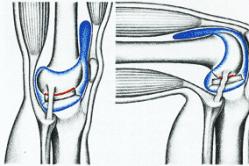
Antipyretics for children are prescribed by a pediatrician. But there are emergency situations for fever when the child needs to be given medicine immediately. Then the parents take responsibility and use antipyretic drugs. What is allowed to give to infants? How can you bring down the temperature in older children? What medicines are the safest?
Content
Breast cancer is a devastating disease modern world wide use. Advances in medicine with such a diagnosis help save patients' lives. Mastectomy - surgical method problem solving. What are the indications for operations, what is the difference between the methods used, how does postoperative recovery occur - information, useful to women any age.
What is a mastectomy
A tumor found in the breast becomes a physiological and psychological female problem. To resolve it, a mastectomy is used - an operation to remove the mammary gland, which has options for performing. Surgeons, trying to save a woman's breasts, choose the least traumatic method in all respects. Tasks of doctors:
- eliminate a dangerous disease;
- create conditions for the subsequent restoration of the breast;
- improve women's quality of life.
During surgery, depending on the type of technique, the removal of the mammary gland, large, small pectoral muscles, fatty tissue containing lymph nodes is performed. A cancerous tumor is dangerous because of the rapid growth of metastases. Surgical intervention has features that depend on the stage of development of the pathology, the age of the woman. Indications for breast removal are:
- the risk of oncology is more than 51%;
- sarcoma;
- purulent inflammation;
- genetic predisposition to cancer;
- gynecomastia.
There are restrictions for the removal of the mammary glands. Contraindications for performance:
- violation of cerebral circulation;
- hepatic, renal failure;
- decompensated diabetes mellitus;
- swelling in the gland, passing to the chest;
- severe form of cardiovascular insufficiency;
- multiple metastases in the lymph nodes with swelling of the hands;
- tumor growth in tissue chest.

Types of mastectomy
The earlier a woman is diagnosed with breast cancer, the less traumatic the surgery will be. The subsequent measures for breast reconstruction also depend on this. Several techniques have been developed for mastectomy. In addition to the removal of the mammary gland, they mean:
The most minimally invasive method with the possibility of subsequent breast reconstruction is subcutaneous mastectomy. The affected glandular tissue is scraped out through a small incision. Modified types of radical intervention are used together with elimination mammary gland:
Indications
Before performing a mastectomy, doctors assess the condition of the woman, the degree of tumor development, and the structure of the cancer. This is taken into account when choosing the method surgical intervention. Each has its own indications:
|
Methodology |
Indications for holding |
Performance |
Chemotherapy |
|
Subcutaneous |
Neoplasm close to the nipple, size up to 20 mm |
Access to the tumor through a small incision |
Not required |
|
According to Pirogov |
1.2 stage of cancer, cellular damage |
Remove part of the chest and muscles |
|
|
By Madden |
Stage II cancer with lymphedema |
Removal of breasts, lymph nodes |
Required |
Oncologists choose a modification of mastectomy in accordance with the indications for carrying out, the degree of severity of the process:
|
Methodology |
Indications for holding |
Performance |
Chemotherapy |
|
Bilateral (bilateral mastectomy) |
Multiple tumors of stage 3-4 with lesions of both mammary glands, genetic mutations |
removal |
Done before surgery |
|
The size of the tumor is not more than 4 cm, the presence of pain, burning |
The mammary gland is removed with subcutaneous tissue, chest muscle |
Not assigned |
|
|
Radical |
third stage cancer with pain |
Elimination of all chest muscles |
The choice of the method of surgical intervention is a crucial moment for surgical oncologists. The need for chemotherapy is determined by the doctor. Common types of mastectomy:
Tumor in last stage with metastases are treated with surgical operation carried out according to the following methods:
Preparing for the operation
Before proceeding with the mastectomy, the doctor conducts an initial examination of the woman, collects an anamnesis. An examination is scheduled, and the method of the operation is selected based on the results. Preoperative measures include:
- general, biochemical analysis blood;
- mammography of the breast;
- urine test;
- tissue biopsy;
- computed tomography;
- blood clotting test;
- research on tumor markers;
- prescribing a light diet;
- reception restriction medicines that promote blood thinning;
- prohibition on the operational day of drinking, eating.

Operation
When choosing a surgical intervention scheme, it is taken into account that it is carried out according to the plan - the removal of one mammary gland (unilateral mastectomy) - or both are removed. The operation is performed under general anesthesia. The duration is from one to three hours, depending on:
- the patient's condition;
- stages of cancer;
- tumor localization;
- the presence of metastases.
There is a general algorithm of actions when performing the removal of the mammary glands in women:
- anesthesia is performed;
- rifling is marked with a special marker;
- skin incision is performed;
- subcutaneous tissue, mammary gland is separated from it;
- tissue is removed, including, if necessary, lymph nodes;
- in accordance with the method of operation, excision of fatty tissue, pectoral muscles is carried out;
- vascular links are traced, nerve endings;
- a drain is installed for the outflow of fluid;
- stitches are applied, which are removed after 12 days.
According to Halstead
This type of mastectomy is considered a classic option, used for stage 1-3 cancer. The method bears the names of the doctors who developed it - Halsted-Meyer. For the patient, this is the most traumatic method of intervention, which is used in case of extensive metastasis of the lymph nodes, chest muscles. During the operation, simultaneously remove:
- mammary gland;
- small, large pectoral muscles;
- subcutaneous fatty tissue - subscapular, axillary, subclavian;
- lymph nodes;
- nipple;
- skin.
The Holder-Meyer mastectomy is used when other methods are powerless. Contraindications for surgery must be taken into account. The technique causes a serious complication - limited mobility shoulder joint due to muscle removal and nerve damage. As a result of the elimination of a large number of tissues, problems arise during the plastic reconstruction of the breast:
- restoration of the symmetry of the glands;
- correction of volume, shape;
- reconstruction of the nipple-areolar complex.
Radical mastectomy according to Madden
The type of surgery developed by Madden is considered more gentle and less traumatic. Mastectomy is used to treat women with nodular cancer. During the event:
- the mammary gland, axillary, subscapular, subclavian lymph nodes with subcutaneous tissue are removed;
- all muscle groups are preserved;
- there is no heavy bleeding;
- vascular and nerve endings are preserved.
As a result of the Madden mastectomy behavior due to the reduction in the volume of surgical intervention, the reduction in trauma, complications rarely occur. After operation:
- going on fast healing wounds;
- the mobility of the shoulder joint is not disturbed or restoration is carried out with the help of special gymnastics, massage;
- successful plastic reconstruction of the mammary glands;
- there is a possibility of recovery in a short time.

Amputation of the breast
When choosing a method for performing an operation, oncologists take into account the stage of the disease, the degree of cancer activity, the growth rate of the tumor, and the hormonal state. female body. Amputation of the breast is a simple mastectomy. It does not apply to radical interventions. It is supposed to remove the mammary gland and fascia of the pectoralis major muscle, nipple and areola. Indications for carrying out are:
- cancerous tumor stage 4;
- decaying malignant neoplasms;
- pathology of 2-3 degrees when it is impossible to perform a radical surgical intervention.
This type of surgery is used for preventive purposes in the presence of a genetic predisposition to the development of breast cancer. Indications are the large size of the neoplasm. Features of surgical intervention:
- a biopsy of the nearest lymph nodes;
- with a cancerous tumor size of up to two centimeters, the areola and nipple are not removed;
- followed by radiation and chemotherapy.
By Pati
During the operation according to the method of this doctor, the pectoralis major muscle is not removed. The Pati method contributes to the preservation of the functions and cosmetic appearance of the remaining tissues. During surgery:
- the mammary gland, fascia of the pectoralis major muscle is removed;
- the small one is excised, providing access to the axillary lymph nodes;
- they are removed;
- subcutaneous tissue is cut out, the skin around the malignant neoplasm;
- drainage is installed;
- stitches are applied.
Patey's technique - a modified radical mastectomy - is considered to be less traumatic, and is widely used in oncology. After the operation, there is a minimum number of complications. The disadvantages include:
- the appearance of scars in the subclavian vein;
- difficulties in breast formation with artificial implants;
- a slight but quickly recoverable limitation of the mobility of the shoulder joint.
Postoperative period
In order for a woman to quickly restore her shape after the operation, it is necessary to carry out rehabilitation measures prescribed by the doctor. This will help remove pain syndromes, increase the mobility of the shoulder joint, restore lymph flow, eliminate complications. In the postoperative period it is necessary:
- refuse to visit the solarium, baths;
- avoid lifting weights;
- use an elastic bandage;
- wear special soft clothes;
- drink more fluids;
- avoid injury;
- get regular check-ups with a doctor.
The postoperative condition requires careful attention to health. A woman is recommended:
- limit working hours;
- reduce movement;
- perform a special complex of exercise therapy;
- visit the swimming pool;
- use a bandage;
- exclude exposure to heat;
- wear specialized underwear - bra, swimsuit;
- do gymnastics;
- do not inject into the arm from the side of removal;
- conduct a course of psychological recovery;
- see a doctor if you feel unwell.
During rehabilitation after a mastectomy, you will need:
- normalize nutrition - use a low-calorie diet;
- carry out physiotherapy;
- perform massage, hydromassage;
- use simulators to restore mobility of the shoulder joint;
- limit prolonged stay in an inclined position;
- use a compression sleeve for air travel;
- use a healing wrap;
- drink the drug Tamoxifen to exclude relapses;
- perform reconstructive plastic surgery.

Complications
Having a mastectomy can have serious consequences. Complications appear after surgery and in the subsequent, remote period. After the operation, the occurrence of problems is not ruled out:
- suppuration of the postoperative wound;
- bleeding;
- breathing problems;
- the appearance of blood clots in the lower extremities;
- lymphorrhea - prolonged outflow of lymph as a result of injury to the lymph nodes;
- drug allergy;
- marginal tissue necrosis;
- damage to the nerve endings of the muscles of the back, arms, chest;
- organ infection abdominal cavity.
During the recovery period after a mastectomy, long-term complications may appear:
- pain, stiffness in the hands;
- problems of mobility of the shoulder joint;
- lymphostasis - swelling of the hands caused by a violation of the outflow of lymphatic fluid;
- rough postoperative sutures;
- proliferation of connective tissue;
- disorder of outflow of venous blood due to overlap during the operation of the lumen of the axillary, subclavian vein.
The most serious for a woman are postoperative psychosexual problems. Breast removal causes:
- depression;
- feeling of own inferiority, inferiority;
- difficulties in communicating with the opposite sex;
- restriction of social contacts;
- fear of recurrence of the disease;
- fictional and real difficulties of sexual life;
- the difficulty of establishing new acquaintances;
- problems in family relationships.
Breast reconstruction
The women go to plastic surgery for breast reconstruction due to psychological discomfort. In addition, there are problems at the physical level associated with an imbalance of loads on the spine. After a mastectomy, there are:
- change in posture;
- omission of the shoulder on one side;
- rachiocampsis;
- violation of the lungs, heart.
Often, reconstruction is carried out in conjunction with a mastectomy, or six months after the operation. As a result of activities at the site of removal of the mammary gland, restoration is carried out:
- the volume of subcutaneous adipose tissue, skin;
- cut tissues located nearby, chest muscles;
- nipple-areolar complex;
- in addition to the operated breast, the second mammary gland to adjust the size and shape.
There are several reconstruction techniques that differ in execution and results. One of the most popular methods is the use of endoprostheses. Features of plastic surgery:
- performed after subcutaneous mastectomy;
- an expander is inserted through the incision - a special device;
- stretching of the skin occurs, the formation of a cavity for the subsequent installation of the implant;
- advantages - low trauma;
- disadvantages - the unnaturalness of the breast to the touch and outwardly, the risks of tissue necrosis, the presence of restrictions on the installation of the implant.
To create a natural in appearance and sensations of the mammary gland, transplantation of one's own tissues is used, which are taken from the back, anterior abdominal wall. This technique - the TRAM patchwork method - is characterized by:
- the complexity of the operation;
- high trauma;
- the need for prolonged anesthesia;
- the presence of a possibility of tissue rejection;
- long recovery period;
- no problems associated with implant displacement.

Another reconstructive method is the use of vacuum devices. When using them:
- a domed cup is placed on the chest;
- a vacuum is created under it;
- stretching of the skin occurs;
- its excess is formed;
- a place is formed for the subsequent installation of a silicone implant, transplantation of adipose tissue;
- the disadvantage of the method is that it requires a long wearing of the device, the appearance of stretch marks is not excluded, it is difficult to stretch to big size implant.
Often, a combined breast reconstruction technique is used. Breast plastic surgery includes a combination of methods:
- replenishment of tissue deficiency by transplanting flaps of the patient's own muscles, subcutaneous tissue, skin of the patient;
- correction of the shape, size, symmetry, reconstruction of volume, elimination of cavities is carried out using silicone implants.
Price
Mastectomy in Moscow is performed in specialized clinics, oncology centers. Surgery includes only removal of the breast or simultaneous plastic reconstruction. The cost depends on the stage of cancer, the specifics of the implementation process, the qualifications of specialists, the status of the clinic. Operation price in rubles:
Video
Mastectomy is the removal mammary glands when the risk of developing cancer reaches 51% or more percent. The operation to remove the mammary gland differs in its features and age category.
Types of operations to remove glands
Mastectomy according to Madden is the removal of the breast together with the lymph nodes of the armpit. After removal, rehabilitation is prescribed. Reconstruction of the breasts is required to recreate the shape and volume.
Patey's mastectomy is the removal of the breast, tissue in the armpit, and part of the pectoral muscle.
Subcutaneous mastectomy- this is the removal of glandular tissue by scraping through a small incision. At the end of the operation, a prosthesis is inserted into the skin, which is sewn inside. Subcutaneous mastectomy is convenient for women in terms of the possibility of restoring the shape of the breast. This allows them to maintain volume and make inconspicuous incisions, as in plastic surgery. Subcutaneous mastectomy can be bilateral, depending on the extent of breast involvement. Subcutaneous mastectomy is also performed for sarcoma, breast cancer, and purulent inflammation. 
After a double mastectomy (bilateral), a woman does not have a single mammary gland, but there is an opportunity to do plastic surgery.
Mastectomy according to Pirogov is the removal of the mammary gland with a lymphocele, when cancer is detected at stage 1-2. After surgery, lymphostasis of the arm or upper and lower limb. After removing the wish. swelling of the hand may pass, but it is reversible, that is, it can go away in a year and a half.
Radical mastectomy is the Halsted method, which involves the removal of all muscle groups of the mammary cavity, axillary lymph nodes, fiber, and the breast itself. Radical mastectomy can be performed using different methods, it all depends on the degree of complexity of the operation. Radical mastectomy is done only after the discovery of an abscess the size of the entire pier. wish.
Indications for types of operations
According to completely different indications, the operation can be prescribed depending on the course of the disease, the structure of the cancer, the tumor, the state of health, etc. The table shows clearly which mastectomy is prescribed when, why, and what happens after the removal of the mammary gland.
|
Type of mastectomy |
Indications |
Holding |
After the mastectomy |
|
Subcutaneous |
The tumor is 2 cm in size close to the nipple. Chest pain, |
The removal process occurs through an incision. Chemotherapy is not required. |
After removal, rehabilitation is required for at least 1 year. Tamoxifen treatment, massage, bra. |
|
Bilateral |
Tumor on both sides. wish. Pain, stage 2-3 cancer. |
The pier is removed. wish. completely after chemotherapy. |
Rehabilitation reaches 2 years. Possible swelling of the upper limb. |
|
The tumor growth threshold is up to 4 cm. The value may vary due to the progression of the disease. There is pain, burning. |
Chemotherapy is not required. Breast removal is carried out together with fiber and pectoral muscle. |
Swelling of the limb. The period of recovery procedures reaches 1-2 years. Exercise, massage, bra |
|
|
By Madden |
Cancer of the 2nd degree, lymphostasis, pain in the left side of the cell. |
Chemotherapy is not required. Removal of the breast with lymph nodes. |
It is possible to insert implants. wish. tamoxifen treatment, massage, bra |
|
According to Pirogov |
Cancer of 1-2 degrees with cellular damage. |
Removal of part of the muscle, part of the mol. wish. |
Lymphostasis of the limb. Exercise, tamoxifen treatment, massage, bra |
|
Radical |
Grade 3 cancer, chest pain. |
Chemotherapy is not required. Removal of all muscle groups, chest. |
Lymphostasis. You can return the form. wish. plastic, massage, bra |
|
Radical Extended |
Stage 4 cancer, chest damage, unbearable pain. |
Chemotherapy is not required. Removal of all muscle groups, they say. zhel., lymph nodes and chest skin. |
Lymphostasis, swelling of the hand. Exercise and gymnastics, bra |
|
Hemimastectomy |
Cancer grade 3, chest pain, swelling of the glands. |
A type of surgery to remove half of the fatty and glandular tissue. Chemotherapy is not required. |
Lymphostasis, swelling of the hand. Possibility of performing one-stage plastic surgery. Exercise, massage. |
|
Lymphadenectomy |
Cancer, an abscess the size of a tumor. |
A type of surgery to remove half of the fat and glandular tissue while sparing muscle. |
Lymphostasis, swelling of the arm, treatment with tamoxifen. |
|
Quadrantectomy |
Localized cancer of the last stage. |
A type of surgery to remove the glands and serratus fascia. Chemotherapy is not required. |
Swelling of the hand. Possibility of performing one-stage plastic surgery. Exercise and Diet |
Separately, there is a type of preventive mastectomy, which is performed in order to exclude possible complication current cancer risk. Operations are performed when there is a high probability (from 70%) of the development of a cancerous tumor. To prevent complications, such a removal of the chest is performed.
Postoperative period
The period after the completion of the operation may be accompanied by such consequences as:

At the end of surgery, reconstructive plastic manipulations are also carried out in order to return the shape to mind. During the first three months, everything hurts - the head hurts, the joint hurts, the back hurts. The heart also hurts due to the load on the body. The joint hurts, gives to the nerve endings. Massage, recommendations, treatment, diets should be followed. For a speedy recovery, treatment involves a bandage, underwear and exoprostheses, exercises and much more.
Today, Anita underwear, exoprostheses and prostheses are produced for women, which have a special sleeve for comfortable wearing. Distinguish:

The bandage may have a sleeve that is worn on one side. The bandage does not include a sleeve for both sides. The sleeve is only on the side where exoprostheses are not inserted.
Exoprostheses are inserted into swimwear, bra, clothes for any occasion. Swimwear and their structure includes a sleeve, fasteners and support in the form of a belt. Swimsuits also have sleeves, bowls.
 The texture hides chest problems, and the sleeve is perfectly complemented by the fabric. This structure allows you to hide the stitches left due to the mastectomy. Swimwear must be worn, these are the recommendations of doctors. So a woman can influence men, and regain her mental health.
The texture hides chest problems, and the sleeve is perfectly complemented by the fabric. This structure allows you to hide the stitches left due to the mastectomy. Swimwear must be worn, these are the recommendations of doctors. So a woman can influence men, and regain her mental health.
It is swimsuits that are an open part of clothing that allows a woman, despite the circumstances, to show herself in all her glory. Observing the recommendations, nutrition, prescriptions of doctors, do not forget about femininity. Swimwear can be ordered in a store for a holiday at the sea, pool, lake, but continue to heal your "life". The main thing is to heal yourself from the inside, and think about how beautiful life is.
Many ladies are afraid of losing men with their transformations. Men have no understanding of what kind of life a woman had. Because of this, rejection appears in men, many men's families collapse, because the appearance of a woman has changed. Wives and young girls are afraid that men will lose their desire to be around, and only men if they put everything they have into a woman to restore her smile. Men do not have questions about how nutrition should be, why the body hurts and gives to the back. After all, no one knows how long a person lives or how much is left for a person. Appreciate life, give support.
Attention! The following video presents video clips of microsurgical operations.
Viewing these videos is strongly not recommended: for persons under 16 years of age, pregnant women, as well as persons with an unbalanced psyche.
Diseases that you can't get rid of. They require intense attention, examination and treatment. Among oncological diseases in women, breast cancer ranks first, among other diseases - the second. Consequences are not always predictable.
The importance of prevention and timely treatment. In some cases, an operation is inevitable - radical.
What is a radical mastectomy
Radical, i.e., removing entirely, completely, with a root. The term mastectomy has Greek origin- mastòs "chest" and ek tome "I remove". The term is over 100 years old.
Several types of mastectomy are practiced. Each of them is effective, they differ in the degree of trauma. Radical mastectomy is a complex operation, but sometimes only it can solve an existing problem.
There are three main types of mastectomy:
- by Madden,
- by patey,
- according to Halsted.
Madden's radical mastectomy is considered the most sparing.
Carefully! Video showing radical mastectomy (click to open)
[hide]
Kinds
By Madden
The method involves the preservation of both pectoral muscles, which makes it as gentle as possible. The mammary gland is removed as a block with lymph nodes and a subcutaneous fat layer.
After the extraction of the mammary gland, all nerve endings and vascular links can be traced, which helps to avoid blood loss. This type of operation is endowed with a significant advantage: the preservation of radicality, relatively low trauma, and a low percentage of complications.
According to Halstead
The Halsted-Meyer mastectomy is a classic operation. A single complex removes the mammary gland, skin, subcutaneous tissue, pectoral muscles, subcutaneous fatty tissue (subclavian, axillary and subscapular region), lymph nodes.
The method often causes complications, the main of which is the restriction of mobility of the shoulder joint. It is used extremely rarely when other methods will not help to cope with the problem, for example, extensive ones that affect the pectoral muscle, lymph nodes, etc.
By Pati
Patey's mastectomy is a modification of the previous type and has the full name - modified radical mastectomy. Its founder, Dr. Patey, proposed a wide excision of the skin and preservation of the pectoralis major. During the operation, only a small muscle is removed, which makes the method more gentle and avoids serious complications.
According to Pirogov
The mammary gland and fiber of the axillary region are removed.
Simple mastectomy
The mammary gland and fascia of the pectoralis major muscle are removed.
Tram-flap technique
A method of breast restoration, which is carried out simultaneously with a mastectomy or six months after the operation. In this case, the patient's own tissue is moved, which is called the TRAM flap, which is a tissue with preserved blood flow. This may be an iliac-femoral flap or a greater omental flap. Sometimes a flap of the rectus abdominis muscle on the leg (together with the skin) is used.
Subcutaneous surgery technique
A technique that allows you to save the radicalness of the surgical intervention and achieve the highest possible aesthetic results. This is a method of extended subcutaneous mastectomy, when the mammary gland with muscular fascia (sheath) and lymph nodes are removed, while maintaining muscle and fatty tissue. P
When using this technique, it is also possible to perform a breast reconstruction operation at the same time. This can be an operation using own tissues or using an implant for which a "pocket" is previously formed.
Carefully! The photo shows the breast after a radical type mastectomy (click to open)

[hide]
Indications for holding
- varying degrees,
- Purulent mastopathy (in rare cases),
- Correction of previous treatment,
- Individual indications (prevention, etc.).
Contraindications
General contraindications:
- Violation of cerebral circulation.
Contraindications for tumor localization:
- Breast edema extends to the chest wall,
- Multiple with edema of the upper limb,
- Germination of a tumor of the chest.
Carefully! The video shows the radical mastectomy(click to open)
[hide]
Operation
Preparation
Preparation for the operation consists of several stages:
- Medical checkup, which is fundamental. The doctor examines the history and prescribes an examination,
- survey, including a series of tests and tests: (a photograph of breast tissue), and a blood test for clotting ().
- The doctor prescribes sparing (light) diet, warns about the restriction of reception (or complete cessation) medicines that thin the blood (aspirin, etc.). They are excluded a week before the operation. On the day of the operation, it is unacceptable to drink and eat.

Operation progress
The operation is performed under general anesthesia. Its duration is from 1 to 3 hours.
Carrying out algorithm:
- Marking is applied with a marker for upcoming incisions,
- The skin is cut in the necessary places,
- Subcutaneous tissue and mammary gland are separated from the skin,
- Removal occurs in a single block, including lymph nodes,
- Depending on the method, the pectoral muscle, fatty tissue, etc. are sequentially removed,
- Tracing nerve endings and vascular links,
- Drainage is installed through a special hole, which is removed on the 5th - 6th day,
- Stitches are applied, which are removed on the 10th - 12th day.
Drainage installation is an important point. The doctor monitors the outflow of fluid.
Rehabilitation
After a mastectomy, rehabilitation measures are extremely important. These include gymnastics, physiotherapy, taking medications.
Gymnastics
Gymnastics, some examples of exercises:
- Squeezing a rubber ball
- hair combing,
- Putting your hands behind your back, as if you are trying to fasten a button from behind,
- Circular movements of the hands, swaying, etc.
Physiotherapy
 If there are no complications, then physiotherapy can be prescribed as early as a week after the operation. What can be done from this side:
If there are no complications, then physiotherapy can be prescribed as early as a week after the operation. What can be done from this side:
- Pool,
- Various simulators aimed at developing the shoulder joint,
- Massotherapy,
- Hydromassage,
- (apply),
- Bandage,
- Medical wrap.
Rehabilitation rules
- Using an elastic bandage
- Refusal to visit the bath and solarium,
- You can not lift weights during the year,
- Staying in an inclined position for a long time
- Try to avoid injuries, do not use traumatic objects (bracelets, etc.),
- Increase the amount of fluid you drink
- Compression sleeves must be worn during air travel.
- An examination is required every six months
- If you feel unwell, contact your doctor immediately.
Lipofilling of the mammary glands after RM
This is a means of breast reconstruction after a mastectomy, for which the patient's tissue is used, and not implants. One session for the recovery procedure will not be enough, they will definitely need several.
It is also a serious moment that requires thorough preparation.
- The surgeon determines the areas from which the necessary material can be taken,
- Assigns an examination similar to that required for any plastic surgery,
- Surgery is performed under general anesthesia
- Before taking adipose tissue, Klein's solution is injected into it,
- Selected fat cells are placed in a centrifuge, where they are stratified into 3 parts,
- The middle part is used for direct reconstruction,
- The prepared adipose tissue is injected with a syringe in small portions into the targeted areas.
The operation is performed under general anesthesia and lasts from 2 to 5 hours. After lipofilling, and are formed, which persist for 3-4 weeks. Repeated operation is possible not earlier than in 4 months. For a stable result, 2-5 procedures are required.
Lipofilling involves the use of a special system (BRAVA), which protects the transplanted cells from external influences. This system is put on and worn for 7 to 14 days.
Consequences and complications
 The number of complications after mastectomy continues to be high today (from 20 to 87%), despite the equipment and new technologies. Complications may be early or late.
The number of complications after mastectomy continues to be high today (from 20 to 87%), despite the equipment and new technologies. Complications may be early or late.
Early
- Lymph leakage, which may necessitate a second operation,
Prices vary a lot, which is not surprising. Each operation has its own characteristics, apply different methods. Pricing also plays a role. Approximately the minimum price threshold is 35 thousand rubles. It is possible to have a simple mastectomy at a lower cost, but this is unlikely. Average prices for an operation range from 60 to 120 thousand rubles.
State Institution "Dnepropetrovsk Medical Academy"
Ministry of Health of Ukraine
Essay
"Mastectomy"
Performed
2nd year student, 103b group
Salivonchik V.A.
Dnepropetrovsk
Plan
1.Definition
2. Types of operations
3. Indications for mastectomy
4. Performing a surgical operation
5. Postoperative period and complications
6. Used literature
Definition
A mastectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the breast. The main and predetermining indications for this surgical intervention are: breast cancer or sarcoma and gangrene resulting from a purulent process in the chest. The latter is extremely rare. Also, removal surgery is indicated in the following cases: when the tumor is found in more than one area of the breast; when the patient has very small breasts, as a result of the operation there will be very little tissue left, and there will be a pronounced deformation of the mammary glands; when it becomes impossible to conduct a course of radiation therapy after lumpectomy (removal of a palpable tumor within healthy tissues without extensive tissue excision).
According to statistics from the Ministry of Health, breast cancer is the most common malignant neoplasm in Russian women. And every year this incidence rate is growing. Cancer treatment is usually divided into local (surgical intervention and radiation therapy) and systemic (chemotherapy, hormone therapy, "targeted" therapy). To date, the technique of surgical interventions on the basis of breast cancer has made great progress. However, it is always necessary to remember that any operation is a stress for the body, which can bring a number of consequences.
The surgical treatment of breast cancer is specific and requires certain skills, knowledge and experience from the oncologist. If an adequate, radical operation is performed in accordance with the individual characteristics of the growth and spread of the patient's tumor process, the method is called radical. Treatment of breast cancer should be carried out only in specialized medical institutions, which fully include the Kartasheva Clinic, where mammology is a priority.
Operation types
There are several options for radical mastectomy - according to Halsted, according to Paty, Madden, Urban-Holdin, etc. Currently, in most cases, mastectomy in the modification of Paty and Madden is used, as it is less traumatic and disabling, compared to the Halsted operation. It is to them that the article is devoted to a greater extent.
Mastectomy according to Halsted (Halsted-Maer) involves the removal of the mammary gland, as well as axillary tissue with the pectoralis major and minor muscles. Due to the fact that these muscles play an important role in the movement of the hand, in postoperative period patients often have dysfunction of the upper limb. In numerous studies, scientists have proven that the radicality of the intervention due to the removal of muscles does not increase, therefore, at present, this operation is abandoned in most cases. A Halstead mastectomy is performed if the tumor has grown into the pectoralis major muscle.
Extended radical mastectomy (with removal of parasternal lymph nodes) In this operation, the mammary gland is removed along with the pectoralis major and minor muscles, fatty tissue of the armpit, subscapularis, subclavian and parasternal regions. Technically, it is performed as a Halsted operation, with the exception of adding one more stage - opening the chest and removing the lymph nodes lying on the inside of the sternum.
Patey's mastectomy involves the removal of the mammary gland with axillary tissue in a single block with the pectoralis minor muscle.
Mastectomy according to Madden involves the removal of the breast with axillary tissue, but without the removal of the pectoralis major and minor muscles. Mastectomy according to Madden combines sufficient radicalness and at the same time functionality. Preservation of the pectoral muscles greatly reduces the number of complications such as impaired mobility of the shoulder joint.
Simple mastectomy. The operation consists in removing the mammary gland with fascia (thin elastic tissue covering the muscle) of the pectoralis major muscle, but without removing the pectoral muscle and fatty tissue of the armpit.
Mastectomy according to Pirogov
The operation consists in the removal of the mammary gland with fiber in the armpit.
Hemimastectomy with lymphadenectomy. Remove one half of the mammary gland with fatty tissue of the axillary, scapular and subclavian zones. The pectoralis major and minor muscles are not removed.
Simple mastectomy, mastectomy with lymphadenectomy, hemimastectomy with lymphadenectomy are not currently widely used, due to the fact that they most often fail to completely remove fatty tissue with lymph nodes.
Subcutaneous mastectomy with immediate reconstruction
The mammary gland is removed as a single block with the fascia of the pectoralis major muscle, subcutaneous adipose tissue and lymph nodes of the axillary, subclavian and subscapular regions. This operation involves a one-stage reconstruction. Skin incisions are made taking into account the location and size of the tumor.
Subtotal radical resection of the mammary gland with simultaneous mammoplasty
When performing a subtotal radical resection of the mammary gland with subsequent reconstruction after dissection of the skin of the mammary gland, at least 75% of its tissue is removed with a tumor, a skin area above it, retreating at least 5 cm. It is necessary to remove the subareolar zone of the gland. Excision is carried out in the entire thickness of the mammary gland together with the fascia of the pectoralis major muscle. The nipple-areolar complex is not removed.
Radical mastectomy with simultaneous mammoplasty using a transverse musculocutaneous flap of the anterior abdominal wall on one rectus abdominis muscle
It is possible to reconstruct the mammary gland with a free TRAM flap using vascular anastomoses between the lower deep epigastric vessels with the subscapular and intrathoracic vessels.
Organ-preserving operations
Lumpectomy (tumorectomy) - removal of a breast tumor within healthy tissues (indentation - 1 cm) + lymph node dissection of 1-3 levels (with medial localization, the operation is performed from two incisions)
Quadrantectomy (segmentectomy) - removal of the sector, including the tumor node (indentation from the edge - 3 cm) with the fascia of the pectoralis major muscle + lymph node dissection of 1-3 levels (with medial localization, it is performed from two incisions).
In domestic practice, CCA is commonly called radical resection - removal of a sector of breast tissue with the fascia of the pectoralis major muscle, including the tumor node, lymph node dissection of 1-3 levels.
A) Indications for mastectomy by Pati:
- Absolute readings
: multicentric tumors, stage T4 tumors, large tumor in relation to the size of the breast. Be sure to combine with axillary lymphadenectomy.
- Alternative operations: Quadrantectomy for smaller tumors or patients in very poor general condition.
b) Preoperative preparation. Preoperative examinations: mammography, chest x-ray, ultrasonography(armpit, abdominal organs), bone scan.
V) Specific risks, informed consent of the patient. Lymphedema of the hand (in 10% of cases).
G) Anesthesia. General anesthesia(intubation).
e) Patient position. Lying on the back, the arm is abducted, the armpit is accessible.
e) Operational access when removing the mammary gland according to Pati. Horizontal elliptical excision of the mammary gland with the transition to the axillary region.
and) Stages of a mastectomy according to Pati:
- Patient position
- Incision
- Caudal dissection of the breast
- Expansion of the scope of the operation
- Wound closure
h) Anatomical features, serious risks, operational methods:
- The long thoracic nerve runs along the lateral chest wall (serratus anterior), the thoracic nerve lies dorsal to it (the latissimus dorsi muscle).
- Avoid circular lymph node dissection around the axillary vein (the cranial edge of the axillary dissection is the intercostal-brachial nerve).
- Apply an elastic bandage after the operation.
- "Non-fixed" macropreparation must be immediately sent to the pathoanatomical department for the determination of estrogen and progesterone receptors, as well as for histological examination tumors.
And) Measures for specific complications. None.
To) Postoperative care after breast removal for cancer:
- Medical care: remove the active drain after 2 days.
- Activation: hand movements as the pain is overcome.
- Physiotherapy: to restore lymphatic drainage.
- Period of incapacity for work: 2 weeks, depending on the occupation and further medical measures.
l) Operative technique of mastectomy according to Pati:
- Patient position
- Incision
- Caudal dissection
- Cranial breast dissection
- Expansion of the scope of the operation
- Dissection in the axillary vein
- Resection of the pectoralis minor muscle
- Wound closure

1. Patient position. The patient is positioned on the operating table with the arm abducted, the armpit is shaved. The shoulder on the side of the operation can be slightly raised with a flat pillow placed under the back.
2. Incision. The incision is made transversely and includes a scar from a previous biopsy. For axillary intervention, the incision can be extended laterally.

3. Caudal dissection of the breast. The incision is deepened to the fascia of the pectoralis major muscle. The fascia is separated from the muscle and released in a cranial direction. The ventral arteries and intercostal vessels are coagulated or ligated with suture. The dissection of the breast tissue, together with the fascia of the pectoralis major muscle, continues into the axilla. Dissection is performed with a scalpel or diathermy.
4. Cranial breast dissection. Dissection from the cranial part of the incision is carried out in the same way, with a guaranteed separation of the fascia of the pectoralis major muscle to the axilla.

5. Expansion of the scope of the operation. The dissection should continue along the axillary fat pad along the lymphatic collectors into the axilla itself. The most cranial point is the apex of the armpit. When deepening into the axilla, the pectoralis major muscle is retracted medially to expose the pectoralis minor muscle. The fascia of the pectoralis minor muscle and the lymph nodes between the pectoral muscles are removed. Care must be taken not to disrupt the innervation of the pectoralis major muscle. For this, a wide intermuscular dissection should not be performed. After reaching the armpit, its contents are gradually separated from the anterior serratus muscle. During dissection, the long thoracic and thoracic nerves are exposed and protected.
6. Dissection in the axillary vein. The axillary tissues, together with the breast tissue, are transected between the Overholt forceps at their most cranial point at the axillary vein. To avoid damage to the lymphatics, the dissection should not continue cranial to the vein.

7. Resection of the pectoralis minor muscle. If the tumor is located near the pectoralis minor, the muscle can be cut at its insertion and removed. To do this, it is released from under the pectoralis major muscle and cut off using diathermy. We usually do not remove this muscle.
8. wound closure. The operation is completed by two active drainages, subcutaneous and skin sutures. In some situations, it is possible to perform a one-stage reconstructive operation.