biopsy ( take a piece of tissue for examination) of the hip joint. Most often, a biopsy of the articular cartilage is done, etc.Laboratory study of hip effusion
Effusion ( pathological fluid) of the hip joint is obtained with the help of its puncture - a therapeutic and diagnostic manipulation, in which the joint is punctured with a special needle. The resulting effusion is delivered to the laboratory, where it is analyzed. This study consists of determining the transparency, the nature of the effusion ( serous, purulent, bloody), ascertaining the presence and number of cells ( leukocytes , neutrophils and etc.), biochemical components ( protein, crystals, etc.).Also, the effusion of the hip joint is sent for microbiological studies to determine its sterility ( those. determination of the presence of microorganisms in it). In purulent arthritis, microbiological studies help determine the type of pathogen and conduct an antibiogram ( bacterial susceptibility testing antibiotics ). Laboratory research pathological fluid helps to quickly determine the cause of inflammation of the hip joint.
Features of pain in the hip joint
 Hip pain can vary in intensity. Sometimes they cause slight discomfort when moving the leg, and sometimes the pain can be very strong when sensitive nerve endings are affected. Some diseases of the hip joint are often accompanied by irradiation ( bestowal) pain in the areas adjacent to this joint - groin, buttock, thigh, knee. Pain can appear when walking or, conversely, be constant and not decrease at rest. There are also pathologies that are accompanied by pain only during certain movements in the affected hip joint, for example, when abducting or bending the leg, etc.
Hip pain can vary in intensity. Sometimes they cause slight discomfort when moving the leg, and sometimes the pain can be very strong when sensitive nerve endings are affected. Some diseases of the hip joint are often accompanied by irradiation ( bestowal) pain in the areas adjacent to this joint - groin, buttock, thigh, knee. Pain can appear when walking or, conversely, be constant and not decrease at rest. There are also pathologies that are accompanied by pain only during certain movements in the affected hip joint, for example, when abducting or bending the leg, etc. Why does the hip joint hurt and give to the leg?
Some diseases of the hip joint cause not only pain in it, but also pain that radiates ( give back) in various areas of the leg and pelvis. The main places on the leg where they radiate ( give back) pain is the knee joint, inguinal and gluteal region. Irradiation mechanism ( pain relief) is associated with inflammation, damage or rupture of the nerves that simultaneously innervate both the hip joint and the thigh, knee, as well as the pelvic and gluteal zones. For example, pain in the hip joint often occurs when the branches of the femoral and sciatic nerves are damaged.The following diseases are distinguished, in which irradiation of pain in the leg occurs:
- Juvenile epiphysiolysis. Juvenile epiphysiolysis is a disease of the hip joint, which is caused by the slow exit of the femoral head from the joint, rupture of its structures ( e.g. ligaments of the femoral head, joint capsules) and their inflammation.
- Legg-Calve-Perthes disease. Pain in the hip joint, radiating ( bestowing) in the leg and occurring in this disease is caused by necrosis ( deadness) cartilaginous articular surface of the femoral head.
- Fracture of the head or neck of the femur. This pathology is caused by a violation of the anatomical integrity of the areas of the femoral bone located in the cavity of the hip joint. Fracture of the head or neck of the femur is often accompanied by rupture of various intraarticular tissues ( including nerves.), which is the main reason for the appearance of irradiating ( giving) in the leg pain.
- Infectious arthritis of the hip. This pathology consists in damage to the structures ( including nerves.) of the hip joint by microorganisms various kinds.
- Tumors of the hip joint. Tumors of the hip joint arise as a result of a violation of the reproduction of tissue cells that form this joint. irradiating ( bestowing) in the leg pain appears due to mechanical compression and inflammation nerve endings hip joint.
Why does pain occur when walking in the hip joint?
Pain that occurs when walking in the hip joint is a consequence of inflammation of the cartilaginous articular surfaces of the femoral head and the acetabulum of the pelvic bone that come into contact when walking. Sometimes the cause of these pains can be damage to other articular structures, which can often be found with mechanical injuries of the hip joint. For example, pain can often be observed with fractures of the femoral head, rupture of the capsule or lip of the acetabulum. Also, the cause of pain in this joint that appears when walking can be inflammation of the tissues located near the hip joint ( muscles, periarticular capsules, ligaments, etc.).The intensity and nature of pain that occurs in the hip joint when walking fully depends on the type of damaged structures located in the hip region, on their number, the cause of their cause and its severity.
Depending on the nature of the appearance, pain in the hip joint that occurs when walking can be divided into the following groups:
- starting pains;
- gradually increasing pain;
- evening pains;
- persistent mild or moderate pain;
- constant severe pain.
Starting pains occur at the very beginning of walking and gradually subside with it. This often occurs with inflammation of the periarticular bags ( trochanteric, ischial, iliac-scallop) located in the hip area.
Gradually increasing pain
There are situations when pain in the hip joint does not occur immediately, but after a while from the start of walking. Such pain with each step taken intensifies more and more. This feature is typical for such pathologies as Koenig's disease, Legg-Calve-Perthes disease, coxarthrosis and other diseases that are accompanied by inflammation of the articular surfaces of the hip joint.
Evening pains
Evening pains in the hip joint are more common in pathologies that are accompanied by destruction and deformity of the articular cartilage of the femoral head and / or the acetabulum of the pelvic bone. Examples of such diseases are coxarthrosis, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetic osteoarthropathy, etc.
If a patient, for example, is ill with any of these pathologies, then when moving ( while walking, running, exercising) in the hip joint, its deformed articular surfaces begin to intensively rub against each other. This prolonged friction causes the articular cartilage in the hip joint to become inflamed and painful by the evening.
Persistent mild or moderate pain
Constant mild or moderate pain in the hip joint appears with minor injuries of the hip or pelvic bone, accompanied by bruises. Sometimes they are caused by an infectious or reactive lesion of the joint or the structures that surround it. Quite often, these pains are observed in tuberculosis, brucellosis, septic and reactive arthritis.
Constant severe pain
Constant severe pain localized in the area of the hip joint indicates a serious pathology. They are often accompanied by immobilization ( no active movement) joint, severe impairment of its functions. Typically, such pain is characteristic of a dislocation of the hip, a fracture of the head or neck of the femur.
Why does the hip joint hurt when the leg is abducted?
main reason Pain in the hip joint during leg abduction is inflammation of those anatomical structures that are directly involved in this action. These structures are the abductors of the thigh ( gluteus maximus, medius, minimus, etc.), their tendons and periarticular bags of the hip joint. Various diseases hip joint can also be the cause of these pains, however they ( diseases) most often cause pain not only when the leg is abducted, but also during its other motor actions ( flexion, extension, adduction, etc.).There are the following main causes that cause pain in the hip joint when the leg is abducted:
- bursitis;
- myositis abductor muscles of the thigh.
Bursitis is a pathology that occurs due to inflammation of the periarticular bag. The latter is a hollow, small, bag-like formation filled with serous fluid, which prevents friction between bone tissues and softer structures - muscles, ligaments, etc. Most common cause pain that occurs in the hip joint when the leg is abducted is trochanteric bursitis. This bag is located near the greater trochanter and the initial site of the femoral neck.
Tendinitis
Tendinitis is an inflammation of the tendon areas of the muscles. Pain in the hip joint that occurs when the leg is abducted causes, in most cases, tendinitis of the hip abductors. They are the gluteal muscles ( large, medium, small), piriformis muscle and a muscle that strains the wide fascia of the thigh.
Myositis of the abductor muscles of the thigh
Myositis is an inflammation of the muscle tissue of one or more muscles. Myositis of the abductor muscles of the thigh occurs with injuries of the buttocks and the lateral surface of the thigh, with various infectious diseases, anomalies in the development of muscles and bones, prolonged physical exertion, etc. Pain in the hip joint with myositis of these muscles increases with pressure on them or with even stronger hip abduction . In the future, inflammation of the abductor muscles of the thigh leads to their atrophy, which is accompanied by muscle weakness, due to which there is a restriction of movements in the hip joint and a decrease in working capacity.

What pathologies are characterized by severe pain in the hip joint?
 Many pathologies of the hip joint are characterized by the appearance of pain of varying intensity. Some of them are dominated by mild soreness or discomfort in the hip area. This can often be observed with bruises of the upper lateral part of the thigh, intermittent hydrarthrosis, tumors of the hip joint, osteoporosis and others. Moderate pain prevails in destructive diseases - infectious, reactive, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetic osteoarthropathy, etc. Strong pain syndrome more typical for pathologies accompanied by serious injuries of the hip joint, such as fractures and dislocations.
Many pathologies of the hip joint are characterized by the appearance of pain of varying intensity. Some of them are dominated by mild soreness or discomfort in the hip area. This can often be observed with bruises of the upper lateral part of the thigh, intermittent hydrarthrosis, tumors of the hip joint, osteoporosis and others. Moderate pain prevails in destructive diseases - infectious, reactive, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetic osteoarthropathy, etc. Strong pain syndrome more typical for pathologies accompanied by serious injuries of the hip joint, such as fractures and dislocations. Severe pain in the hip joint is most often found in the following pathologies:
- pseudogout;
- dislocation of the hip joint;
- fracture of the head and/or neck of the femur.
With pseudogout, calcium crystals are deposited in the cavity of the hip joint. Most often, calcium is deposited in the articular cartilage and causes them to harden, as a result of which they lose their elasticity and cushioning properties. characteristic clinical sign Pseudogout are severe pains in the area of the affected joint that appear spontaneously in the form of attacks. They appear for 1 - 2 days and then disappear.
Dislocation of the hip joint
Dislocation of the hip joint is a pathological condition caused by the exit of the femoral head from the cavity of the acetabulum of the pelvic bone. Severe pain in this pathology occurs as a result of rupture of some structures of the joint ( capsules, ligaments of the femoral head, etc.) and damage to the cartilaginous articular surfaces of the hip joint.
Fracture of the head and/or neck of the femur
Fracture of the head and / or neck of the femur is a pathology of the bone tissue of the femur, accompanied by the destruction of its normal anatomical structure. Bone fragments formed during femoral fractures affect extra-articular and intra-articular structures located in the fracture zone. Therefore, with fractures of the femur, severe pain often appears.
What to do if the hip joint hurts?
 The severity of the pathology of the hip joint, in most cases, is directly proportional ( directly depends on) the intensity of pain and the ability of the joint to carry out motor actions characteristic of it in the norm.
The severity of the pathology of the hip joint, in most cases, is directly proportional ( directly depends on) the intensity of pain and the ability of the joint to carry out motor actions characteristic of it in the norm. It is conditionally possible to distinguish three degrees of intensity of pain in the hip joint:
- mild pain;
- average ( moderate) pain;
- severe pain.
Sudden mild pains mainly occur with minor bruises of the hip joint that occur during mechanical injuries. In such cases, you can apply ice to the sore spot and drink non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (ibuprofen , aspirin and etc.). After 1 - 2 days, you should contact a traumatologist for your own insurance and prevention of accidental complications.
If mild pain sensations began gradually, exist for a long time and do not go away, then you should not try to treat pain in the hip joint on your own, but consult a rheumatologist.
Medium ( moderate) pain
Moderate pain is common in many diseases of the hip joint. They may be accompanied by fever, dysfunction of the joint, lameness, irradiation ( bestowal) pain in other areas of the leg. Such pains often have an increasing character and are aggravated by physical exertion ( walking, running, jumping, etc.). With the appearance of moderate pain in the hip joint, it is recommended to consult a rheumatologist as soon as possible. If the pain arose after an injury, then it is better to go to a traumatologist.
severe pain
Severe pain most often accompanies a dislocation of the hip joint, fractures of the head and / or neck of the femur. With these pathologies, pain is associated with limited mobility of the joint, the inability to step on the affected leg, and the absence of active movements in the hip joint. When severe pain It is necessary to limit mobility in the damaged joint as much as possible. Do not try to get to the hospital on your own, but it is better to call an ambulance.
What folk remedies are used for pain in the hip joint?
 Folk remedies as the main method of treating pain in the hip joint are rarely used, since their use, in most cases, does not allow you to get rid of the cause that caused these pains. Therefore, many folk remedies are used as symptomatic treatment to reduce pain.
Folk remedies as the main method of treating pain in the hip joint are rarely used, since their use, in most cases, does not allow you to get rid of the cause that caused these pains. Therefore, many folk remedies are used as symptomatic treatment to reduce pain. Also, folk remedies are not able to eliminate the consequences of some pathologies that are accompanied by a violation of the anatomical structure of the hip joint and, in particular, the deformation of the articular surfaces of the joint, which is often found in rheumatoid arthritis, coxarthrosis, diabetic osteoarthropathy, etc. Folk remedies cannot be used for fractures or dislocations of the hip joint .
In general, it can be noted that the use of folk remedies is permissible only in cases where the patient has previously consulted with the attending physician and he approved their use.
There are the following folk remedies that can help with pain in the hip joint:
- A decoction of the roots of dog rose hips. Pour 15 g of dog rose roots into one glass of water. After that, the resulting mixture should be boiled for 20 minutes. Then remove from heat and strain after 1 hour. Drink half a glass in the morning and evening.
- A decoction of lingonberry leaves. Place two teaspoons of lingonberry leaves in one glass of water. Then this water must be boiled over low heat for 15 to 20 minutes. The solution is then cooled and filtered. A decoction of lingonberry leaves must be drunk during the day.
- A decoction of pine buds. Take ten grams of pine buds and mix with one glass of water, which then needs to be boiled for 10 - 15 minutes. This decoction should be drunk during the day after it has been pre-filtered and cooled.
- Decoction of dandelion officinalis. Pour 6 grams of roots and medicinal dandelion herbs with one glass of water, boil ( 10 – 15 minutes). Let the solution brew for 30-60 minutes. Folk remedy It is recommended to use one tablespoon 2-3 times a day.
- A decoction of burdock roots. Place 10 g of dry burdock roots in 1 glass of water. After that, the water should be boiled for 20 minutes. Strain the resulting broth and cool. It is necessary to use a decoction of burdock roots 3 times a day, 1 tablespoon.
Why does the hip joint hurt during pregnancy?
 The main cause of pain in the hip joint in pregnancy it is considered an increase in the mechanical load on this joint due to an increase in the body weight of the pregnant woman, which, in turn, is caused by the growth of the child inside the placenta. With a long static position ( standing, walking, running) in the articular surfaces of the hip joint, there is strong friction and their slight trauma, which provokes inflammatory process which is the cause of the pain.
The main cause of pain in the hip joint in pregnancy it is considered an increase in the mechanical load on this joint due to an increase in the body weight of the pregnant woman, which, in turn, is caused by the growth of the child inside the placenta. With a long static position ( standing, walking, running) in the articular surfaces of the hip joint, there is strong friction and their slight trauma, which provokes inflammatory process which is the cause of the pain. There are the following reasons that cause pain in the hip joint during pregnancy:
- Increased mechanical load on the hip joint. As the fetus grows, its weight increases, which means that the load on the main supporting joints of the mother increases - the hip, knee joints, spine, etc.
- Violation of immunity. During pregnancy the immune system mother is often weakened due to lack of vitamins and minerals. This is mainly due to the transport of these substances through the placenta to the tissues of the fetus. The weakened immune system of the mother makes her susceptible to various pathogens that can cause infectious arthritis of the hip.
- Deficiency of minerals. Pain in the hip joint, in particular, causes a lack of calcium, which is actively washed out of the mother's bones to build the tissues of the unborn child. Especially often this happens with inferior nutrition