Antipyretics for children are prescribed by a pediatrician. But there are emergency situations with fever when the child needs to be given medicine immediately. Then the parents take responsibility and use antipyretic drugs. What is allowed to be given to infants? How can you lower the temperature in older children? What medications are the safest?
Trochanteritis is an inflammatory disease that affects the trochanter of the femur. This is the highest point of the thigh, to which a large number of tendons and muscles are attached.
At first glance, it is very difficult to distinguish between trochanteritis and a disease such as (). But in approximately half of the cases in patients diagnosed with coxarthrosis, a detailed examination reveals that the cause of pain is trochanteritis. This is by no means a rare pathology, it is simply often not recognized.
Important to remember! Trochanteritis responds well and quickly to treatment if it does not become chronic. Therefore, it is necessary to exclude this disease, first of all, in case of pain in the hip joints.
The essence of the disease
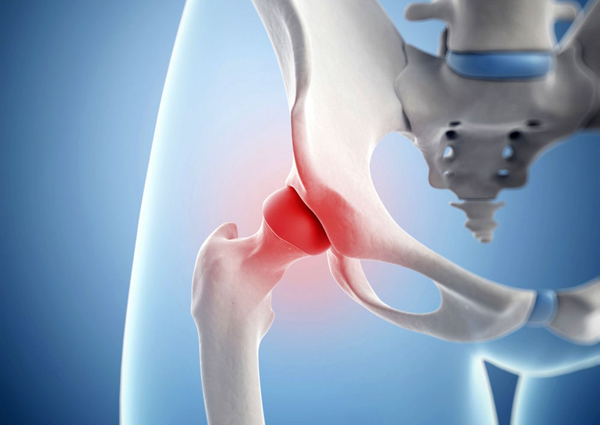
As already said, pathological changes with trochanteritis, the greater trochanter (trochanter) of the femur (the outermost point of the thigh) and the tendons that attach to it are affected. This is where the name of the nosological form of pathology comes from. This inflammation can be caused by both infectious and non-infectious causes.
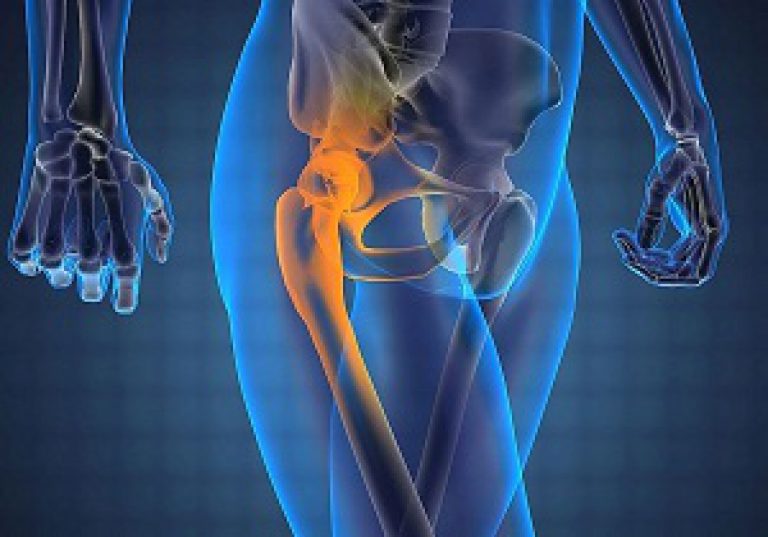
With trochanteritis, the greater trochanter of the femur becomes inflamed
The main function of the trochanter is that it acts as the attachment point for a large number of muscular tendons of the gluteal region and thigh area. Above this bony structure, on top of the muscles under the skin, is a small bursa, which serves a protective role and also helps facilitate movement in the hip. This anatomical formation is very often drawn into the pathological process and becomes inflamed, and hip bursitis develops. Therefore, sometimes you can find another name for trochanteritis - trochanteric bursitis.
Remember! With trochanteritis, the greater trochanter of the femur, the muscle tendons that attach to it, and the synovial bursa located nearby become inflamed. The process is most often unilateral, but bilateral lesions can also occur.
According to ICD-10 (international classification of diseases, 10th revision), this pathology is assigned the code M70.6.
Causes of trochanteritis and its types
Trochanteritis mainly affects women, since men initially have tendons that are stronger and more resilient, designed to withstand various types of stress. The peak of pathology is observed during menopause, which is associated with the development of osteoporosis, weakening of ligament tension, and a decrease in their elasticity against the background of a deficiency of estrogen hormones. But the disease cannot be ruled out in younger patients, but this requires prolonged exposure to provoking factors.
As a rule, trochanteritis debuts after severe overload hip joint (long walk, running, carrying heavy objects), symptoms also appear against the background of colds and other infectious diseases. Sometimes inflammation of the trochanter begins after an injury in the hip area (even a minor one). Very often, patients note that hip pain appeared after they suddenly gained weight, so excess body weight is also a predisposing circumstance.

With every extra kilogram, the chance of developing trochanteritis increases
Risk factors for developing trochanteritis:
- being female;
- age (the older a person is, the more likely he is to get sick);
- system ;
- metabolic and endocrine diseases;
- excess body weight;
- deforming osteoarthritis;
- too active or, conversely, passive lifestyle;
- previous injuries in the hip area;
- frequent infectious diseases, foci of chronic infection in the body;
- tuberculosis (active or in history).
Types of trochanteritis:
- A septic, or non-infectious. The most common variant of the pathology, which is based on inflammation due to overload of the tendons that are attached to the trochanter.
- Septic or infectious. Occurs when pathological microorganisms (bacteria, viruses) penetrate into soft periarticular tissue. The infection can get here through the blood during general infectious diseases from chronic foci of infection.
- Tuberculous. This is a rare form of pathology. It is a separate variant of tuberculosis infection. In this case, not only the greater trochanter and soft periarticular tissues are affected, but also other parts of the bone with the development of osteomyelitis. This is a serious disease that is difficult to treat. Occurs mainly in children.
Symptoms of trochanteritis
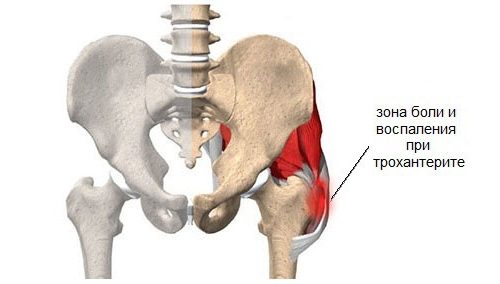
Most often, patients with trochanteritis tell the doctor about a symptom such as pain. It occurs in the area of the greater trochanter, which can be easily felt under the skin. The pain intensifies with pressure on this area and with active movements. At rest painful sensations pass.
The pain spreads along the outer side of the thigh (in the riding breeches area). But if the process becomes chronic and there is no treatment, the pain becomes very intense and bothers the person even at night, preventing him from falling asleep. You can also note the characteristic symptom of increased pain when positioned on the painful side.
Important to remember! Unlike arthrosis of the hip joint, with trochanteritis there is no restriction of movement in the hip. Due to pain, the patient can spare the affected limb, but passive movements are not limited. This can be easily checked by a doctor during an examination.
If the described clinical picture is accompanied by elevated temperature, swelling on the outside of the thigh, redness of the skin in this area, then septic or tuberculous trochanteritis should be suspected.
Pain in the hip area is the main symptom of trochanteritis
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of trochanteritis is purely clinical, since there are no specific diagnostic methods. Main clinical criteria of pathology:
- pain in the hip when lying on the side;
- pain in the riding breeches area when you press some points in this area with your finger;
- preserved mobility in the hip joint.
Other additional research carried out in order to exclude similar diseases, primarily coxarthrosis.
Diagnostic program:
- General analysis blood and urine biochemical research, rheumatic tests.
- Ultrasound of joints and soft tissues.
- In severe cases, CT or MRI is performed.
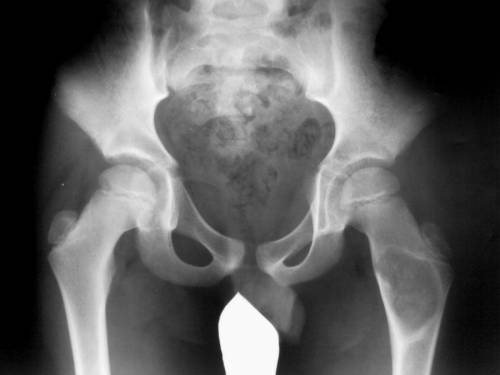
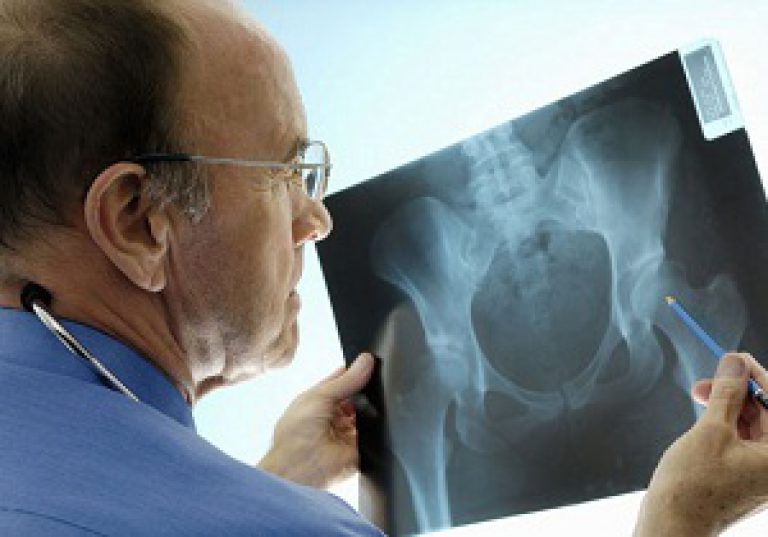
X-ray of the hip joints allows to distinguish trochanteritis from coxarthrosis
Treatment of trochanteritis
Trochanteritis should be treated in accordance with its etiology. First of all, it is necessary to exclude the infectious nature of the inflammation, since in this case the therapy is specific. It differs from the treatment of the aseptic form of the disease. Patients are prescribed antibacterial, and in the case of tuberculosis, anti-tuberculosis therapy.
As a rule, with adequately selected medications drug treatment enough. But sometimes complications develop in the form of suppuration, the formation of abscesses and cold leaks in the thigh area. This situation already requires surgical treatment. All ulcers are opened and sanitized.
Most often you have to deal with aseptic trochanteritis, in the treatment of which several methods are used.
Mode
Perhaps this is one of the main principles of successful therapy. The diseased limb needs to be given complete functional rest. Otherwise, stress will only increase inflammation and pain.
Drug therapy
To eliminate inflammatory changes and pain syndrome medications from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used. They are prescribed in injections, tablets, and also in the form of ointments or gels for external use. Most often they resort to the use of drugs such as diclofenac, ibuprofen, aceclofenac, meloxicam, ketorolac, indomethacin, celecoxib. As a rule, 7-10 days of regular administration of these medications are sufficient to eliminate pain.
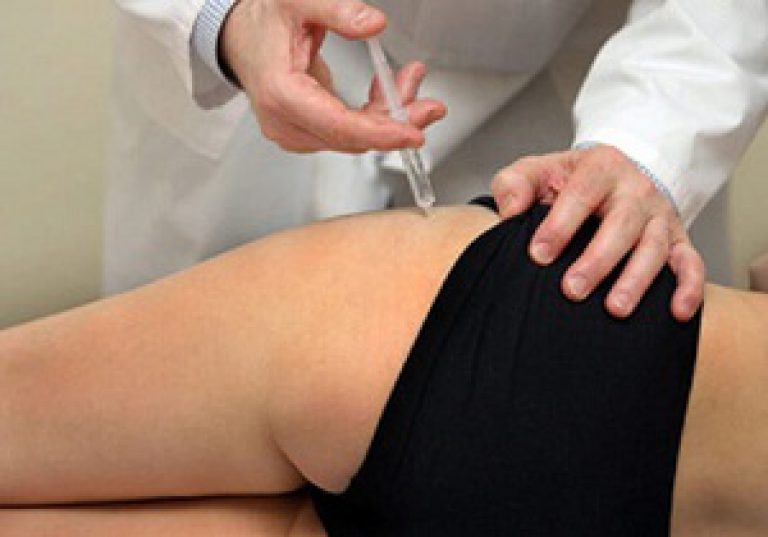
In severe cases, when the pain cannot be eliminated with medications from the NSAID group, they resort to local administration of glucocorticoids periarticularly (into the soft periarticular tissues). This procedure is called a blockade. Long-acting corticosteroids are used for this, for example, Kenalog. Local anesthetics (lidocaine, novocaine) are also added to such injections. As a rule, 1-3 such procedures are necessary to eliminate pain.
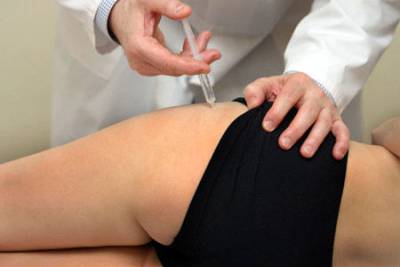
Hip block is effective and quick way eliminate pain
Physiotherapeutic treatment
Among the physiotherapeutic procedures that are particularly effective for the treatment of trochanteritis are:
- laser therapy,
- shock wave therapy,
- paraffin thermal applications,
- magnetotherapy,
- phonophoresis with hydrocortisone,
- electrophoresis.
This is a special therapeutic technique that is designed specifically for the treatment of tendon and muscle pathology. Postisometric relaxation consists of interaction between a doctor and a patient, during which passive stretching of the necessary ligaments or muscles occurs by giving certain positions to parts of the sick person’s body.
As a rule, in 90% of cases, to treat trochanteritis you need to take a course of 8-10 sessions (20 minutes each) every other day. And this may be enough for healing. The only negative is the waste of time, so patients rarely resort to this treatment method, and it is absolutely in vain.
Post-isometric relaxation session
Physiotherapy
Gymnastics for trochanteritis is mandatory, but after elimination acute pain. Physical exercise are able to strengthen the thigh muscles, activate blood flow in this area, which promotes a speedy recovery. It is only important to remember that you should not perform movements that lead to the progression of damage to the diseased tendon. The exercise therapy complex should be gentle.
Traditional treatment
Home folk remedies will help reduce pain from inflammation of the greater trochanter, but, unfortunately, they do not affect the cause of the disease. Therefore you should not use folk recipes as primary treatment, they can only be used as an adjunct to primary therapy.
Thus, trochanteritis is a fairly common, but often undiagnosed disease, which leads to the pathology becoming chronic and the development of constant pain in the hip. Often people perceive symptoms such as arthrosis and do not seek help, believing that nothing can be done. This is a very big mistake, since in half of the cases the cause of this pain is inflammation of the greater trochanter of the femur, which responds very well to treatment.
As a result of excessive loads on the hip tendon, the latter are stretched and torn. Particularly susceptible to injury are the areas of tendon fibers that directly connect the bone and the tendon itself.
“Notches” appear on the fibers, swelling, inflammation and the process of destruction begins.
Inflammation will make itself felt by pain
Trochanteritis forms in the area of attachment of the gluteal muscles to the synovial bursa of the greater trochanter of the femur. This pathological process can also affect nearby muscles and ligaments in either one or both hip joints at the same time.
Typically, inflammation of the femoral tendons, or trochanteritis, occurs after severe strain on the legs.
Sources may include:
- long run/walk;
- carrying weight;
- non-compliance with the regime during a cold or hypothermia.
Sometimes the disease occurs as a complication after the flu. Excess weight and injury, in turn, are also risk factors.
Trochanteritis of the hip joint occurs under the influence of infectious and non-infectious agents.
Infectious/septic form of the disease characterized by the presence of pathogenic microorganisms: mainly staphylococcus, less often streptococcus, E. coli. Usually, this is an exacerbation of osteomyelitis of the femur or sepsis. Accompanied by high temperature, fever, suppuration and destruction of bone tissue.
Non-infectious/aseptic form of the disease. With it, pathogenic microorganisms do not affect the development of the disease.
The non-infectious form of the disease is accompanied by inflammation of the trochanteric bursa
The culprits are: injuries, hypothermia, anatomical features skeleton, increased physical activity. Accompanied.
The tuberculosis form of the disease is caused by the penetration of the tuberculosis pathogen into the tissues of the greater trochanter and is a type of bone tuberculosis. Quite often observed in children.
For choosing treatment tactics it is important determine the localization of inflammation in the greater trochanter area: bone is affected or soft fabrics.
Who is at risk?
Taking into account the specifics of the development of the disease, a group of people prone to its development is identified:
- Patients with pulmonary tuberculosis (there is a risk of developing tuberculous trochanteritis);
- Persons who have foci of chronic infection, especially against the background of weak immunity. Septic trochanteritis can develop as a consequence of sinusitis, tonsillitis, and dental diseases. The likelihood of development increases against the background of traumatic microdamages to foci of infection;
- Women over 35 years old. Due to hormonal changes, tendons and ligaments of the limbs weaken, metabolism is disrupted, including metabolism in bones/ligaments/joints;
- Patients with rheumatic diseases that provoke disruption of the natural structure of bone tissue.
This becomes the impetus for the development of its defectiveness under everyday stress.
Diseases include – osteoporosis, rheumatoid arthritis;
- Pregnant women and people who have gained a fair amount of weight in a short period of time. Weight gain increases the load on the hip joints;
- Imbalance physical activity: from excess loads to a sedentary lifestyle;
- Persons who have suffered trauma;
- Persons exposed to hypothermia during vigorous physical activity.
Symptoms
The prognosis is preliminarily made based on pain attacks (pulsating or aching) in the patient according to outer surface hips. Often intense pain disturbs during movements, but subsides somewhat at rest. In more advanced cases, increased pain also occurs at night - from the pressure of body weight on the inflamed tendons when lying on one's side.
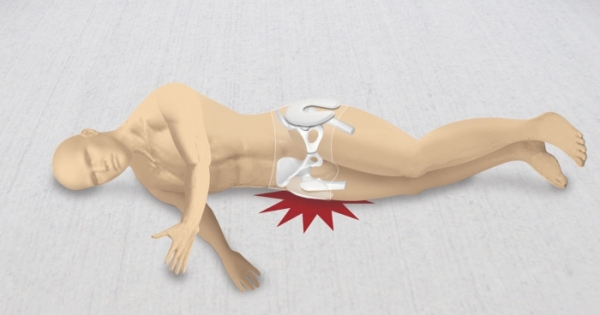
Pain may occur at night due to pressure on the joint
With inflamed tendons on both legs, bilateral trochanteritis is diagnosed.
Manifestations of trochanteritis:
- Aching or throbbing intense pain with preserved joint mobility. Often appears during hip flexion/extension/abduction;
- The occurrence of pain in the foot of an unhealthy leg;
- Repeated point pain in the lateral area of the hip joint, especially after prolonged intense exercise;
- In the presence of high temperature, swelling and redness of the hip joint area - there is a high probability of developing a septic or tuberculous type of trochanteritis.
How to detect symptoms of inflammation of the femoral tendons, or trochanteritis?
When conducting an examination, specialists pay increased attention to examining the patient. A general blood test, an X-ray of the hip joint, and rheumatic tests help exclude other diseases with similar symptoms. Ultrasound, MRI, X-ray data can confirm/refute the diagnosis.
X-ray will confirm the diagnosis
About everyone modern methods Diagnosis of joint diseases read
Before visiting a doctor, you have the opportunity to independently diagnose the disease. If, while lying on the sore side or when palpating (pressing) the area of the hip joint, you feel increased pain, you should consult a specialist. A qualified doctor will recheck the symptoms of trochanteritis and prescribe treatment.
How to treat trochanteritis of the hip joint?
Treatment options for the disease depend on the type of trochanteritis. For the tuberculosis form of the disease, anti-tuberculosis medications are prescribed, and if necessary, the abscess is punctured and the affected tissue of the isolated tuberculosis focus is removed.
Therapy for septic trochanteritis is based on the use of impressive doses of antibiotics. In some cases it is recommended surgical intervention in order to eliminate part/all of the femoral trochanter.
Treatment of aseptic trochanteritis is aimed at eliminating inflammation and fully restoring the functions of the joint.
Conservative treatment in this case includes:
- Providing rest to the affected limb is the most important condition of the treatment process;
- The use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications - capsules, powders, tablets, and in some cases injections;
- Local application, which includes anti-inflammatory agents;
- Performing blockades - administering glucocorticoids in combination with local anesthetics directly into the site of inflammation;
- – electrophoresis, ultrasound, magnetic therapy, shock wave therapy, paraffin compresses, laser therapy;
To learn how to carry out the shock wave therapy procedure for trochanteritis of the hip joint, watch the video:
- For inflammation of the femoral tendons - trochanteritis - treatment is supplemented with exercise therapy. The mission of this component of the treatment process is to support the muscle tone of the leg and optimize blood circulation against the background of a weakened regime.
Treatment of trochanteritis of the hip joint with folk remedies
An integrated approach successfully helps to get rid of most diseases. Inflammation of the femoral tendons is no exception.
Good reviews for the treatment of trochanteritis of the hip joint folk remedies received tinctures and ointments from wormwood, chamomile and sage, calendula.
In order to prevent the question “how to cure trochanteritis?”, we advise you to take preventive measures:
- avoid the same type of actions with emphasis on the thigh;
- control your weight;
- keep your thigh muscles flexible, firm and strong.
Trochanteritis of the hip joint is a pathology in which destructive processes occur in the tendon bursa of the gluteal muscle. The affected area is the junction with the lesser and greater trochanter (or trochanter) of the femur.
Acute and subacute forms of the disease require timely treatment. In the absence of competent measures, the use of ineffective homemade compounds instead of potent drugs, complications are possible, functional disorders in the hip joint. Trochanteritis can seriously complicate life.
general information

Types of trochanteritis:
- tuberculous– develops as a complication of a severe infectious disease;
- aseptic– the cause is heavy loads, injuries, lack of physical activity, age 50 years or more, inflammatory process practically absent;
- septic– occurs after the penetration of pathogenic bacteria and viruses. Tests often reveal staphylococcal infections and influenza strains. Sometimes the septic form develops against the background of osteomyelitis and sepsis.
Causes
Tendon damage most often occurs under the influence of several negative factors. Doctors have established clinically proven causes of tendon problems.
Learn more about the signs, symptoms and treatments for shoulder pain.
Methods for treating psoriatic arthritis with folk remedies at home are described on the page.
Main factors:
- excessive stress on the joints for a long time. The main category of patients suffering from trochanteritis of the hip joint are professional athletes, more often track and field athletes;
- overweight. With a high degree of obesity, the joints suffer more often than other parts of the body from unbearable loads;
- osteochondrosis lumbar region spine. Negative processes cause injury to the tendons due to their stretching, increased tone of the gluteal muscles;
- frequent injuries to the hip joint. The main factor is not the severity, but the repetition of bruises and habitual hip dislocations over a long period;
- female, age over 40 years. Problems in the hip joint arise when hormonal levels fluctuate;
- penetration into the body of acute viral infections. The influenza virus often affects not only the respiratory organs, nasopharynx, but also joints.
Important! Trochanteritis in the hip area often occurs with a combination of several negative factors. The more reasons for tendon damage, the more severe the degree of pathology.
Signs and symptoms

Characteristic symptoms occur when the composition and volume of synovial fluid changes. A sufficient level of lubrication prevents excessive friction of the articular heads and maintains the elasticity of cartilage. Any changes in one direction or another negatively affect the condition of the joint elements. Inflammation and swelling disrupt the functioning of the affected joint, causing pain.
The first signs appear after two to three days or later, after 10–15 days. The initial period of the disease depends on the factors that activated negative changes in the tendons.
Subacute form
The main reason is the penetration of infection in combination with hypothermia. Trochanteritis often develops against the background of influenza.
Characteristic features:
- clinical symptoms appear gradually;
- joint pain does not occur immediately (after a week, 10 days or more);
- discomfort is mild, pain increases with palpation of the affected area, pressing on the hip joint;
- at night the patient suffers from pain, it is difficult to sleep on the affected side, he often has a fever and breaks out in a cold sweat;
- The motor function of the joint is almost completely preserved; pain slightly interferes with walking, going up and down stairs.
In the subacute stage of trochanteritis, treatment is protracted, NSAIDs, home remedies, and modern physiotherapy are required. Many patients use cabbage compresses or raw potatoes to reduce inflammation. The method is good, but without drugs that suppress the activity of the virus or pathogenic bacteria, the disease becomes chronic and complications develop.
Acute stage
Negative changes occur against the background of injuries, excessive loads on the joint when performing heavy work. Sometimes painful sensations in the hip joint appear during long hiking trips with ascents and descents.

Characteristic features:
- the picture is brighter than in the subacute form, the disease develops rapidly: clinical manifestations are noticeable already on the second or third day;
- the peak of pain occurs on the first day;
- discomfort is clearly visible, pain torments the patient constantly;
- touching the bony protrusion between the thigh and buttock causes severe pain, the affected area swells, and the local temperature rises;
- burning, sharp pains spread down the thigh;
- in the acute form of trochanteritis, fever develops and health worsens.
Timely consultation with a doctor can cure the disease in less than a week. An integrated approach is required, a combination of medications, physiotherapy and folk methods. In mild cases, resting the problem area helps. dry heat, taking general health-improving medications, herbal infusions and teas for joint health. After injuries, unilateral trochanteritis often develops; when synovial fluid becomes infected, bilateral tendon damage occurs.
Diagnostics
In addition to a visual examination, conversation with the patient, finding out clinical picture, the doctor performs a special limb abduction test in a lying position. The idea of the development of trochanteritis is suggested by pain in the area of the greater trochanter.
The following studies will help clarify the diagnosis:
- radiography to determine lesions in the lesser and greater trochanter;
- ultrasound, magnetic resonance and CT scan allow us to examine inflammation in the tendon bursa.
Important! Treatment of diseases of the musculoskeletal system is carried out by a rheumatologist, orthopedist and arthrologist. In case of hormonal imbalances in women, you will need to consult a gynecologist and endocrinologist.
Effective treatments
The success of therapy depends on compliance with the following rules:
- rest for the affected limb;
- application of physiotherapeutic methods;
- drug treatment;
- special exercises after relieving acute pain.
Medications
Compositions for external and internal use:
- specific antibiotics for the treatment of tuberculosis. Long-term therapy, from 6 months or more, is carried out under the supervision of a TB doctor. The patient is treated on an outpatient basis or in a hospital, depending on the severity of the disease, the results of bacterial culture (“closed” or “open” form);
- glucocorticosteroids in the form of intra-articular injections (for severe cases), non-steroidal anti-inflammatory compounds for local and oral use (for mild and moderate forms of septic trochanteritis);
- compositions for external use that alleviate the condition of the affected area. Dikul balm and Alezan ointment are effective;
- antibiotics or antiviral drugs depending on the type of pathogen in the septic form articular pathology. For aseptic trochanteritis, antibacterial compounds are not recommended;
- general strengthening agents, vitamin and mineral complexes to strengthen the immune system.
Find out about characteristic symptoms and treatment options for grade 3 hip joint.
ABOUT beneficial properties and the use of Shark oil preparations for the treatment of joints is written on the page.
Go to the address and read about what to do if you sprain your ankle.
Physiotherapy procedures
The following methods have been proven effective:
- shock wave therapy;
- ultrasound;
- electrophoresis with drugs.
Folk remedies and recipes
In addition to modern physical treatments and drug therapy, many patients use home remedies. Most often, patients take herbal decoctions, make compresses, and rub the problem area. Homemade formulations are made from natural ingredients, but caution is required when choosing products.
For example, in case of acute inflammation, you should not heat the hip area, take hot baths, or apply dry heat. With this method of “treatment,” septic trochanteritis will rapidly progress, and the infectious agent will invade new areas.
Popular folk recipes:
- cabbage leaf compress. Many herbalists advise chopping the leaf to actively release the juice, then lubricate it with thin honey and apply it to the affected area;
- anti-inflammatory collection for oral administration. Herbs for preparing a healing decoction: calendula, chamomile, mint, sage (a teaspoon). To prepare tea you will need 1 liter of boiling water. Every day you need to take 100 ml of the mixture in the morning, before lunch and in the evening. The components have a positive effect on the joints and the entire body;
- compress of grated raw potatoes. Keep the mixture on the inflamed area for 45 minutes under a clean cloth. A daily procedure relieves swelling, relieves pain, reduces inflammation;
- alcohol tincture with herbs. Medicinal herbs improve the condition of a sore joint: wormwood, chamomile, sage, calendula. For 500 ml of vodka, it is enough to take a teaspoon of natural raw materials. After a week, the rubbing is ready.
Treatment of acute and subacute form trochanteritis in the hip joint area is successfully treated in most cases. Inattention to the problem worsens the prognosis: in advanced cases, the patient is practically unable to use the affected leg, and surgical intervention is required. Timely contact with an experienced arthrologist, rheumatologist or orthopedist will reduce the risk of complications.
A set of therapeutic gymnastics exercises for treating the hip joint can be seen in the following video:
Attention! Only today!
Often pain in the hip area are caused by inflammation or damage to the hip tendons. This inflammation, caused by overload or injury to the femoral tendons, is called trochanteritis: literally “inflammation of the trochanter” (trochanter is the place where the femoral tendon connects to the femur). Another name for the disease is peritrochanteritis, i.e. “inflammation near the trochanter.”
Are sick trochanteritis most often women over 30 years of age (men get sick less often because their tendons are stronger to begin with). Moreover, the peak incidence in women occurs during menopausal changes in the body, when the tendon and muscle tissue. Although there are cases when very young women get sick with trochanteritis, for this, as a rule, several unfavorable moments must arise at once.
Usually trochanteritis begins after a significant overload of the legs - after an unusual long walk, running or carrying heavy objects. Especially if such overload is combined with a cold or hypothermia. Rarely, the hip tendons become inflamed after the flu. Sometimes the disease is triggered by injury (a blow or a fall on the side). In addition, many patients noted that shortly before the illness they had gained a lot of weight, and because of this, the load on their legs had clearly increased. So excess weight, quite obviously, can also be considered a risk factor for the development of trochanteritis.
Trochanteritis can be either unilateral, when only one leg becomes ill, or bilateral, when the tendons on both legs become inflamed. Trochanteritis manifests itself as attacks of pain on the outer surface of the thigh (in the “breeches” area). Pain most often bothers the patient when moving, walking; then the pain can be quite intense. At night, with rest, the pain usually subsides.
However, in advanced cases, quite strong night pain when lying on one's side- pain occurs from the pressure of body weight on the inflamed tendons. Occasionally, the “classic” hip pain for trochanteritis can be projected into the groin area, confusing doctors and leading them to think about arthrosis of the hip joint.
In general, it should be noted that at least half of the patients with trochanteritis who come to me come with a previous diagnosis of “arthrosis of the hip joint.” When during an examination it turns out that they do not have coxarthrosis, such sick people cannot believe their happiness for a long time. Usually, as a counter-argument, they begin to show me their x-rays, where, as these people say, the doctors saw manifestations of arthrosis of the hip joint. I have to patiently explain over and over again that X-rays also need to be able to be read or deciphered. And the mistake is most often due to the fact that normal age-related changes are mistaken for coxarthrosis.
Meanwhile, even without X-ray data, making a diagnosis of trochanteritis can be quite simple. The doctor just needs to properly examine the patient: firstly, trochanteritis has characteristic pain points when pressed. And secondly, with trochanteritis There is practically no restriction of movement in the hip joint, i.e., unlike arthrosis of the hip joint (coxarthrosis), the leg rotates freely in all directions. This is especially true for passive movements.
To put it more clearly, the patient himself (due to pain) is unlikely to be able to freely move and rotate the affected leg. But if I ask a sick person to completely relax, after which I begin to rotate the patient’s leg in different directions, the movement in the joint will be completely free. And the pain will begin to arise only when I use the diseased tendon during movement. Usually, after the first such examination of a patient suffering from trochanteritis, the diagnosis becomes 90% clear, and all that remains is to confirm it with the help of diagnostic examinations.
A disease associated with inflammation of the greater trochanter (trochanter) of the femur along with the adjacent tendons, bursa and ligaments is called trochanteritis. It is necessary to analyze in more detail what the essence of this pathology is, the causes of development, symptoms, which doctor to turn to for help and the main methods of treatment.
The essence of the disease and the causes of development
It is necessary to consider the essence of trochateritis by defining the concept of what the greater trochanter is and what role it plays in the human body.
The junction of the muscular tendons of the pelvis and thigh, ligaments and bursa in the upper outer part of the femur is considered to be the greater trochanter (trochanter). Tendons and ligaments are involved in the motor activity of the hip joint. The synovial bursa (bursa), which is a fluid layer, is designed to soften their movements.
In these bone structures due to various reasons An inflammatory process may occur, which subsequently easily spreads to the bursa, tendons and ligaments. Another name for the disease is trochanteric bursitis. Based on medical practice, trochanteritis at the site of localization is rarely bilateral. Usually one of the joints becomes inflamed.
Depending on the reasons that triggered the inflammatory process, there are 3 forms of pathology:
- aseptic;
- septic;
- tuberculosis.
The most often diagnosed is aseptic trochanteritis - a form of the disease that is not associated with the activity of pathogenic microorganisms. The reasons for its occurrence should be considered:
- injuries in the hip area;
- excessive overload of the hip joint due to heavy lifting and sports;
- excess weight;
- climacteric period of body restructuring in older women;
- systematic hypothermia;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- concomitant rheumatic pathologies, etc.
Usually, for the occurrence and development of the disease, a combination of several of these unfavorable factors is necessary.
The other two forms of pathology are based on an infectious component.
Septic (infectious) trochanteritis is formed due to the penetration of a generalized infection of various origins through the blood into the periarticular tissues. Staphylococcal infection is detected more often than others.
The cause of the pathology of the tuberculosis form is a specific infectious agent - Koch's bacillus. The infectious process involves not only the greater trochanter and the soft tissue adjacent to it, but also other structures of the femur. This form of the disease most often affects children.
Symptoms
To determine trochanteritis of the hip joint, the symptoms and treatment of which should be considered in more detail, you need to consult a specialist.
Trochanteritis in its course is:
- spicy;
- chronic.
The chronic form of the disease has smoother and more diffuse symptoms.
The main sign of the pathology is pain in the hip joint, which in the acute course of the disease intensifies sharply with any movement or when pressing on the area of inflammation. At rest, pain stops. It is worth noting that despite the pain, there are no restrictions in movement with this disease.
At chronic form trochanteritis, excruciating pain begins to disturb the patient even in a motionless state, preventing him from falling asleep at night.
Inflammation of the femoral tendons of infectious origin can manifest itself with the following symptoms:

- pain, swelling and redness in the area of the left or right hip joint;
- high body temperature.
It is important to detect this disease in a timely manner and carry out proper treatment in order to prevent it from becoming a protracted, chronic form in the future.
Diagnosis and general treatment regimen
To make a correct diagnosis, it is necessary to carry out a series of diagnostic measures. It is necessary to distinguish between this disease and pathologies with similar symptoms. No photo can convey features diseases, instrumental and laboratory confirmation is required. The diagnosis and treatment of trochanteritis is determined by an orthopedic traumatologist.
Diagnosis of this pathology includes:
- patient complaints;
- thorough visual inspection;
- pressing on the sore spot;
- testing hip mobility;
- Ultrasound of soft tissues;
- X-ray of the hip area;
- MRI or CT;
- general and biochemical laboratory research urine and blood tests, rheumatic tests.
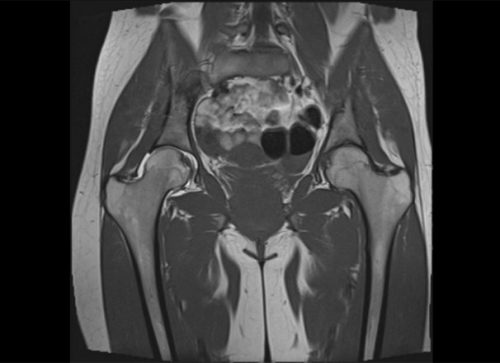
How to treat trochanteritis, after making an accurate diagnosis and determining its etiology, the specialist decides individually for each patient.
Almost always, the treatment of this pathology is conservative. Timely identified, uncomplicated trochanteritis can be completely cured with proper therapy.
For this pathology, the following treatment methods can be used:
![]()
- drug therapy;
- physiotherapeutic measures;
- post-isometric relaxation;
- physiotherapy;
- use of traditional medicine;
- surgical intervention.
Each treatment method for trochanteritis should be considered separately.
Drug therapy
The basis of drug therapy for the aseptic form of the disease is to eliminate pain and relieve inflammatory reactions in the affected hip joint using NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs). They can be prescribed for internal use - in tablets, capsules, injections, for external use - in gels and ointments.
Such drugs as Ibuprofen, Meloxicam, Diclofenac, Ketorolac, etc. have shown their effectiveness in the treatment of trochanteritis. Positive reviews obtained from the use of modern medicines for external use: Diclak gel, Dolobene, etc. The course of treatment with these drugs is 7–10 days.
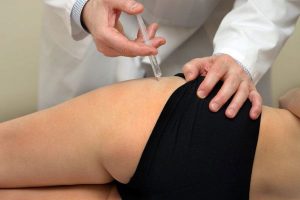 For some patients with severe disease, a medicinal periarticular blockade is used, during which long-acting glucocorticoids are injected into the soft tissues around the affected area of the hip joint: Kenalog, Diprospan, Loracort, Hydrocortisone, etc. According to indications, anesthetic drugs can be added to the injections: Novocaine, Lidocaine. The pain syndrome is eliminated after 1–3 of these procedures.
For some patients with severe disease, a medicinal periarticular blockade is used, during which long-acting glucocorticoids are injected into the soft tissues around the affected area of the hip joint: Kenalog, Diprospan, Loracort, Hydrocortisone, etc. According to indications, anesthetic drugs can be added to the injections: Novocaine, Lidocaine. The pain syndrome is eliminated after 1–3 of these procedures.
If the disease is infectious, antibacterial or antituberculosis therapy is carried out. Drugs are selected on the recommendation of the attending physician on an individual basis.
To strengthen the bone-tendon system during therapy, calcium preparations are often prescribed - Calcium D3, Calcemin.
Other methods of complex treatment
An effective method of treating trochanteritis in the composition complex therapy is considered to be a course of physiotherapeutic procedures. These include:
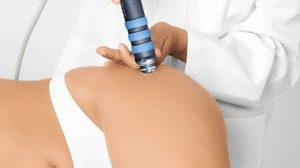
- laser therapy;
- electrophoresis;
- magnetic therapy;
- paraffin thermal applications on the hip joint area;
- phonophoresis with the use of drugs.
A modern method of combating pathologies of muscles and tendons is post-isometric relaxation. Its essence is the passive stretching of certain muscle groups and ligaments by giving parts of the patient’s body the required poses. It is recommended to complete 10 sessions of 20 minutes each.
A significant improvement in blood supply to the damaged area of the hip joint and strengthening of the tendons can be achieved with properly selected therapeutic exercises, massage, manual therapy. Exercise therapy is carried out after pain has been eliminated at home or in a special room. All movements must be performed smoothly, without jerking.

Treatment with folk remedies is used as an addition to the main therapy. It cannot eliminate the cause of the disease, but it effectively reduces the inflammatory process of the damaged area and relieves pain. For external use, alcohol tinctures from medicinal herbs- cinquefoil, chamomile, sage, wormwood, etc.
The attending physician must approve the specified treatment.
In advanced forms of trochanteritis, surgical intervention may be required. Indications for surgery are various suppurations in the area of the greater trochanter of the hip joint. During surgical procedures, the abscesses are opened and washed with antiseptic solutions. The wound is drained until it is completely cleared of purulent formations.
Thus, timely detection of trochanteritis - inflammation of the greater trochanter of the hip area and competent selection of complex therapy will lead to complete healing of the patient.



