Antipyretics for children are prescribed by a pediatrician. But there are emergency situations for fever when the child needs to be given medicine immediately. Then the parents take responsibility and use antipyretic drugs. What is allowed to give to infants? How can you bring down the temperature in older children? What medicines are the safest?
X-ray diagnostics is a research method that helps to identify many pathologies. The modern version of such studies is called MSCT. abdominal cavity. This type of diagnosis belongs to the variety computed tomography performed using the latest generation of machines that allow you to make thinner "cuts".
MSCT has another name - doctors call it spiral computed tomography, or multilayer X-ray tomography. Unlike a standard CT scanner, the helical tomograph is equipped with several rows of emitters and detectors that pick up the signal. These design features allow:
- shorten the duration diagnostic procedure;
- get a clearer picture;
- reduce radiation exposure to the body;
- get an image of the whole organ in one rotation (additional “rolling” is not needed);
- fix the processes occurring in the organs;
- reduce the number of defects in the images as a result of the natural movements of organs.
Such tomographs differ from the MRI unit by the type of radiation and the technologies used:
- when examining MRI, a magnetic field is used, while CT and MSCT involve the use of x-rays;
- magnetic resonance imaging better shows the structure and structure of soft tissues and organs, and CT is used when it is necessary to examine bone structures and tissues with high density in detail;
- the MRI procedure is not always suitable for examining the intestines and other hollow organs, while a CT or MSCT study using contrast solutions reveals the slightest changes in the intestinal mucosa and internal cavities of organs.
Before referring a patient to an abdominal examination with contrast, the doctor weighs all the points - indications and contraindications, the patient's current condition, indications of previous examinations - and then chooses which is better: standard or contrast MRI, computed tomography or more advanced multilayer tomography with contrast.
The use of a multislice tomograph in the diagnosis of pathologies of the abdominal organs and retroperitoneal space allows you to create flat images of organs and structures located in the study area, as well as simulate a 3D image of the abdominal organs (ABP).
What does MSCT OBP show
With the help of MSCT of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space, the doctor examines the organs and structures located in this area. Unlike computer scanning, this diagnostic method is used when it is necessary to examine hollow organs. If there are symptoms that indicate violations, the use of a contrast solution is indicated (most often it is Trazograph with triiodide or a barium solution).
An examination by MSCT with contrasting establishes the position (including mutual), condition, structure of the organs located in the abdomen. Diagnostics reveals:
- dysfunction of the OBP;
- pathological changes (inflammation, necrotic processes and infectious foci);
- trauma;
- tumor processes, including at stage 1.
It is important to understand what MSCT shows as a black-and-white image that only a radiologist can read.
When is MSCT prescribed?
Assign MSCT of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space in the case when other diagnostic methods cannot give clear unambiguous results. Direct indications for diagnostics on a spiral tomograph are:
- jaundice, especially asymptomatic;
- sudden weight loss for no apparent reason;
- chronic digestive disorders;
- chronic forms of dysfunctions of the intestines, stomach and other organs;
- acute injuries of the anterior abdominal wall and penetrating wounds of the abdominal cavity.
Also, MSCT is used for patients who are preparing for surgery on the abdominal organs or undergoing a complex course of therapy that requires control of even minimal changes.
Contraindications to MSCT
Radiologists say that such a study as MSCT is much safer than conventional computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. The only significant limitation to the procedure is pregnancy. Lactating women, if necessary, are advised to temporarily interrupt breastfeeding.
The list of relative contraindications for MSCT includes:
- intolerance to the drug Trazograph or its analogues, as well as barium;
- children's age (up to 14 years MSCT is performed in case of urgent need);
- kidney failure, in which barium or the contrast agent Trazograph will be excreted from the body too slowly;
- a severe form of diabetes mellitus (with this disease, the contrast solution Trazograph cannot be used);
- the presence of metal elements in the patient's abdomen that can distort the result.
Do not perform MSCT and obese patients weighing more than 130 kg, as the installation is not able to accommodate large patients.
Important! In the presence of relative and strict contraindications, MSCT is replaced by MRI, X-ray or ultrasound examination.
Preparation for the procedure
8 hours before the diagnosis on a spiral tomograph, the patient is advised to refuse food. Also, preparation for a study using contrast agents requires a short-term diet. A day before the start of the procedure, it is advisable to exclude from the menu products that cause increased gas formation:
- carbonated drinks and alcohol;
- legumes;
- pastry and bread;
- apples;
- dairy products;
- cabbage.
It is important to remember that it is better to find out from the doctor in advance about the use of contrast and the method of administration of drugs, since it is possible to prepare for MSCT correctly only if all recommendations are followed.
How is the procedure
The examination procedure does not cause discomfort and pain. The patient is dressed in disposable clothing and placed on the tomograph couch. If it is necessary to check the liver and other internal organs (not hollow), a contrast agent (Trazograph or its analogues) is injected into the vein at the elbow bend. This is done by bolus (using a special pump) or the classic way (with a regular syringe). If it is planned to examine the intestines with the help of contrast, the patient is given a barium solution to drink.
Important! Immediately after the contrast enters the body, the patient may experience nausea, dizziness, or headache. About appearance unpleasant symptoms should be reported to the radiologist.
Next, the scan begins, during which the doctor will be in the next room. This procedure lasts about half an hour. Upon completion, the doctor proceeds to decipher the data, and the patient can change clothes and wait for the result at home.
Diagnostic results
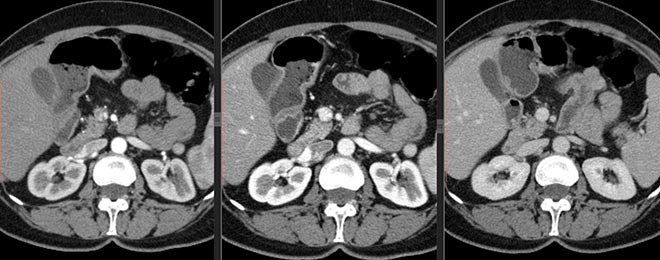
The fight against the disease begins with the diagnosis - the more accurately the diagnosis is established, the better the result of the treatment. If the diagnosis is incorrect, the disease not only cannot be treated, it progresses further or becomes chronic form. Modern spiral computed tomography (SCT) is the latest, extremely popular diagnostic method in medicine.
The essence of diagnostics
The first spiral tomograph appeared in 1988 and became an indispensable assistant for doctors.
This method is based on scanning the body with X-rays, which are converted into electrical signals and then processed by a computer. It allows you to quickly get an accurate result with an unprecedented error of only 1 mm.
During the session in the clinic, the table with the patient moves, but around the patient, as if in a spiral, the X-ray tube with the surface on which the detectors are located additionally rotates.
The device recognizes neoplasms up to 1 mm in size. This is extremely important when oncological diseases for timely detection and elimination of the focus of the disease. One anatomical region is scanned on an outpatient basis within 3-5 minutes. The laser camera takes large-format pictures.
Amazing results can be obtained on modern 64-slice (multi-slice or multislice) high-speed tomographs - fast acquisition of two-dimensional and three-dimensional images of excellent quality at a low level of radiation.
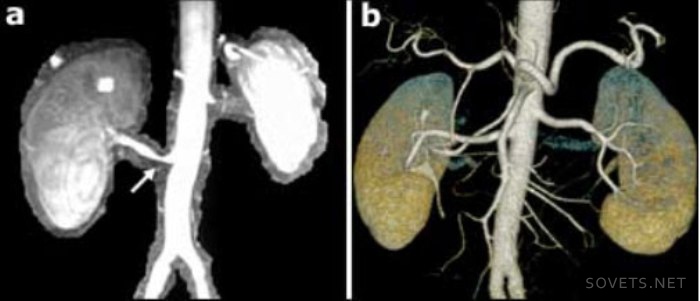
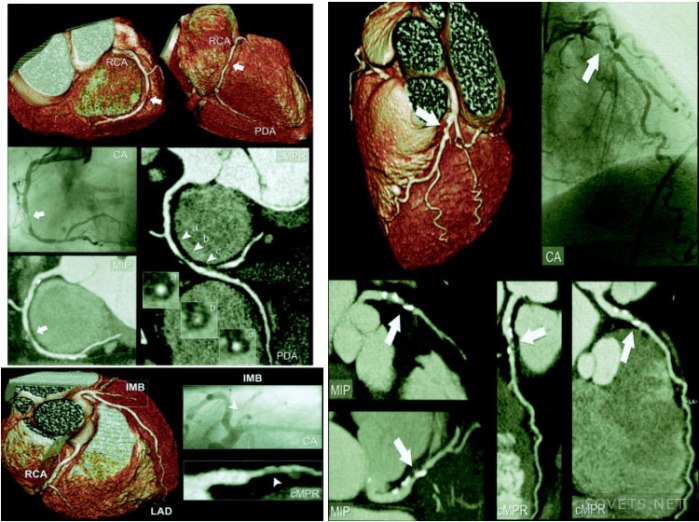
Such an examination is indispensable for injuries, bone fractures and injuries. internal organs, malignant tumors and strokes, when it is necessary to obtain information about the diseased organ in the shortest possible time. This technology replaces many modern methods research, for example ultrasound diagnostics.
The order of the procedure
4 hours before the examination procedure, food and water intake is stopped.
Before examining some organs, the patient must undergo preparation - drink a contrast agent (urografin). Detailed instructions preparation for the procedure will be given by a specialist who will conduct the examination.
Dinner before the procedure is light, for breakfast it is better not to eat solid food, preferably liquid porridge and juice.
The patient lies on a movable table that drives into a special tunnel - a scanning device. For the convenience of the patient, the table is equipped with special pillows and belts, they help to limit his movements during the procedure, so that the photos are clear and not blurry.
Patients who cannot lie still for a long time and briefly hold their breath (children or nervously excited patients), or who are prone to claustrophobia, is administered depressant.
In another office there is a computer station, a doctor-technologist works at it, controlling the scanner using the screen. During the procedure, he talks with the patient and gives the necessary instructions.
The helical computed tomography procedure is quite safe. Although the patient receives a small dose of x-ray radiation, it is so negligible that it does not cause any harm to the body. There is a risk with the introduction of a contrast agent or sedatives. The patient must inform the doctor about the allergic reaction on medicines or iodine, which is part of the dye.
If the subject has diabetes, asthma, kidney failure, heart disease, or thyroid gland, you also need to tell the doctor about this.
Examination is contraindicated for pregnant women. In case of urgent need, it is still carried out, but the uterus is covered with a lead screen. Patients with pacemakers, ferromagnetic implants, patients weighing over 130 kg are also not examined.
Next, the radiologist conducts a thorough analysis of the images.
Advantages of the latest diagnostic method
SCT has a number of differences and advantages over conventional computed tomography:
- High speed of information collection (scanning). In a short period of time (up to 20 seconds), an image of one anatomical region (abdomen, lungs) is formed. The quality of the pictures is very high.
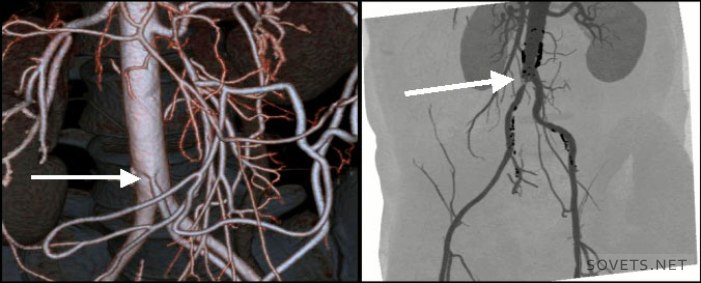
- Obtaining more accurate spatial 3D images. Three-dimensional models more accurately show the nature and location of the pathology. The use of spiral scanning techniques allowed the use of angiography, i.e. examination of the arteries, to identify vascular aneurysms, narrowing, their length.
- Non-invasive compared to ventriculography, myelography.
- The absence of artefacts from blood flow in the picture.
- Reduced x-ray exposure of the patient compared to conventional tomography. Even when examining several anatomical zones at the same time, radiation doses are not summed up.
Spiral computed tomography of the abdomen
The procedure forms a multilayer image of organs (liver, spleen, pancreas, etc.). Indications for its implementation are pain in the abdomen, pelvis, as well as a number of diseases of the small and large intestines, internal organs.
It is used in the diagnosis:
- Appendicitis, pyelonephritis, formed kidney stones and bladder, diverticulitis, abscesses
- pancreatitis, cirrhosis of the liver, inflammatory processes and polyps in the intestines, internal bleeding
- Cancer of the organs located in the abdominal cavity
- Diseases of the vessels and lymph nodes
Before the procedure, the patient must be prepared, a contrast agent is used.
Lung tomography
Before the procedure, an iodine-based contrast agent is injected into the patient's vein. Therefore, if he has an allergy to iodine, it is necessary to inform the doctor. There is no pre-treatment of the patient.
Tomography of the brain
It is widely used in the diagnosis of head injuries in patients in severe and super-severe condition, symptoms of changes in blood circulation in the brain, high intracranial pressure, and various neurological disorders. We see changes in tissue density already in the early stages. The device captures pathology (abscesses, neoplasms, cavities), which can not be seen with a conventional tomograph. The procedure helps prevent and detect diseases such as stroke and heart attack.
The survey is used for:
- Determining the causes of headaches, systematic clouding of consciousness, sudden paralysis, impaired sensitivity of certain parts of the body, various visual disorders. And also if you suspect a brain tumor, intracranial bleeding, rupture of an aortic aneurysm.
- Diagnosis of dysfunction of the inner ear with hearing loss.
- Developing a plan for an upcoming operation or evaluating the success of an already performed brain operation.
- Determination of brain damage and stroke care.
- Ensuring safe access and eliminating the possibility of brain injury during a biopsy.
In some cases, the procedure is carried out with the introduction of a contrast agent intravenously, which facilitates the detection of tumors, cysts, metastases, atherosclerotic plaques, blood clots.
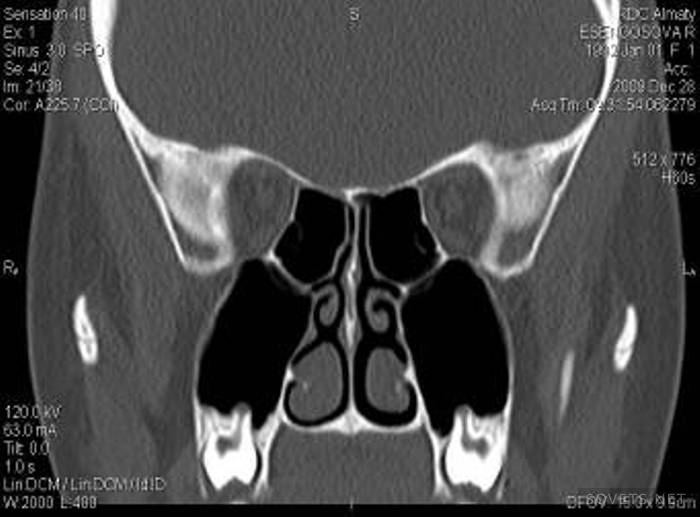
CT scan of the brain does not require pre-training sick.
Tomography of the kidneys
This method of examining the kidneys is used:
- For the timely detection of benign and malignant formations in the kidneys, stones, anomalies in the development of the kidneys, abscesses, polycystosis.
- To diagnose kidney injuries.
- During a kidney biopsy to monitor the correctness of tissue sampling.
- After transplantation or removal of the kidney, to monitor the condition of the operated area.
During the procedure, a contrast agent is used to improve the clarity of the image. The day before the examination, the patient is prepared according to the generally accepted scheme.
Tomography of other organs
SCT of the eyes, facial fragments and sinuses is widely practiced. The device finds violations in the structure of these organs and foreign bodies that have penetrated into them.
SCT of the spine shows cracks, fractures of the spine, infected areas on the spinal canal, abscesses, osteochondrosis, arthritis, osteoporosis, neoplasms and metastases in the spine and other organs, congenital anomalies development of the skeletal system.
In case of injuries of the limbs, injuries of the joints, tomography is prescribed to clarify the diagnosis.
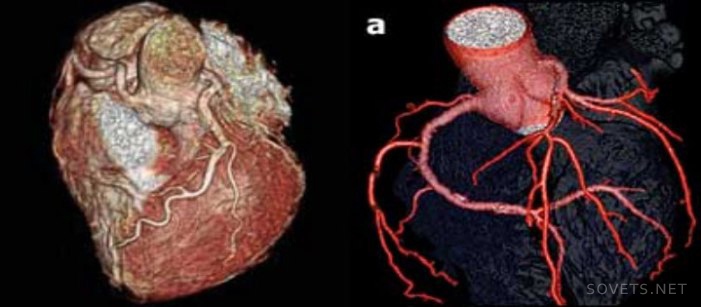
SKT chest detects diseases of the heart, lungs, coronary arteries, esophagus, larynx, large blood vessels. With its help, tuberculosis, aortic aneurysms, tumors are detected. It is not recommended to eat food 4 hours before the procedure. This is what a heart image taken during the examination looks like.
For more information on how and for what purpose a study of the internal organs of a person is carried out on a multispiral tomograph, see the video.
During the course of their lives, many people have to undergo a CT scan. Which one is better - ordinary, spiral, magnetic resonance, share your opinion on this topic in the comments, let's discuss this issue together.
The information presented in the article is for informational purposes only. The materials of the article do not call for self-treatment. Only a qualified doctor can make a diagnosis and give recommendations for treatment based on the individual characteristics of a particular patient.
Advantages of multislice computed tomography (MSCT) as a diagnostic method
Due to the high resolution of the multispiral computed tomography method, the use of scanning algorithms with very thin slices, it is possible to see changes in the size of a few millimeters and identify pathological processes at a minimal stage.
The use of modern X-ray contrast agents during scanning significantly increases the contrast of tissues and allows for differential diagnosis of various formations. Therefore, to obtain the maximum amount of information on the detected pathology, a study with bolus intravenous contrast is usually required.
The ability to use a variety of modern algorithms for post-processing image processing on computed tomographs, which our departments are equipped with, such as MPR, MIP, MIP Thin, SSD, VRT, allows us to obtain highly informative images that provide all the necessary information to the radiologist, as well as the attending physician for correct interpretation results. This, in turn, helps to make the correct diagnosis, and subsequently choose an effective treatment.
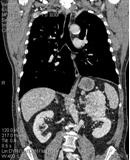
Tissue formation of the retroperitoneal space on the left. The images obtained in the frontal projection make it possible to assess the relationship of the formation with other organs, the growth of the formation in other organs and tissues.
The examination is carried out in our centers equipped with multispiral (16 spiral) computed tomographs of the company SIEMENS characterized by high speed and quality of work.
Multislice computed tomography of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space.
MSCT of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space is a highly informative research method based on layer-by-layer X-ray scanning in axial projection with subsequent spatial reconstruction of the obtained images. MSCT is usually performed with intravenous bolus contrast for a more reliable assessment of the state of organs and tissues, detection pathological changes in them and conducting a possible differential diagnosis of the nature of the identified changes.
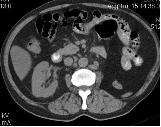
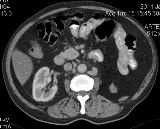
For comparison: axial images of the patient, taken at the same level, on the left without contrast (native), on the right with bolus intravenous contrast.
Abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space is a complex of tissues, organs and systems, including the following structures:
- liver, gallbladder and bile ducts (intrahepatic bile ducts, common hepatic duct, cystic duct, common bile duct);
- pancreas;
- spleen;
- gastrointestinal tract or gastrointestinal tract (stomach, intestines);
- adrenal glands, kidneys, urinary tract;
- The lymph nodes, vascular structures, fiber of the abdominal cavity, tissues of the abdominal walls.
Traditionally, the boundaries of the study area are:
- above - the dome of the diaphragm;
- below - the upper edge of the pelvic bones (wings of the ilium).
The retroperitoneal space includes the kidneys, adrenal glands and lymph nodes surrounded by fatty tissue.
As well as during MRI, MSCT evaluates:
- position and size of organs;
- their structure;
- the presence of pathological formations or diffuse changes;
- the state of intra- and extrahepatic bile ducts;
- presence of radiopaque stones gallbladder, bile ducts, in the kidneys, ureters);
- condition of the lymph nodes;
- the presence of fluid in the abdominal cavity;
- changes in the spine and ribs (as screening for pathology).
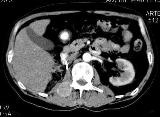
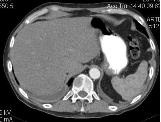
Images in axial projection in MPR mode. Both images were obtained during the study of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space. On the left - a formation (metastasis of kidney cancer) in the bone structures of the lumbar vertebra with spread to the adjacent soft tissues. On the right - kidney cancer metastasis in the vertebral body, the presence of fluid in the pleural cavities is also noted.
For MSCT organs of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space restriction of intake of solid food and carbonated drinks within 4-6 hours prior to the study is required. x You will be given a drink of Urografin x-ray contrast diluted in water, which will allow you to contrast the lumen of the upper gastrointestinal tract.
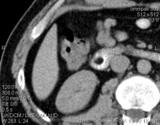
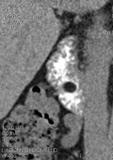
Lipoma 12 of the duodenum against the background of contrasted contents. Images in axial and frontal projections, MPR mode.
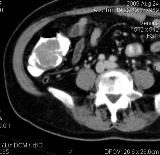
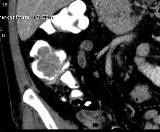
Education (tubular adenoma) in the previously contrasted lumen of the ascending colon. Images in axial and frontal projections, MPR mode, after intravenous contrast.
You must bring all available medical documentation with you to the examination: postoperative extracts, data from previous studies of the area of interest (MRI, MSCT, ultrasound - images and conclusions), a referral from the attending physician. This information is needed by our specialist before the diagnostic procedure for optimal planning of the course of the study and the correct placement of accents during its implementation.
Multispiral is a study in which X-rays pass through human tissue. This results in an image in various shades of gray, depending on the density of the tissue or the existing pathology. Its great advantage is the ability to view organs shown almost as accurately as in an anatomical atlas.
Such a study is called multispiral because the x-ray emitter moves along the annular line around the patient's body, at the same time it moves in the direction of the longitudinal axis. X-ray tubes are located around the perimeter of the chamber, which resembles a tunnel, due to which the layers of the body are examined from different sides and at different angles.
If you draw the trajectory of the emitter for the entire time of the procedure, then a spiral comes out. Each of the turns of the spiral corresponds to a picture of one zone of the body from different angles. Snapshots are called slice. One slice can be from 0.5 to 11 mm thick.
Thanks to computed tomography, it is possible to distinguish between such components of the abdominal cavity as the stomach, small and large intestines, and parenchymal organs such as the liver, spleen, kidneys, adrenal glands and pancreas. The tomogram also shows the biliary tract, and in special occasions you can perform cholangiography, which reflects them more accurately.
Due to the ability to view several areas of the body in the shortest possible time, computed tomography of the digestive organs has become a frequently performed study. It is especially useful for diagnosing emergencies in hospital wards. emergency care: abdominal trauma or acute pain in the stomach, as it is well tolerated by patients, and at the same time very effective.
Studies can be carried out both with the introduction of a contrast agent (angiography), and without it. Angiography is useful in detecting malformations of vascular disease (congenital defects), aneurysms and angiomas, stenosis renal artery. It happens that it is performed before the embolization procedure - the targeted closure of the lumen of the vessel for treatment.
2 Indications for carrying out
- Cancer of the intestines, stomach, pancreas, biliary tract, liver (for diagnosis and assessment of the degree of development).
- Inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis).
- Acute conditions such as obstruction, perforation, appendicitis, trauma.
- Spleen injury.
- Cholelithiasis.
- Acute and chronic pancreatitis (for differentiation and evaluation of complications).
- Kidney inflammation.
- Kidney calcifications.
- Nephrolithiasis (sensitivity is almost 100%).
- Diseases of the renal vessels.
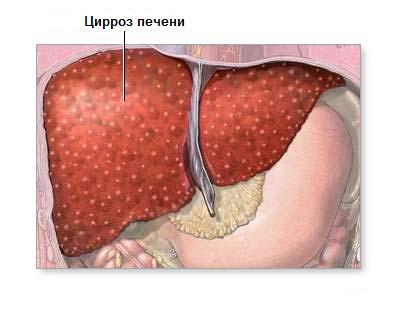
- Cirrhosis of the liver.
- Budd-Chiari syndrome (i.e. thrombosis of the veins of the liver or inferior vena cava).
3 Preparations
The study is safe and painless for the patient, but some preparation is required before MSCT. Before the examination, the doctor will take a medical history (sometimes you need to fill out a prepared questionnaire), you should report any allergies or an early reaction to the injection of a contrast agent. It is also necessary to report about pregnancy, lactation period, claustrophobia, tendency to bleeding. It is worth bringing the results of other imaging methods to the study.
Before the CT scan, the patient must remove all things made of metal. The mobile phone should be removed.
The patient should come to the examination of MSCT of the digestive organs on an empty stomach and after drinking a large amount of liquid (2-3 l). It is important to have an up-to-date creatinine test result with you.

Before scanning small intestine the patient is injected intravenously with a contrast agent, such as dilute barite. This is a liquid substance that absorbs X-radiation to a greater or lesser extent than the surrounding tissues.
When preparing for the procedure, the following rules must be observed:
- In order for the results of the diagnosis of the large intestine to be reliable, 2 days before the study, you must follow a diet (exclude milk, bread, cheese, fruits and vegetables) and use laxatives.
- The day before the CT scan, a liquid diet plus a laxative is used, and on the day of the exam, the patient is given an enema. A relaxant (eg, hyoscine) may also be administered to the patient.
- In preparation for gastric examination, the patient drinks 750 ml of water on an empty stomach immediately before the procedure to obtain the correct contrast between the stomach wall and surrounding structures.
- Before the examination of the pancreas, drink 500-1500 ml of water approximately half an hour before performing a CT scan to fill the intestines.
In some cases, people who are unable to lie still for the duration of the study need to be given sedatives or even general anesthesia. In the case of examination of children, they are given a sedative, or general anesthesia is used. Before the study, you need to inform the child about the progress of the MSCT procedure. He must know that a CT scan is painless method, which does not last long.
All questions regarding the preparation for a tomographic examination must be discussed with the doctor in advance!
4 How is the diagnosis carried out?
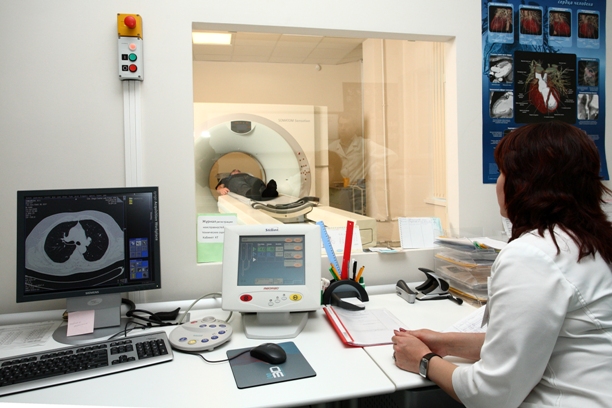
The study of multislice computed tomography is carried out in a special laboratory where the tomograph is located. The patient lies on his back on a table that moves automatically. The examined area of the body is installed in the area of action of X-ray lamps located along the circumference.
X-ray radiation, passing through various tissues of the patient's body, is weakened.
The degree of weakening depends on the type of tissue. The images are obtained in the transverse plane, but a corresponding reconstruction is also possible.
During a CT scan, a doctor or technician is in an adjacent room and instructs the patient through a microphone on when to lie still or hold their breath to improve the quality of the pictures, he monitors the progress of the examination. The patient should report any alarming symptom that occurs during the study: nausea, dizziness, shortness of breath.
5 Possible complications
Complications after MSCT may be associated primarily with the use of a contrast agent, but this is very rare. Contraindications are:
- pregnancy;
- kidney failure;
- previously identified allergies to contrast agents.
Before performing MSCT, each time you should inform the doctor about chronic diseases, such as diabetes(especially which is treated with pills). Computed tomography is a study that can be repeated several times, it can also be performed on children.
The study should be avoided in women in the second half of the menstrual cycle, as they have the possibility of fertilization.
MSCT is an abbreviation for the name of a relatively new medical method for examining the body - "multilayer (or multislice) computed tomography."
This diagnostic technique is based on the unique abilities of x-rays. For its implementation, special equipment is used, which is both a source of X-ray radiation and a means of perception and analysis of the rays that have passed through the tissues of the body.
Due to the fact that in the process of passing through tissues with different densities, the radiation wastes its power, fixing it at the output allows you to create a display of internal organs and media. The resulting image is used by doctors for diagnostic purposes.
How is MSCT different from CT?
The main difference between MSCT - multilayer computed tomography and CT - conventional computed tomography - lies in the special capabilities of the equipment used.
For MSCT, devices of the latest generation are used, in which one X-ray beam is captured by several rows of detectors. This allows you to simultaneously obtain up to several hundred sections and significantly reduces the duration of the study: an entire organ is scanned in one rotation of the radiating element. The clarity of sections is increased and the number of defects associated with the movement of internal organs is minimized.
The high speed of MSCT makes it possible to study not only the structure of organs, but also the processes occurring in them, causing minimal damage to the patient: the dose of radiation received by him is reduced by a factor of three compared to conventional CT.
Which is better, MSCT or MRI?
The fundamental difference between MSCT and MRI is that the first technique is based on the properties of X-rays and involves exposure of the patient to X-rays. In the second case, the diagnosis is carried out using an electromagnetic field, which has a more gentle effect on the human body.
However, MRI has much more wide range contraindications - it cannot be used if the patient has metal prostheses, implants and tattoos applied with metal-containing dyes. Another limitation is the fear of closed spaces and mental disorders. In addition, MRI is more expensive and most clinics only use it for certain indications.
How is MSCT performed?
To perform a conventional MSCT, the patient is placed on a special couch equipped with a lift, which easily moves into the capsule of the X-ray machine. The maximum residence time in the device is several tens of minutes, but the radiation time does not exceed a minute.
The procedure is not accompanied by discomfort, does not require special training or instructions from medical personnel.
To improve the image quality, an iodine-containing contrast agent is injected into the patient's body before MSCT. Before organ examination digestive system it is offered to drink, and when examining tissues and blood vessels, it is injected through a vein. In this case, the study is carried out several tens of seconds after the injection of contrast and generally differs from standard multislice tomography only by an increase in duration.
How often can MSCT be done?
The frequency of MSCT is not as important as the amount of radiation received during the diagnostic process. The threshold recommended by the Chief Sanitary Doctor of Russia for preventive examinations is 1 mSv (millisievert) per year, with a dose of 5 mSv considered to be the most harmless.
The average dose of radiation received in the process of conducting multislice tomography ranges from a few hundredths to several tens of millisieverts. Each dose received is recorded in a special sheet of radiation exposure. The possibility and necessity of each subsequent examination is determined individually, based on general condition patient and the need for new diagnostic data.
How to prepare for MSCT?
A day or two before the multislice tomography of the internal organs, foods that cause strong gas formation should be excluded from the diet.
A few hours before the upcoming study, food intake is stopped. Liquid (pure water or water with a contrast agent dissolved in it) is taken evenly, in small portions.
Before examining the pelvic organs, it is necessary to empty the intestines, if necessary - by administering an enema.
The forthcoming MSCT of the head or the osteoarticular apparatus does not require special preparation.
How long does an MSCT study take?
The unique capabilities of the equipment used for MSCT can significantly reduce the duration of the study.
So, conventional multislice computed tomography lasts from several minutes to several tens of minutes, depending on the area and depth of the area under study.
The duration of the examination procedure using a contrast agent can be increased up to an hour. In some cases, the reception of a contrast agent begins a few hours before the study, then the entire diagnostic process takes several hours.
What is the radiation dose for MSCT?
The dose of radiation that a patient receives during MSCT (multispiral computed tomography) is determined by the area and depth of the tissues to be examined, the type of apparatus used in the work and the examination method.
As a rule, the radiation exposure in the study of one anatomical region is within 3-5 mSv (millisieverts). A smaller load is accompanied by the study of bones and joints (the dose is about 0.0125 mSv), more is the diagnosis of internal organs. With a deep examination of the organs of the chest or abdominal cavity, these values can increase markedly, reaching several tens of millisieverts.
How much does MSCT cost?
The price for conducting multislice computed tomography is determined not only by the pricing policy medical institution, but also the quality of the equipment used during the study, the level of complexity of the procedure, as well as the qualifications of the medical staff.
In 2015, the average cost of studying one anatomical region using MSCT is within a few (2-3) thousand rubles. The cost of studying blood vessels is much higher, especially with the use of a contrast agent - it is about 10 thousand rubles. A heart examination is estimated even higher, the cost of which reaches 17-18 thousand.



